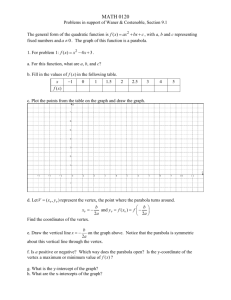
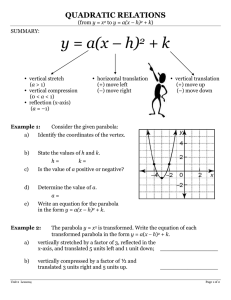
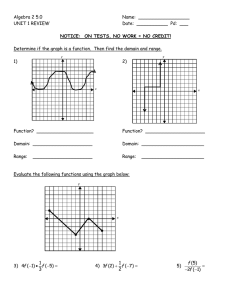
Complete the following graphic organizer to summarize the roles of a, h and k-look at chapter 4 Investigation – What are the roles of a, h and k? You can use Desmos.com With a partner and using the Parabola Function graphing tool, investigate the roles of a, h and k in the vertex form of the quadratic function. Record your findings. Role of a: As I increase the value of a (larger than 1), I notice… Role of h: As I increase the value of h, I notice… As I decrease the value of a (smaller than -1), I notice… As I decrease the value of h ( h becomes negative), I notice… As I change the value of a between -1 and 1, I notice… When the value of h is zero, I notice… y = a(x – h)2 + k Role of k: As I increase the value of k , I notice… As I decrease the value of k (k becomes negative), I notice… When the value of k is zero, I notice… Source: Edugains.ca Other Observations: Complete the following graphic organizer to summarize the roles of a, h and k-look at chapter 4 Demonstrating understanding of the roles of a, h & k in y = a(x – h)2 + k Equation Value of a Value of h Value of k Vertex (h, k) y = 3(x - 2)2 + 1 a=7 h=2 k=1 (2, 1) y = -2(x - 3)2 + 3 y= 1 (x +1)2 +5 2 y = 0.3(x + 2)2 + 15 2 y = − ( x − 4) 2 - 8 3 y = 2x2 + 9 y = -3(x + 5)2 Source: Edugains.ca Step Pattern from Vertex # of x-intercepts None Transformations Starting from y = x2 • • • Vertical stretch by a factor of 3 Translated 2 units right Translated 1 unit upwards Complete the following graphic organizer to summarize the roles of a, h and k-look at chapter 4 Role of a: Role of h: Direction of Opening: • When a is positive, the parabola opens ____ ________. • When a is negative, the parabola opens____________. Properties: • If h > 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated horizontally h units to the _______________. • If h < 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated horizontally h units to the _____________ . Shape: • If a > 1 or a < -1, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is ___ _________to the graph of y = x2. • If a is between -1 and 1, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k ______________relative to y = x2. Relation to the Vertex: • The value of h is the ________ - coordinate of the vertex. y = a(x – h)2 + k Example: y = -2(x – 3)2 + 5 Role of k: Properties: • If k > 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated vertically k units ____________. • If k < 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated vertically K units ___________. State: a) Direction of opening: b) Stretch or Compression: • Relation to the Vertex: The value of k is the _____ - coordinate of the vertex. The graph has been translated ___________ • X-Intercepts: • If k = 0, then the graph has __________ zero (x-intercept). • If k > 0,a>0 then the graph has ______ zeros (x-intercepts). • If k < 0, a<0 then the graph has ____ __ zeros (x-intercepts). • If k>0,a<0 then the graph has ________ (two x-intercepts) • If k<0,a>0 then the graph has ________ (two x-intercepts) Source: Edugains.ca Transformations: The graph has been translated ___________ c) Coordinates of the vertex:) d) Number of x-intercepts: Complete the following graphic organizer to summarize the roles of a, h and k-look at chapter 4 Summarizing the roles of a, h & k in y = a(x – h)2 + k (Solution) Role of a: Direction of Opening: • When a is positive, the parabola opens ____up________. • When a is negative, the parabola opens______down______. Shape: • If a > 1 or a < -1, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is vertically stretched relative to the graph of y = x2. • If a is between -1 and 1, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k vertically compressed relative to y = x2. Role of h: Properties: • If h > 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated horizontally h units to the _left______________. • If h < 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated horizontally h units to the __________right_____ . Relation to the Vertex: • The value of h is the __x___ - coordinate of the vertex. Example: y = -2(x – 3)2 + 5 Role of k: Properties: • If k > 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated vertically k units _____up_______. • If k < 0, then the graph of y = a(x – h)2 + k is translated vertically K units _____down______. State: e) Direction of opening: down f) Stretch or Compression: vertically stretched • Relation to the Vertex: The value of k is the ___y__ - coordinate of the vertex. The graph has been translated 3 units right • X-Intercepts: • If k = 0, then the graph has ______one____ zero (xintercept). • If k > 0,a>0 then the graph has ___No___ zeros (xintercepts). • If k < 0, a<0 then the graph has ___No__ zeros (xintercepts). • If k>0,a<0 then the graph has two zeros (two x-intercepts) • If k<0,a>0 then the graph has two zeros (two x-intercepts) Source: Edugains.ca Transformations: The graph has been translated 5 units up g) Coordinates of the vertex: (3,5) h) Number of x-intercepts: two x-intercepts because a<0 and k>0 Complete the following graphic organizer to summarize the roles of a, h and k-look at chapter 4 Source: Edugains.ca