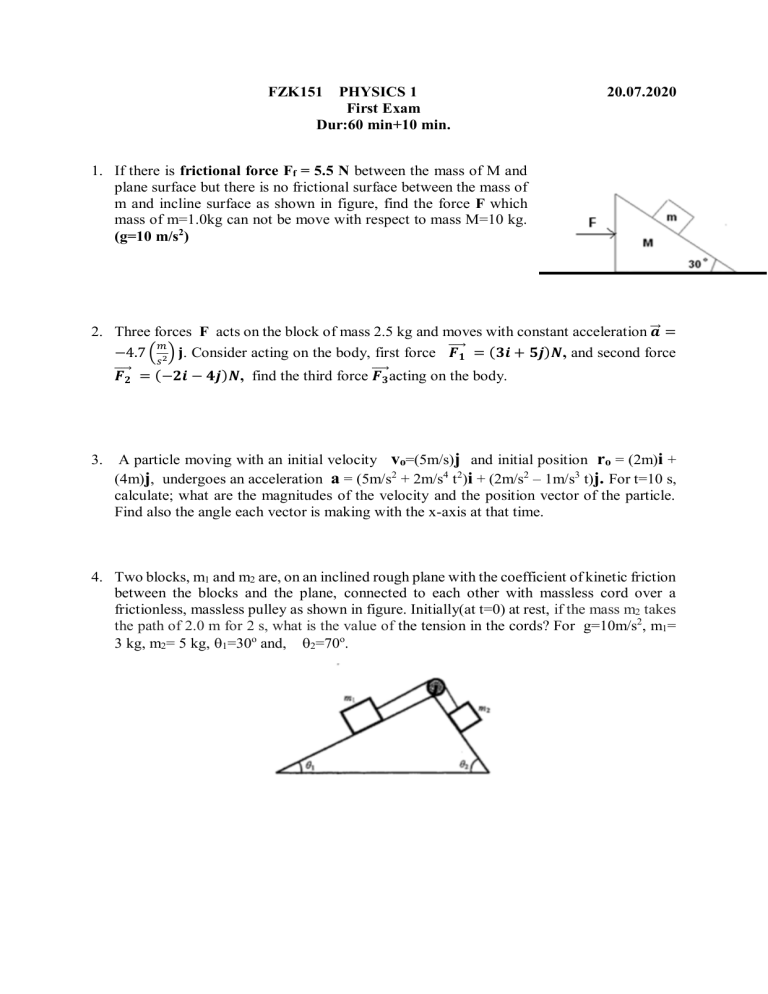
FZK151 PHYSICS 1 First Exam Dur:60 min+10 min. 20.07.2020 1. If there is frictional force Ff = 5.5 N between the mass of M and plane surface but there is no frictional surface between the mass of m and incline surface as shown in figure, find the force F which mass of m=1.0kg can not be move with respect to mass M=10 kg. (g=10 m/s2) ⃗ = 2. Three forces F acts on the block of mass 2.5 kg and moves with constant acceleration 𝒂 𝑚 ⃗⃗⃗⃗𝟏 = (𝟑𝒊 + 𝟓𝒋)𝑵, and second force −4.7 (𝑠 2) 𝐣. Consider acting on the body, first force 𝑭 ⃗⃗⃗⃗𝟐 = (−𝟐𝒊 − 𝟒𝒋)𝑵, find the third force 𝑭 ⃗⃗⃗⃗𝟑 acting on the body. 𝑭 3. A particle moving with an initial velocity vo=(5m/s)j and initial position ro = (2m)i + (4m)j, undergoes an acceleration a = (5m/s2 + 2m/s4 t2)i + (2m/s2 – 1m/s3 t)j. For t=10 s, calculate; what are the magnitudes of the velocity and the position vector of the particle. Find also the angle each vector is making with the x-axis at that time. 4. Two blocks, m1 and m2 are, on an inclined rough plane with the coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and the plane, connected to each other with massless cord over a frictionless, massless pulley as shown in figure. Initially(at t=0) at rest, if the mass m2 takes the path of 2.0 m for 2 s, what is the value of the tension in the cords? For g=10m/s2, m1= 3 kg, m2= 5 kg, 1=30o and, 2=70o. 5. A particle of mass m=2kg moves on xy plane under the influence of a constant force F=12j(N). The particle is initially at the origin and its initially velocity vector at t=0 is given by vo = 3i (m/s) as shown in figure. Find the angle in degress between the position vector and the velocity vector at t=2s? 6. A plane flies at 198 km/h (=55 m/s) and a constant elevation toward directly a point A. The pilot wants to release a block so that it hits the point A as shown below. What should be the speed (magnitude) and the angle, , of the pilot’s line of sight to the point when the release is made. g=10m/s2, 7. A box of mass m=25kg is released from rest and slides down a frictionless ramp with height h=2.0m. At the bottom of the ramp, the box has the speed of 4m/s, and moves the rough plane with the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the plane. If the box slides on the rough plane d=10 m, find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the plane? For =30o and, g=10m/s2, 8. A ball is kicked from the ground at an nagle of =37o and with a speed of vo=20 m/s as shown in the figure. Find the instant (time) when the coordinates of the ball are such that x=2y? g=10m/s2 9. In figure (a), block 1 is pushed horizontally while block 2 stands without motion on the block 1 and both move without sliding. In Figure (b), block 1 is pushed horizontally while block 2 is in contact with block 1 and non-motion. The masses of the blocks are m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg, and for both cases the static coefficient of friction between block 1 and block 2 is s = 0.5. (A) Find the force F for which block 2 just starts to slide on block 1 for the system as shown in figure (a), (B) Find the force F that would prevent block 2 form sliding downward for the system as shown in figure (b). g=10 m/s2 10. A block with mass m is given an initially velocity 6.0 m/s up along a =30o inçline as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction fort he incline’s surface is k=0.6. Find the total time ttotal until the box returns to its starting point. For k=0.5 and g=10 m/s2

