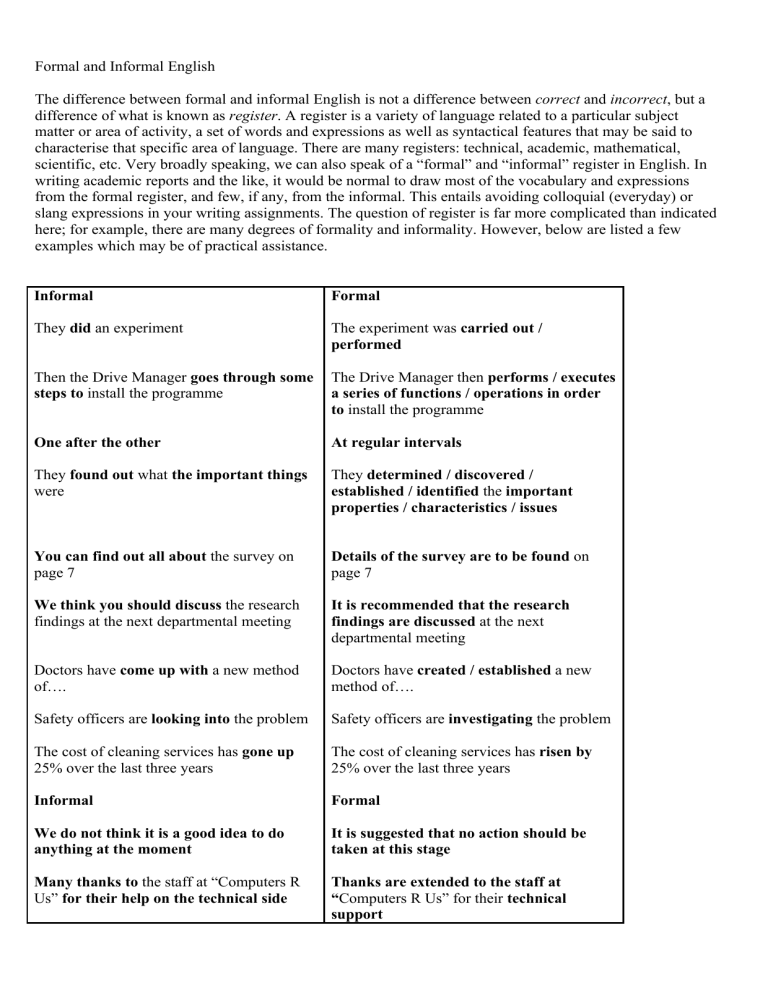
Formal and Informal English The difference between formal and informal English is not a difference between correct and incorrect, but a difference of what is known as register. A register is a variety of language related to a particular subject matter or area of activity, a set of words and expressions as well as syntactical features that may be said to characterise that specific area of language. There are many registers: technical, academic, mathematical, scientific, etc. Very broadly speaking, we can also speak of a “formal” and “informal” register in English. In writing academic reports and the like, it would be normal to draw most of the vocabulary and expressions from the formal register, and few, if any, from the informal. This entails avoiding colloquial (everyday) or slang expressions in your writing assignments. The question of register is far more complicated than indicated here; for example, there are many degrees of formality and informality. However, below are listed a few examples which may be of practical assistance. Informal Formal They did an experiment The experiment was carried out / performed Then the Drive Manager goes through some steps to install the programme The Drive Manager then performs / executes a series of functions / operations in order to install the programme One after the other At regular intervals They found out what the important things were They determined / discovered / established / identified the important properties / characteristics / issues You can find out all about the survey on page 7 Details of the survey are to be found on page 7 We think you should discuss the research findings at the next departmental meeting It is recommended that the research findings are discussed at the next departmental meeting Doctors have come up with a new method of…. Doctors have created / established a new method of…. Safety officers are looking into the problem Safety officers are investigating the problem The cost of cleaning services has gone up 25% over the last three years The cost of cleaning services has risen by 25% over the last three years Informal Formal We do not think it is a good idea to do anything at the moment It is suggested that no action should be taken at this stage Many thanks to the staff at “Computers R Us” for their help on the technical side Thanks are extended to the staff at “Computers R Us” for their technical support (Slightly less formal: We would like to thank ….) You need to get the patient’s help when doing these hearing tests When conducting these audiological tests, the active participation of the patient being tested is required. There were no big differences between the three different groups we tested No significant differences emerged between the three different groups tested A lot of Many / much / a great deal of This seemed to fix the problem This appeared to rectify the problem Enough Sufficient This shows that … This demonstrates… Numbers are going up Numbers are increasing They put the plan into action The plan was implemented / carried out This let them keep the same temperature during the whole experiment This allowed / permitted / resulted in / ensured a constant temperature throughout the experiment / for the entire experiment These results are because of factors like weight, age … These results are dependent on factors such as weight, age … Differences between formal and informal English Formal English Used in official, literary, academic, etc. content. Informal English Used in everyday, personal conversations. Typically used in "improvised" speech — when the speaker Typically used in careful, edited writing — when the is speaking without preparation, as in a conversation (in writer has a lot of time to polish his text. Formal real life or over the phone). Informal English also occurs in English also occurs in speech, usually when the writing, usually whenever the writer is writing quickly and speaker is saying something that was prepared without editing (for example, in an Internet chatroom or in beforehand (for example, reading the news or delivering quick, personal e-mails). an official speech). Because informal English is "improvised", it is sloppy. Speakers (and sometimes writers) often do the following: Use "delaying expressions" to give themselves time: Well, I Sentences are longer and more complicated, for think they should have asked us first, you know? example: Toyota's US sales bounced back in March as Use "correcting expressions" to correct themselves: He's substantial discounts helped to win back customers not well. I mean, he's not sick, but he's very tired. who