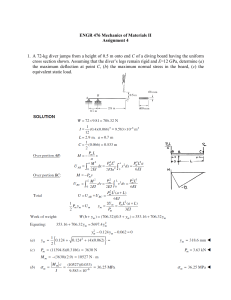
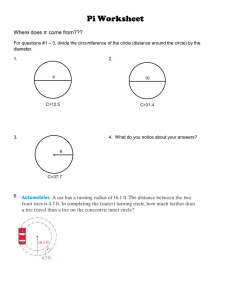
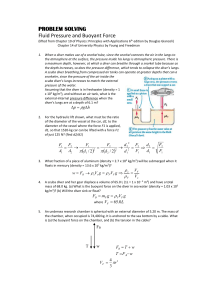
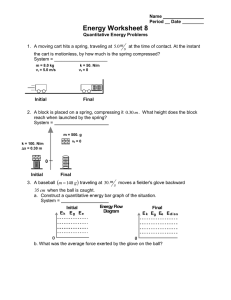
Name: Date: Per. Boyle’s Law & Scuba Diving Purpose: To introduce the gas laws in the context of scuba diving. Background: Pressure = Force per area. Pressure consists of two variables. A weight which is called a force and an area over which this weight or force is applied. Boyle’s Law – As the pressure on a trapped volume of gas increases, the volume of gas decreases (inversely related). As a diver descends, the pressure around him increases _____ atmosphere for every _____ feet of descent in salt water. Density of a gas – The density of a gas varies directly with the pressure. If you increase the pressure, the density will increase. This is due to the fact that the mass of the gas remains constant, but the volume decreases. Buoyancy – the ability to float or rise in a substance. Procedures / Activities 1. Fill the plastic bottle with water leaving a 2-4cm air space. 2. Place the eye dropper (scuba diver) in the bottle so it floats on top. 3. Screw the cap on the bottle. 4. Experiment with your diver to determine how to get the diver to sink. 5. Experiment with your design multiple times, changing the amount of water in the dropper (diver) and squeezing the bottle with varying pressures to make the diver positively buoyant, negatively buoyant, and neutrally buoyant. Questions A. How did you get the diver to sink? B. What two substances occupy the diver? C. What does it mean when we say that gases are compressible? D. What happens to the volume of air in the diver when you apply pressure to the bottle? What happens to the volume of air in the diver when you release the pressure? How is this related to Boyle’s Law? E. Try to get the diver to float in the middle of the bottle without applying any pressure. How is this accomplished? F. Describe the conditions in which the diver was positively buoyant negatively buoyant neutrally buoyant G. Imagine that you have inflated a balloon. The size of the balloon would increase / decrease (circle one) when you take the balloon into the mountains? Why? The size of the balloon would increase / decrease (circle one) when you take the balloon SCUBA diving? Why? H. What is the atmospheric pressure at sea-level? 33 ft below sea-level? 66 ft below sea-level? Approximately 100 ft below sea-level? I. Since the pressure is greater, what happen to the volume of air in the lungs? J. A diver descends to a ship wreck 80 ft deep and takes a deep breath. If the diver hold his breath during the ascent, how will this affect his lungs? What gas law explains this? K. Provide an explanation for your observations. Be sure to use each of these words in your answer. (float, sink, air, volume, pressure, compressible, buoyant, Boyle’s Law)