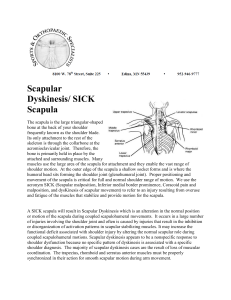
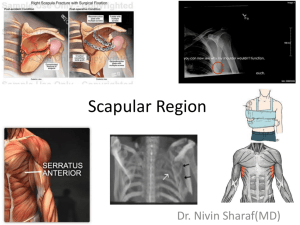
Shoulder girldle Upper Trap O: occiput, nuchal ligament on cervical spinous processes I: lateral clavicle, acromion process A: Scapular elevation and upward rotation N: Spinal accessory Middle Trap O: spinous processes of C7-T3 I: scapular spine A: scapular retraction N: Spinal accessory Lower Trap O: spinous processes of middle and lower thoracic I: base of scapular spine A: Scapular depression and upward rotation N: Spinal accessory Levator Scapulae O: C1-C4 transverse process I: superior angle of scapula A: scapular elevation and downward rotation N: dorsal scapular and C3-C4 Rhomboids Major and minor O - nuchal ligament and spinous process of C7-T5 I - medial border of scapula N - dorsal scapular nerve A - scapular retraction, elevation and downward rotation Serratus Anterior O: first 8 ribs I: medial border of scapula N: long thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7) A: scapular protraction and upward rotation PEC minor O: ribs 3-5 I: coracoid process A: scapular depression, protraction, downward rotation and tilt N: Medial pectoral (C8-T1) Force couples Muscles pulling in different directions to accomplish the same motion UT + LT + SA → upward rotation Levator + Pec minor + Rhomboids→ downward rotation Shoulder part 2 Rotator Cuff - Supraspinatus - Infraspinatus - Teres Minor - Subscapularis Force couple acts to hold the humeral head into the glenoid fossa Anterior Deltoid O: lateral 1/3 of clavicle I: deltoid tuberosity A: shoulder abduction, flexion, medial rotation and horizontal adduction (when shoulder flexed to 90) N: Axillary (C5-C6) Rotator Cuff - Supraspinatus - Infraspinatus - Teres Minor - Subscapularis Force couple acts to hold the humeral head into the glenoid fossa Supraspinatus O: supraspinous fossa I: greater tubercle of humerus A: shoulder abduction N: suprascapular n. (C5-C6) Infraspinatus O: infraspinous fossa I: greater tubercle of the humerus A: shoulder lateral rotation, horizontal abduction N: suprascapular n. (C5-C6 Teres Minor O: axillary border of scapula I: greater tubercle of humerus A: shoulder lateral rotation, horizontal abduction N: axillary n. (C5-C6) Subscapularis O: subscapular fossa of the scapula I: lesser tubercle of the humerus A: shoulder medial rotation N: subscapular n. (C5-C6) Pec Major O: (clavicular portion) medial clavicle (sternal portion) sternum, ribs 1-6 I: lateral lip of bicipital groove of humerus A: (claviular portion) shoulder flexion- first 60° (sternal portion) shoulder extensionfirst 60° (from 180°-120°) N: lateral and medial pectoral nn. (C5-T1) Latissimus Dorsi O: spinous processes T7-L5, posterior sacrum, iliac crest and lower 3 ribs I: medial lip of bicipital groove of humerus A: shoulder extension, adduction, medial rotation, hyperextension N: thoracodorsal n. (C6-C8 Teres Major (lats little helper) O: axillary border of scapula I: medial lip of bicipital groove of humerus A: shoulder extension, adduction, medial rotation N: subscapular n. (C5-C6) Coracobrachialis O: coracoid process I: mid-humerus (medial portion) A: stabilizes the shoulder joint N: musculocutaneous n. (C6-C7) Force Couples -Glenohuneral Jt Arthrokinematic motions of roll, spin and glide help to keep the humeral head articulating with the glenoid fossa Abduction begins (deltoid and supraspinatus)→ HH rolls along glenoid→ HH glides inferiorly (rot cuff) to allow abd to continue Note that full abd cannot take place without ER of the humerus….why?? “empty can” vs “full can”