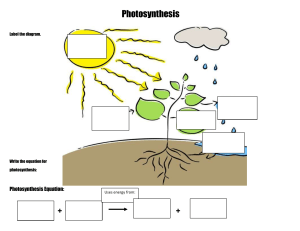
Photosynthesis PPT This PowerPoint was revised June 24, 2008. There is a TEKS Photosynthesis Notes handout to accompany this PPT. (This is the same handout for SM as well.) Review it for possible use in other Biology courses. There is repetition in this PPT used as a learning strategy. The notes section contains guides for discussion. PPT is 27 slides long. Photosynthesis What is the ultimate source of all energy? How does the energy get from the sun into the foods we eat? ener ene rgy gy Why do we see colors? The sun sends downs little packets of light energy called: PHOTONS Photons group together in waves The waves have different lengths Each “wavelength” presents itself as a color Photons Wavelengths Why do we see colors? Pigments absorb wavelengths of light. The wavelengths not absorbed are reflected. The colors we see are the reflected wavelengths. yellow blue red green orange Why do we see colors? What color is chlorophyll? The plant pigment chlorophyll reflects light in these wavelengths. The plant pigment chlorophyll absorbs the red and blue colors of light so these colors are not seen. What colors of light would a plant with purple leaves absorb? What colors are being absorbed and what colors are being reflected? Flowers from Clip Art Chloroplast Structure Chlorophyll pigments are in structures called chloroplasts. Disks called GRANA contain the pigment CHLOROPHYLL. The liquid portion of a chloroplast is the STROMA Where do we find chloroplasts? Cross-section of a Leaf Chloroplasts are found in cells of leaves. Cells containing chloroplast with chlorophyll inside stoma (stomata) Review 1. 2. 3. 4. What is the ultimate source of all energy? In what form does light energy come to the earth? What compounds absorbs wavelengths? How do we see colors? Review 1. 2. 3. 4. Which compound reflects the green wavelengths thereby making plants green? Where would we find this compound? Where in a leaf do we find pigments? What are the small openings in leaves for gas exchange called? How do Plants Make Food? What process captures the light energy and uses it to make food? OVERVIEW OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS SUNLIGHT PROVIDES THE ENERGY overview of photosynthesis FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS light carbon dioxide SUNLIGHT CAPTURED BY CHLOROPHYLL oxygen carbohydrates water PLANTS TAKE IN CO2 AND H2O PLANTS MAKE GLUCOSE AND OXYGEN Photosynthesis What is photosynthesis? Photosynthesis is the process by which: light TAKE IN AND USING water carbon dioxide PLANTS (producers) chlorophyll MAKE oxygen glucose Photosynthesis 2 Phases: Light reactions Dark reactions (aka Calvin cycle) Light Reaction Dark Reaction Who was Calvin anyway? A member of the faculty at UC Berkeley since 1937, Melvin Calvin received the 1961 Nobel prize in chemistry for identifying the path of carbon in photosynthesis. The cycle of reactions in the dark phase of photosynthesis was named after him for his work in identifying the processes taking place. Photosynthesis Light reaction: Occurs in the grana Must have light light LIGHT Light REACTION Reaction grana (chlorophyll) Dark Reaction Photosynthesis Dark reactions (aka Calvin cycle): Occurs in the stroma Occurs in the light and dark Light Reaction DARK Dark REACTION Reaction stroma (liquid) Step 1: Light Reactions O2isiskept light water H energy released is split for the by reacts the dark light reaction with energy the chlorophyll O2 O2 EN ER GY H2 O O2 O O2 O2 H H H2 How does the O2 leave the leaf? Step 1: Light Reactions In GY ER EN H2 O the early 1600’s Van Helmont did an experiment that showed plants get vital growth substances from water. Step 2: Dark Reactions AKA: CALVIN CYCLE glucose H CO the from enters the is the water theHproduct and splitCO in2 2reactants the light reaction is chloroplast combine present CO2 H H CO2 H + CO2 COdoes How CO2 2 CO enter 2 the plant? C6H12O6 Other carbohydrates besides glucose may be made in photosynthesis Photosynthesis Review Light reactions: H2O split into H2 + O Dark reactions: H + CO2 = C6H12O6 O 2 Light Reaction Dark Reaction 2 chlorophyll CO H2O C6H12O6 Photosynthesis Formula How would this be written as a chemical equation? What goes in? (the reactants) What comes out? (the products) CO2 C6H12O6 O2 O 2 H2O chlorophyll Dark Reaction C6H12O6 2 Light Reaction CO H2O Photosynthesis Formula What’s wrong with this equation? The number of atoms is not equal on both sides of the equation. one carbon atom reactant 6 H2O 6 CO2 6 carbon atoms product (1) C6H12O6 6 O2 Balance the equation so that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides. Now balance it as if TWO glucose molecules were being produced. TRY THIS! Think-Pair-Share Analyze the relationship between photosynthesis, biogeochemical cycles, and food chains. Photosynthesis Review What goes in? (the reactants) What comes out? (the products) chlorophyll 6O2 + C6H12O6 O 2 6CO2 + 6H2O light chlorophyll Dark Reaction C6H12O6 2 Light Reaction CO H2O Work Cited Melvin Calvin picture. Online image http://www.lbl.gov/ScienceArticles/Archive/Melvin-Calvinobit.html