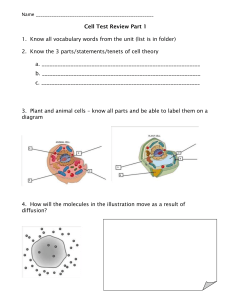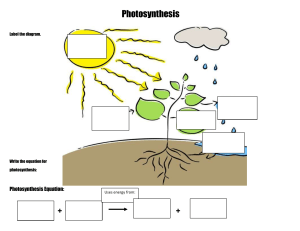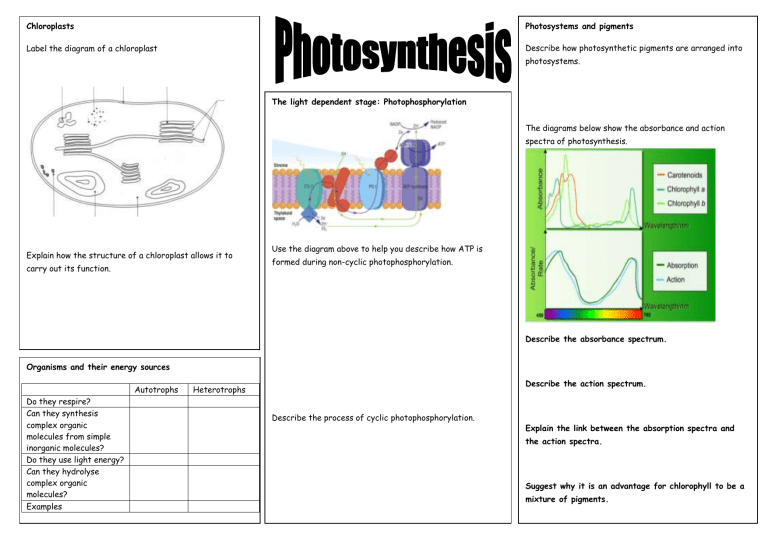
Chloroplasts Photosystems and pigments Label the diagram of a chloroplast Describe how photosynthetic pigments are arranged into photosystems. The light dependent stage: Photophosphorylation The diagrams below show the absorbance and action spectra of photosynthesis. Explain how the structure of a chloroplast allows it to carry out its function. Use the diagram above to help you describe how ATP is formed during non-cyclic photophosphorylation. Describe the absorbance spectrum. Organisms and their energy sources Autotrophs Do they respire? Can they synthesis complex organic molecules from simple inorganic molecules? Do they use light energy? Can they hydrolyse complex organic molecules? Examples Describe the action spectrum. Heterotrophs Describe the process of cyclic photophosphorylation. Explain the link between the absorption spectra and the action spectra. Suggest why it is an advantage for chlorophyll to be a mixture of pigments. Limiting factors Define the term limiting factor. State three factors that may limit the rate of photosynthesis. Describe the pattern shown in the graph. Explain the pattern shown in the graph The light independent stage: The Calvin Cycle Fill in the blanks. Explain how an increase in light intensity will affect the relative concentrations of: RuBP GP TP Investigating limiting factors You are provided with the following equipment: pondweed, small bottles with lids, water baths at 5 different temperatures (20oC, 30 oC, 40 oC, 50 oC, 60 oC), a light source, hydrogencarbonate indicator, a metre ruler, a 30cm ruler. Write a brief method that would allow another student to investigate how temperature affects the rate of photosynthesis in pondweed. Describe the expected pattern of results. Describe the role of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis. Explain the expected pattern of results. Describe the role of rubisco in photosynthesis.