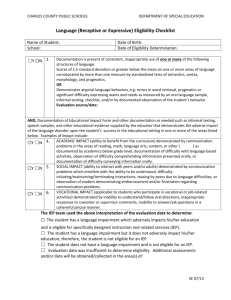
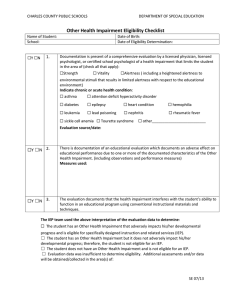
UPDATED ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA SPECIFIC LEARNING DISABILITY (SLD) Specific learning disability means a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes involved in understanding or in using language, spoken or written, that may have manifested itself in the imperfect ability to listen, think, speak, read, write, spell, or do mathematical calculations, including conditions such as perceptual disabilities, brain injury, minimal brain dysfunction, dyslexia, and developmental aphasia. The basic psychological processes include attention, visual processing, auditory processing, phonological processing, sensory-motor skills, cognitive abilities including association, conceptualization and expression. AVASPACE Specific learning disabilities do not include learning problems that are primarily the result of visual, hearing, or motor disabilities, of intellectual disability, of emotional disturbance, or of environmental, cultural, or economic disadvantage. A school district may determine that a child has a specific learning disability using the severe discrepancy method. The severe discrepancy method requires that a student have a severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability in oral expression, listening comprehension, written expression, basic reading skills, reading comprehension, mathematical calculation, or mathematical reasoning. The severe discrepancy must not be primarily the result of limited school experience or poor school attendance. Disorder in One or More Basic Psychological Processes/Other Conditions Severe Discrepancy between Intellectual Ability and Achievement *Note: If the standardized tests do not reveal a severe discrepancy, the IEP team may find that a severe discrepancy does exist, provided that the team documents that the severe discrepancy between ability and achievement exists as a result of a disorder in one or more of the basic psychological processes. The findings shall include a statement of the area, the degree, and the basis and method used in determining the discrepancy. The report shall contain information considered by the team which shall include, but not be limited to: Data obtained from standardized assessment instruments; Information provided by the parent; Information provided by the pupil's present teacher; Evidence of the pupil's performance in the regular and/or special education classroom obtained from observations, work samples, and group test scores; Page 1 of 13 Consideration of the pupil's age, particularly for young children; and Any additional relevant information. Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Student Requires Special Education or Related Services Based on the foregoing, Student DOES/DOES NOT meet the Education Code definition of having a Specific Learning Disability, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 2 of 13 AUTISM (AUT) Under state law, autism means a developmental disability significantly affecting verbal and nonverbal communication and social interaction, generally evident before age three, and adversely affecting a child's educational performance. Other characteristics often associated with autism are engagement in repetitive activities and stereotyped movements, resistance to environmental change or change in daily routines, and unusual responses to sensory experiences. A child who manifests the characteristics of autism after age three could be identified as having autism if these criteria are met. But a student does not meet eligibility under autism if the student’s educational performance is adversely affected primarily because the student has an emotional disturbance. Finally, in order to qualify for special education under this category, your child does not need to meet the medical definition of autism, just the educational definition. Likewise, meeting the medical definition of autism and obtaining a medical diagnosis does not ensure that your child will be eligible for special education services as autistic if he or she does not meet the educational criteria. Verbal Communication Nonverbal Communication Social Interaction Other Characteristics Engagement in Repetitive Activities Stereotyped Movements Resistance to Environmental Change or Change in Daily Routines Unusual Responses to Sensory Experiences Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify as a student with Autism, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 3 of 13 OTHER HEALTH IMPAIRMENT (OHI) Other health impairment means having limited strength, vitality, or alertness, including a heightened alertness to environmental stimuli, that: (1) Results in limited alertness with respect to the educational environment that is due to chronic or acute health problems such as asthma, attention deficit disorder or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, diabetes, epilepsy, a heart condition, hemophilia, lead poisoning, leukemia, nephritis, rheumatic fever, sickle cell anemia, and Tourette syndrome; and (2) Adversely affects a child's educational performance. The health impairment will not qualify the pupil for special education if it is temporary in nature. And while the definition for OHI includes attention deficit disorder (ADD) or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as an example of a chronic illness which could qualify. However, a medical diagnosis of ADD or ADHD alone is not sufficient to make a student eligible for special education services. Limited Strength, Vitality, or Alertness with Respect to Educational Environment Chronic or Acute Health Problem That Isn’t Temporary Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT MEET the requirements for a student with an Other Health Impairment, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 4 of 13 INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY In order for a student to be considered intellectually disabled, a child must show: (1) deficits in adaptive behavior; and (2) significantly subaverage general intellectual functioning. Both must have manifested during the developmental period and adversely affecting educational performance. Adaptive Behavior General Intellectual Functioning