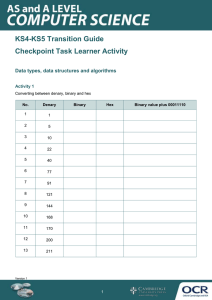
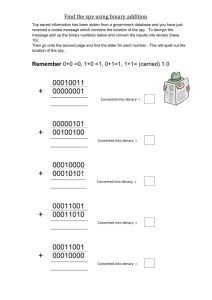
Home learning - Topics • • • • • Networks Ethical and Legal Binary and Denary Search and Sort Algorithms SQL LI: Revision for areas for development Home learning – This week lesson 1 • • • • • Networks Ethical and Legal Binary and Denary (73-77) Search and Sort Algorithms (43-48) SQL LI: Revision for areas for development Binary / Denary Recap • Computers can only process Binary Data. This means that only 0s and 1s can be processed by a computer. (This is called a Base 2 system) • We use a number system to count that uses : 0123456789 This is called a decimal or denary system (Base 10) LI: Revision for areas for development Denary to Binary • Remember when converting Denary (numbers we know – sometimes called decimal) to Binary. Use the table below: 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 • If I was needing the number 80 representing in binary, you would start from the left and add a 1 for all of the numbers you need to make that number. 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 LI: Revision for areas for development Denary to Binary • When given a binary number to convert be careful. If the binary number is 4 digits, you will need the last 4 columns (bits). If I was given 1001, I would do the following: 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 0 0 1 • You would then count the number where a 1 exists. There is a 1 under the 8 column so we add that to the total and we also add the 1. 8+1 = 9 LI: Revision for areas for development How to work out Hexadecimal from Denary (Method 1) • If I started with a Denary number, in this case we will use 100. Convert it to Binary 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 • Then we break the 8 bit number into two. This makes two nibbles of 4bits. The headings change for now too. 8 4 2 1 8 4 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 • Add the numbers and choose the Hex character from the table. The first 4 bit is 6, which stays the same. The second nibble is 4, so this stays as this number. The hex number is therefore 64 LI: Revision for areas for development 0=0 1=1 2=2 3=3 4=4 5=5 6=6 7=7 8=8 9=9 10=A 11=B 12=C 13=D 14=E 15=F How to work out Hexadecimal from Denary (Method 2) • If I started with a Denary number, in this case we will use 100. • As Hexadecimal is Base16 (this means there are 16 possible options per bit) we need to divide it by 16. The remainder is the second nibble. • So… 100/16= 6 with a remainder 4. As the numbers are lower than 10, we keep them as they are so the Hex number is 64 LI: Revision for areas for development 0=0 1=1 2=2 3=3 4=4 5=5 6=6 7=7 8=8 9=9 10=A 11=B 12=C 13=D 14=E 15=F How to work out Denary from Hexadecimal (Method 1 and 2) • If we start with hexadecimal 64, we can change this back in two ways Method 1 64 Change it back to binary 8 4 2 1 8 4 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 Bring them back together and change the headings back. Then add 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 LI: Revision for areas for development =100 Method 2 64 Take the first value and times it by 16 (if a letter convert it to its number from the table) The second digit needs to be multiplied by 1 16 x 6 = 96 4x1=4 0=0 1=1 2=2 3=3 4=4 5=5 6=6 7=7 8=8 9=9 10=A 11=B 12=C 13=D 14=E 15=F The exam paper • Attempt Questions 1-4 on the exam paper • I have also included an addition question to see how you go. LI: Revision for areas for development Search Algorithms There are two types of Algorithm to search for a value in a list Linear LI: Revision for areas for development Binary Linear Search Jane has a list of numbers: 81, 42, 9, 76, 15 To find the number 76…you would need to check each number and to write it you do the following: 81 76 42 76 9 76 76 = 76 STOP LI: Revision for areas for development • Positives • The list doesn’t have to be in order. • It will always find the value Negative • May take a longer time for larger lists Binary Search Jane has a list of numbers: 81, 42, 9, 76, 15 Put the numbers in order 9, 15, 42, 76, 81 • Then choose the median, which is 42. This is too low so you would discard 42 and the numbers to the left. • You would be left with 76, 81 • Choose the median, it would probably choose 81 and it is not the correct value so it would choose the only number lower as the answer. LI: Revision for areas for development • Positives • Much faster for larger lists Negative • Needs to be in order Sort Algorithms There are three types of Algorithm to Sort the values in a list Bubble Bubble Sort Video LI: Revision for areas for development Insertion Merge Insertion Sort Video Merge Sort Video The exam paper • Attempt the remaining questions • Don’t forget to answer and then check the markscheme at the end. LI: Revision for areas for development