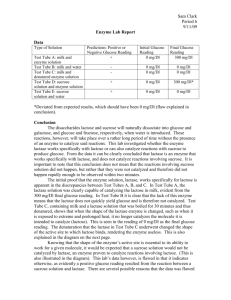
Enzyme Lab Lactase Inhibition Enzymes can be inactivated in several ways. One of them you learned about in biology: denaturing. Denaturing an enzyme involves changing the shape so the active site and substrate can no longer bind. Another way to inactivate an enzyme is by inhibiting it with another chemical. In this lab, you investigate as to whether lactose, sucrose, galactose or glucose are inhibitors for the enzyme lactase. OR, if you want to be very daring, you may choose to test something else (note: you must get the substance approved by your teacher first). Directions: 1. First, remind yourself of the basic reaction that lactase catalyzes: 2. Based on #1 and your background knowledge about enzymes, write a prediction for what you think will happen to the amount of glucose when each of the substances are tested: lactose, sucrose, galactose, glucose. Protocol: 1. Obtain 6 test tubes and label them with tape with the letters A-F, respectively. 2. Place them in a test tube rack. 3. Follow the guide below for what to put into each test tube: A = 8 ml of distilled water B = 4 ml of distilled water and 4 ml of Lactose solution C = 4 ml of Lactose solution and 4 ml of Sucrose solution D = 8 ml of Lactose solution E = 4 ml of Lactose solution and 4 ml of Galactose solution F = 4 ml of Lactose solution and 4 ml of Glucose solution 4. Now, add 2 ml of the Lactase solution to each test tube and gently swirl. Wait one minute. 5. Use a glucose test strip to test the amount of glucose present in each test tube. The units for the test strips are mg/dL. Dip the test strip in the solution and then place it on a paper towel. Wait about two minutes before you read the results and compare it to the color on the guide. 6. Record in a data table. (You will need to make that for yourself!) Name: __________________________________ Enzyme Lab Questions (these will be graded) 1. Which tubes were controls? 2. Your conclusions as to why some tubes either had more or less glucose in them than the control tubes: Water: Extra Lactose: Sucrose: Galactose: Glucose: 3. Based on your results, which substance do you think was “inhibiting” the lactase from working? Why do you think it might be doing this? 4. MAO-inhibitors are drugs that inhibit the action of the MAO enzyme. Some people make a lot of this enzyme naturally and some people make very efficient forms of the enzyme that aren’t inhibited very well by MAO-inhibitors. a) Who would feel the affects of an MAO-inhibitor more profoundly, someone with efficient MAO or someone with less efficient MAO? Explain briefly. b) Your severely depressed friend remarked that when she first started taking MAO-inhibitors she only needed 25 mg, but after 2 years, she now has to take 50 mg. Explain why this might be.