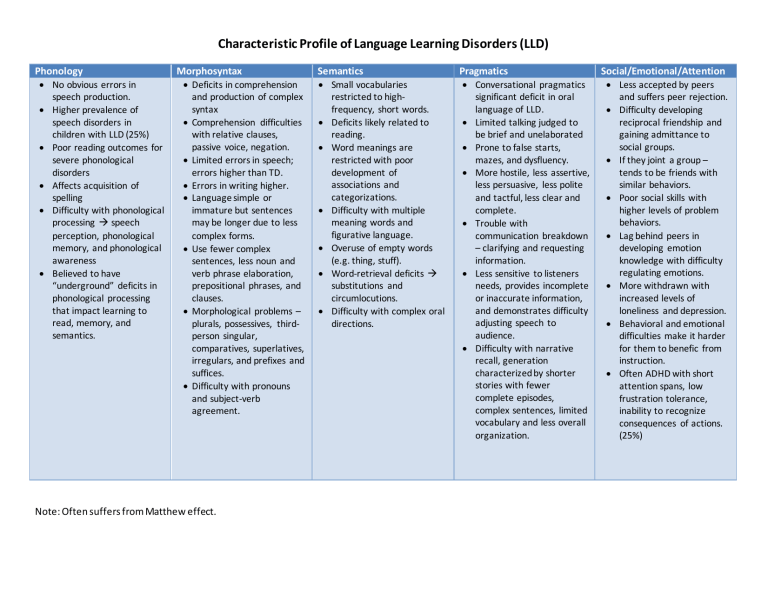
Characteristic Profile of Language Learning Disorders (LLD) Phonology • No obvious errors in speech production. • Higher prevalence of speech disorders in children with LLD (25%) • Poor reading outcomes for severe phonological disorders • Affects acquisition of spelling • Difficulty with phonological processing speech perception, phonological memory, and phonological awareness • Believed to have “underground” deficits in phonological processing that impact learning to read, memory, and semantics. Morphosyntax • Deficits in comprehension and production of complex syntax • Comprehension difficulties with relative clauses, passive voice, negation. • Limited errors in speech; errors higher than TD. • Errors in writing higher. • Language simple or immature but sentences may be longer due to less complex forms. • Use fewer complex sentences, less noun and verb phrase elaboration, prepositional phrases, and clauses. • Morphological problems – plurals, possessives, thirdperson singular, comparatives, superlatives, irregulars, and prefixes and suffices. • Difficulty with pronouns and subject-verb agreement. Note: Often suffers from Matthew effect. Semantics • Small vocabularies restricted to highfrequency, short words. • Deficits likely related to reading. • Word meanings are restricted with poor development of associations and categorizations. • Difficulty with multiple meaning words and figurative language. • Overuse of empty words (e.g. thing, stuff). • Word-retrieval deficits substitutions and circumlocutions. • Difficulty with complex oral directions. Pragmatics • Conversational pragmatics significant deficit in oral language of LLD. • Limited talking judged to be brief and unelaborated • Prone to false starts, mazes, and dysfluency. • More hostile, less assertive, less persuasive, less polite and tactful, less clear and complete. • Trouble with communication breakdown – clarifying and requesting information. • Less sensitive to listeners needs, provides incomplete or inaccurate information, and demonstrates difficulty adjusting speech to audience. • Difficulty with narrative recall, generation characterized by shorter stories with fewer complete episodes, complex sentences, limited vocabulary and less overall organization. Social/Emotional/Attention • Less accepted by peers and suffers peer rejection. • Difficulty developing reciprocal friendship and gaining admittance to social groups. • If they joint a group – tends to be friends with similar behaviors. • Poor social skills with higher levels of problem behaviors. • Lag behind peers in developing emotion knowledge with difficulty regulating emotions. • More withdrawn with increased levels of loneliness and depression. • Behavioral and emotional difficulties make it harder for them to benefic from instruction. • Often ADHD with short attention spans, low frustration tolerance, inability to recognize consequences of actions. (25%)


