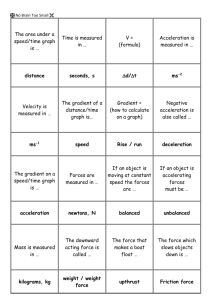
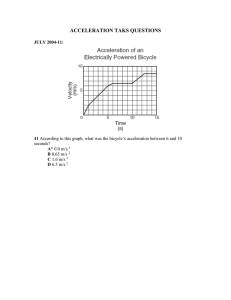
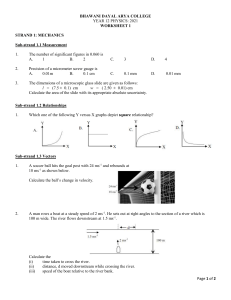
Constant acceleration equations on one direction 1. A vehicle accelerates uniformly along a straight road, increasing its speed from 4.0 ms-1 to 30.0 ms-1 in 13 s. Calculate: a) its acceleration, b) the distance it moves in this time. 2. An aircraft lands on a runway at a speed of 40 ms-1 and brakes to a halt in a distance of 860 m. Calculate: a) the braking time, b) the deceleration of the aircraft. 3. A cyclist accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 6.0 ms-1 in 30 s, then brakes at uniform deceleration to a halt in a distance of 24 m. a) For the first part of the journey, calculate: i) the acceleration, ii) the distance traveled. b) For the second part of the journey, calculate: i) the decceleration, ii) the time taken. 4. A pebble, released at rest from a canal bridge, took 0.9 s to hit the water. Calculate: a) the distance it fell before hitting the water, b) its speed just before hitting the water 5) A spanner was dropped from a hot air balloon, when the balloon was at rest 80m above the ground. Calculate: a) the time taken for the spanner to hit the ground, b) the speed of impact of the spanner on hitting the ground. 6) A bungee jumper jumped of a platform 75 m above a lake, releasing a small object at the instant she jumped off the platform. a) Calculate i) the time taken by the object to fall to the lake, ii) the speed of impact of the object on hitting the water, assuming air resistance is negligible. b) Explain why the bungee jumper would take longer to descend than the time taken in part a) 7)An astronaut on the Moon threw an object 4.0 m vertically upwards and caught it again 4.5 s later. Calculate: a) the acceleration due to gravity on the Moon, b)the speed of projection of the object, c) how high the object would have risen on the Earth, for the same speed of projection. 8) a) Ignoring air resistance, how long does it take an object to fall a distance of: i) 1.0 m, ii) 2.0 m? b) Why is the answer to ii) not twice the answer to i)? 9) A kangaroo was seen to jump to a vertical height of 2.8 m. For how long was it in the air? 10) The best throwers in the world are baseball pitchers. They can release a ball traveling at 40 ms-1. In doing so they accelerate the baseball through a distance of 3.6 m. Calculate: a) the average speed of the ball during the throw, b) the time during which the ball is being accelerated c) the average acceleration of the baseball. 11) The nuclei of helium atoms, alpha particles, leave atomic nuclei with a velocity of 3.5 x 107 ms-1. they travel a distance of 7 cm prior to stopping. What uniform deceleration do they have and how long does it take them to stop?