had been shaken by the firm's mass safety recalls. Use "qualifying expressions" to show that what they said is not exactly right: This whole blogging thing is getting kind of old. The standard of correctness is higher. Some phrases are considered correct (or at least acceptable) in Informal English contains useful "everyday phrases", for example: Here you are. There you go. (when giving something to someone) informal English, but wrong in formal English. For Excuse me?, Come again? (to ask someone to repeat example: something) I have made less mistakes. (formal: I have made fewer What do you mean? (to ask for explanation) mistakes.) So, you're saying that...? (to ask for confirmation) She's liking it. (formal: She likes it.) Exactly!, I couldn't agree with you more. (to agree with I feel real good. (formal: I feel really good.) someone) By the way..., Anyway... (to change the topic) See you. Take care. (to say goodbye) A huge number of words and phrases are used mainly in formal English. For example: nevertheless, to A huge number of words and phrases are used mainly in disclose, to constitute, to undertake, daunting, informal English. For example: dude, freaking, uh-huh, impervious, anew, truly, solace, to enchant, frantically,nope (= no), to puke, trashy, grownup, awesome, to chill sizeable, to clutch, heyday, as it happens, upsurge, out, stuff, hard-up, to tick somebody off, to sell like crazy. retrieval Phrasal verbs are used frequently. For example, in informal situations, people usually say found out instead of Many (but not all) phrasal verbs are avoided. discovered, came across instead of encountered and got away instead of escaped. Words and phrases are sometimes pronounced in a shortened and simplified way, e.g. Lemme go!, I'm doin' fine, Whassup?, Whatcha gonna do? Examples Active and Passive voice (i) Our technician repaired the fault on 12th June. Now it’s your turn to pay us. (f) Although the fault was repaired on 12th June, payment for this intervention has still not been received. Phrasal verbs and Latina (i) The company laid him off because he didn't work much. (f) His insufficient production conducted to his dismissal. Direct and Formulaic (i) I’m sorry but … (i) I’m happy to say that … (f) We regret to inform you that … (f) We have pleasure in announcing that … Use of Slang (i) He had to get some money out of a hole in the wall … (f) He withdrew the amount from an ATM. Personal form & nominators (i) If you lose it, then please contact us as soon as possible. (f) Any loss of this document should be reported immediately … Linking words (i) The bank can’t find the payment you say you’ve made. (f) Notwithstanding that the payment has been sent the bank fails to acknowledge it. Revitalised Sentences (i) Anybody or any company. (f) … any natural person who, and any legal entity which … Modal usage (i) If you need any help give us a call. (f) Should you require any assistance, please feel free to contact us … Singular & Plural Person (i) I can help you to solve this problem. Call me! (f) We can assist in the resolution of this matter. Contact us on our toll-free number. Dictionary of Formal and Informal English Informal About … Agree with … And Bearing in mind Because … Begin But Careful / Cautious Carry out Check Enough Fill me in Find out Follow Get Get in touch Go over Has to be Have to give If … If … or not. If you don't … If you've got any questions … In accordance with … In the red Involve Lost Make sure Many Order Pay Put in writing Sorry! Supply Formal Regarding / Concerning … Be bound by … As well as … Reference being made to … As a result of / due to (the fact) … Commence While / Whereas Prudential Effect Verify Sufficient Inform / Tell Ascertain Duly observe Receive Contact Exceed Shall be Submit Should … Whether … or not. Failing / Failure to… Should you have any queries … Pursuant to Overdrawn Entail Inadvertently mislaid Ensure Several / Numerous Authorise Settle Provide written confirmation We regret … Furnish Take away Tell Trusted We don't want to do this … We'll call the law … When we get … Whenever we like … Write (e.g. Cheque) Written Informal Active Voice Phrasal Verbs Direct Language Possible use of Slang Personal Form Little use of Conjunctions Few Revitalised Sentences Direct Style 1st Person Singular Withdraw Disclose Entrusted This a course of action we are anxious to avoid … We will have no alternative but involving our legal … On receipt Without prior notice … Issue (e.g. Cheque) Shown / Indicated Formal Passive Voice Latinate Verbs Formulaic Language No use of Slang Nominator Linking Words Revitalised Sentences Modal Usage 1st Person Plural