Manifested During the Developmental Period Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT QUALIFY as a student with an Intellectual Disability, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 5 of 13 EMOTIONAL DISTURBANCE (ED) A student is considered emotionally disturbed if, because of a condition the child exhibits one or more of the following characteristics, over a long period of time and to a marked degree, which adversely affects educational performance: (1) An inability to learn which cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors; (2) An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers; (3) Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances; (4) A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression; and (5) A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems. An Emotional Disturbance includes conditions such as schizophrenia, but does not include student’s that are socially maladjusted. Condition One or More of the Following Characteristics An inability to learn which cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems Over a Long Period of Time and to a Marked Degree *Note: The law does not define or specify the “long period of time” required for ED eligibility. An advice letter from the United States Department of Education states that a generally acceptable definition of "a long period of time" is a range of time from two to nine months, assuming preliminary interventions have been implemented and proven ineffective during that period. (Letter to Anonymous (OSEP 1989) 213 IDELR 247.) Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT QUALIFY under the definition of Emotional Disturbance, but the final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 6 of 13 TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) Traumatic brain injury means an acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force, resulting in total or partial functional disability or psychosocial impairment, or both, that adversely affects a child's educational performance. Traumatic brain injury applies to open or closed head injuries resulting in impairments in one or more areas, such as cognition; language; memory; attention; reasoning; abstract thinking; judgment; problem-solving; sensory, perceptual, and motor abilities; psychosocial behavior; physical functions; information processing; and speech. Traumatic brain injury does not apply to brain injuries that are congenital or degenerative, or to brain injuries induced by birth trauma. Brain Injury by External Force *Note: Can be open or closed head injury. Total or Partial Functional Disability or Psychosocial Impairment *Note: Must be in one or more of the following areas: cognition; language; memory; attention; reasoning; abstract thinking; judgment; problem-solving; sensory, perceptual, and motor abilities; psychosocial behavior; physical functions; information processing; and speech. Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify under the definition as having a Traumatic Brain Injury, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 7 of 13 DEAFNESS (DEAF) Deafness means a hearing impairment that is so severe that the child is impaired in processing linguistic information through hearing, with or without amplification that adversely affects a child’s educational performance. Severe hearing impairment Impaired Linguistic Processing Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify under the definition of Deafness, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 8 of 13 HEARING IMPAIRMENT (HI) A student is eligible if the student has impairment in hearing, whether permanent or fluctuating, that adversely affects a child's educational performance but that is not included under the definition of deafness. Permanent or Fluctuating Hearing Impairment Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify under the definition of Hearing Impairment, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 9 of 13 DEAF-BLINDNESS A student is eligible under the category of deaf/blind if the student has both hearing and visual impairments which, in combination, cause such severe communication, developmental, and educational problems that the student cannot be accommodated in a program for children with only hearing impairments or only visual impairments. Hearing and Visually Impaired Severe Communication, Developmental, and Educational Problems Student Cannot be Accommodated in Other Program Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify under the definition of Deaf-Blindness, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 10 of 13 VISUAL IMPAIRMENT Visually handicapped means a visual impairment that, even with correction, adversely affects a child’s educational performance. The term includes both partially sighted and blind children. Visual Impairment Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify under the definition of Visual Impairment, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 11 of 13 ORTHOPEDIC IMPAIRMENT A severe orthopedic impairment is one which adversely affects the pupil’s educational performance and including those caused by congenital anomaly, impairments caused by disease (e.g., poliomyelitis, bone tuberculosis, etc.), and impairments from other causes (e.g., cerebral palsy, amputations, and fractures or burns that cause contractures). Orthopedic Impairment Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify under the definition of Orthopedic Impairment, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 12 of 13 MULTIPLE DISABILITY Multiple disabilities means concomitant impairments (such as mental retardationblindness or mental retardation-orthopedic impairment), the combination of which causes such severe educational needs that they cannot be accommodated in special education programs solely for one of the impairments. Multiple disabilities does not include deaf-blindness. Concomitant Impairments Educational Needs Cannot be Accommodated in Programs for One Impairment Adversely Affecting Educational Performance Requires Special Education and Related Services Student DOES/DOES NOT qualify under the definition of Multiple Disability, but final determination will be made by student’s IEP team. Page 13 of 13