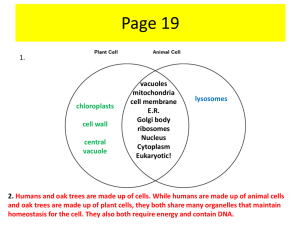
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U—2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; ◦ The liquid is known as cytosol. Source: http://www.yourgenome.org/ Plant vs Animal Cells Plant Chloroplast Central vacuole Cell wall Animal Lysosomes Many small vesicles Nucleus Contains and replicates DNA (genetic information): ◦ DNA is stored as chromatin and, during replication, as chromosomes. Has its own membrane, the nuclear envelope: ◦ The envelope has nuclear pores which regulate nutrient and macromolecule movement. The densest part of the nucleus is called the nucleolus, which is used to synthesize ribosomes; The rest of the nucleus is filled with nucleoplasm. Source: http://0.tqn.com/ Mitochondria The mitochondria breaks down certain molecules to release energy; Has a smooth external membrane, but a folded inner membrane; Also plays a role in regulating apoptosis (self-destruction); Mitochondria has some DNA of its own! Source: https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/ Chloroplast Permits cells to conduct photosynthesis; Light is absorbed by the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll: ◦ This light helps convert water and carbon dioxide into high energy molecules. The chlorophyll is contained in the membranes of diskshaped thylakoids: ◦ A stack of thylakoids forms a granum. Not found in animal cells (but rather plant and algal cells). Source: http://images.tutorvista.com/ Which is more important? Nucleus, mitochondria or chloroplast? Endoplasmic reticulum Part of the endomembrane system; Two types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER), rough & smooth; Rough ER contains ribosomes: ◦ It is attached to the nucleus; ◦ It synthesizes proteins (for the membrane or export). Smooth ER does not contain ribosomes: ◦ It synthesizes lipids; ◦ Also provides other services, such as detoxing alcohol. Source: http://image.tutorvista.com/ Golgi apparatus Part of the endomembrane system; New proteins and lipids are transported from the rough and smooth ER to the Golgi apparatus The Golgi apparatus sorts, packs and distributes these proteins and lipids; Also, the Golgi apparatus produces lysosomes. Source: https://media1.britannica.com Endomembrane system Nuclear envelope; Endoplasmic reticulum: ◦ Rough; ◦ Smooth. Golgi apparatus; Vesicles. Source: https://qph.ec.quoracdn.net/ & Texbook p. 61 Lysosomes and peroxisomes Lysosomes and peroxisomes break down large, harmful and useless molecules; They perform similar functions but through different processes and on different molecules; Lysosomes are not found in plant cells. Source: http://www.gridgit.com/ Vesicles and vacuoles Vesicles are sacs used to store and transport nutrients throughout the cell; ◦ E.g. Transport form the ER to the Golgi apparatus Vacuoles are very large sacs and replace many small vesicles; Vacuoles are not found in animal cells. Source: http://waynesword.palomar.edu Cytoskeleton and cell wall The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and other anchors that give structure to the cell and its organelles; A cell wall is composed of cellulose and give the cell rigidity; The cell wall is not found in animal cells. Source: http://plantcellcrk.weebly.com/ Cilia and flagella Cilia and flagella are appendages that extend outside of the cell; Flagella are few and long, generally used for movement; Cilia are short and many, used for a variety of physical tasks. Source: http://www.microbiologyinfo.com Parts of the Cell Nucleus Contains DNA Mitochondria Converts certain molecules into usable energy Chloroplasts Absorbs light energy, conducts photosynthesis Endoplasmic reticulum Part of protein and lipid synthesis Golgi apparatus Processes proteins and lipids Vesicles and vacuoles Storage and transport of resources (also provides structure, in plants) Lysosomes and peroxisomes Break down molecules Cytoskeleton and cell wall Provides structure Cilia and flagella Mobility and other physical functions Activity: ____ is like… Nucleus Contains DNA Mitochondria Converts certain molecules into usable energy Chloroplasts Absorbs light energy, conducts photosynthesis Endoplasmic reticulum Part of protein and lipid synthesis Golgi apparatus Processes proteins and lipids Vesicles and vacuoles Storage and transport of resources (also provides structure, in plants) Lysosomes and peroxisomes Break down molecules Cytoskeleton and cell wall Provides structure Cilia and flagella Mobility and other physical functions