Physiology Practice Questions: Retina, Reflexes, and More
advertisement

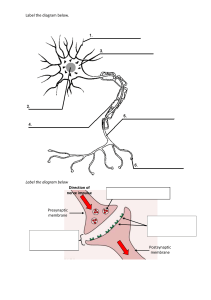
Practice Questions 1. When compared with the cones of the retina, the rods a. Are more sensitive to low-light intensity light b. Adapt to darkness before the cones c. Are most highly concentrated on the fovea d. Are primarily involved in color vision 2. Which reflex is responsible for polysynaptic excitation of contralateral extensors? a. Stretch Reflex b. Golgi tendon Reflex c. Flexor withdrawal reflex 3. Which of the following is a step in photoreception in the rods? a. Light converts all-trans retinal to 11-cis retinal b. Transducin activates a phosphodiesterase c. cGMP levels increase d. Rods depolarize e. Glutamate release increases 4. Patients are enrolled in trials of a new atropine analog. Which of the following would be expected? a. Increased heart rate b. Increased gastric acidity c. Pupillary constriction d. Increased sweating 5. The low resistance pathways between myocardial cells that allow for the spread of action potentials are the a. Gap junctions b. T tubules c. Sarcoplasmic reticulum d. Intercalated disks 6. Which of the following structures has a primary function to coordinate rate, range, force, and direction of movement as well as balance a. Primary Motor Cortex b. Basal Ganglia c. Cerebellum d. Prefrontal cortex 7. Which characteristic or component is shared by skeletal muscle and smooth muscle? a. Thick and thin filaments arranged in sarcomeres b. Troponin c. Elevation of intracellular Ca2+ for excitation-contraction coupling d. Spontaneous depolarization of the membrane potential e. High degree of electrical coupling between cells 8. Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons has been implicated in a. Schizophrenia b. Parkinson disease c. Myasthenia gravis d. Curare poisoning 9. During the upstroke of the nerve action potential a. There is net outward current and the cell interior becomes more negative b. There is net outward current and the cell interior becomes less negative c. There is net inward current and the cell interior becomes more negative d. There is net inward current and the cell interior becomes less negative 10. An inhibitory postsynaptic potential a. Depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening Na+ channels b. Depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening K+ channels c. Hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening Ca2+ channels d. Hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening Cl- channels Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. A C B A A C C B D D *Note: these questions are sourced from BRS physiology 6th edition and only serve as practice questions* Best of luck on your exam!