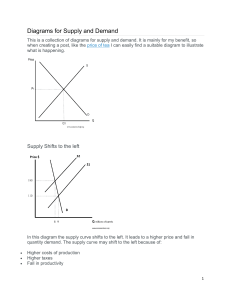
The concept of elasticity for demand is importance for determining the prices of various factors of production. Discuss the various factors that influences the price elasticity of demand The price elasticity of demand (PED) is a measure that captures the responsiveness of a good’s quantity demanded to a change in its price. More specifically, it is the percentage change in quantity demanded in response to a one percent change in price when all other determinants of demand are held constant . the first one is nature of groups which of course you can take take nature of goods means some goods are consumable goods some Goods are durable goods and some words are costly good some words are cheaper goods so like based on the nature of goods demand will be more or less consumable and regular basis good these Goods demand will be always stable whatever will be the changes in the fact that does not make much difference changes in the income that does not make any difference what makes difference is nothing so because of the GU versus consumable and the boots which are luxury then that makes the difference luxury goods if the prices are increasing then demand will be less price is decreasing then demand will be more so like and in the same way another goods also you can take like seasonal Goods according to season it makes difference so based on the nature of goods the demand become more or less taken with availability of close substitutes close substitute product a is our product there are substitutes like BCD many products have their this is our product substitutes are this BCD or the substitutes then any changes in our product which makes difference to the other products price is decreasing by ourself then the other products word is using they'll come down to our product if we are increasing there the product so based on the other products also so our ability of close substitute no substitutes then we have one Apple II so whatever we say people have to a consumer has to follow it once upon a time it was like butter but I was having horrible use and some of the products also one of our technologies you will find a lot of competition anyway this is about the availability of close substitutes and third one is complimentary what other complements since we are giving if you are giving compliment as in the sense like if we are purchasing car do we learn and there are item Utley we have to go for the Patrol so both are attached if car rate is introducing if two wheeler four wheeler any vehicles consumption is more petrol price is also going to be demanded and god price will be whatever it may be price demand will be more for that products so that's what complimentary and goods having several useless and sometimes few goods will be using in many ways when we use it in many ways automatically that demand will be more or less according to usage less there're usages demand weakness more we can use it many times so in the same postponement of purchases some Goods can be postponed and some goods cannot be postponed first affordable Goods not luxury items not required not much argent so these are like AC car inverter this kind of product are can be postponed not require gently this demand will be different and where we need to some products regularly how to purchase it we have to use it so that cannot be postponed so demand will vary it between the postponed able-nan forceful items and in the same way proportionate up in those who spent this already means put in the previous talk they install the income will have demand more areas elasticity of demand will be increasing at facing because of income income is more demand will be more income is less automatically demand will be less the best example which we have taken already the real estate business is a good time according to the time also demand will increase or decrease elasticity of demand will be very ating say for example season and time you can take somewhere for products some few products you have more demand winter few products will have more defined within the rainy season with have more demand for rain course some real of something like that so based on the time also the demand will increase or decrease the price level whenever price is increasing to decreasing most of the time that makes the difference in the demand the price levels increasing demand will be more so when our price is increasing then demand will be decreasing inverse relation whenever fries is decreasing then divide will be more its River inverse relation so based on the price level also you will find elastic demand there's a lot of negatives the same habits habits will be changing habits fashion technology is changing once upon a time for pew-pew product there was a lot of demand now trend has changed little demand for another product best example which you can take telephone muncipal used to use maximum landline phone there was no cell phone at all now land land has decreased because of the technology cell phones got increased passion technology are changes in the taste that also makes difference and the next one is income group income group few people income will be more when income is more so according to that demand will be more income is less demand also will be less so these are the 10 factors which makes difference in the elasticity of demand The price elasticity of demand (PED) is a measure that captures the responsiveness of a good’s quantity demanded to a change in its price. More specifically, it is the percentage change in quantity demanded in response to a one percent change in price when all other determinants of demand are held constant . Factors affecting price elasticity of demand Nature of the Commodity Influence Elasticity of Demand - It mainly depends or the nature of the commodity and the degree of necessity. The elasticity of demand depends on whether a commodity is necessity, comfort or luxury. Normally the demand for necessaries of life such as rice, wheat, salt, etc., will be inelastic as these are essential for existence. So, everyone will demand a minimum quantity whatever be the price. On the other hand the demand for comforts and luxuries may not have inelastic demand. When the prices of these fall, generally, more of the commodities will be demanded. The number of close substitutes – Commodities having substitutes will have elastic demand and goods with no substitutes will have inelastic demand. When the price of a commodity rises, the people would shift their preference to substitute commodities and demand the substitutes with the hope that the price of substitutes will not rise. Consequently the demand will fall heavily for the commodity for which the price has been increased. Suppose the commodity does not have substitute at all like salt, any change in price will not affect the demand and so the demand will be inelastic the more close substitutes there are in the market, the more elastic is demand because consumers find it easy to switch. E.g. Air travel and train travel are weak substitutes for inter-continental flights but closer substitutes for journeys of around lower distance e.g. between major cities in a large country. The degree of necessity or whether the good is a luxury – Electricity is an essential component of modern life. Just one day without electricity, a big city can turn into a living hell. Regardless of the price increase, people will keep using it. Therefore, electricity, as many other necessary goods, is relatively inelastic. However, merely the necessity of a product do not tell us much about its elasticity. Well, the product may be a luxury one, and yet still inelastic. Talking of a jewelry brand. Necessities tend to have an inelastic demand whereas luxuries tend to have a more elastic demand. An example of a necessity is rare-earth metals which are an essential raw material in the manufacture of solar cells, batteries. China produces 97% of total output of rare-earth metals – giving them monopoly power in this market. Whether the good is subject to habitual consumption –. If the consumers are addicted to some habits and customs, then, the demand of the commodity will be inelastic. But if the rise in price persists for a long time, even addicts would try to reduce the demand either by resorting to some alternative substitutes or curbing the habit. Generally, commodities and drugs which are stimulants will have inelastic demand. Consumers become less sensitive to the price of the good of they buy something out of habit . Number and Variety of Uses of the Product - The more the number and variety of uses of a good, the more would be its elasticity of demand. One such good is electricity that is used in a number of ways. For example, use of electricity for the purposes of lighting, heating, cooking, ironing and also use electricity as a source of power in industries. That is why when the price of electricity diminishes (increases), its demand will increase (decrease) in all these uses, and so, in totality, its demand will increase (decrease) considerably, giving us a high value of the (numerical) coefficient of price-elasticity of demand. Proportion of a consumer's income allocated to spending on the good – As this ratio increases, people become more pricesensitive for that particular product. Especially if the same product is sold on other online stores, customers will try to catch the best price. Meaning, a change in the price will be detected by customers and reflected in demand. Products that take up a high % of income will have a more elastic demand . It is concluded then that if the buyers spend a small proportion of their income on a good, then its price-elasticity of demand would be relatively small. On the other hand, if they spend a large proportion of their income on a good, then its elasticity of demand would be relatively high. That is, elasticity of demand for a good depends upon the proportion of income spent on the good. Price of the Goods - The elasticity of demand for a good also depends on its own price. As price changes, quantity demanded of the good changes, owing to the law of demand. Also, at different prices of the product, i.e., at different points on the demand curve for a good, the coefficient of price-elasticity of demand for the good would be different. Generally, the smaller the price of a good, the less is the elasticity of its demand. For, when the price is very small, a change in price would have no considerable effect on demand. On the other hand, the larger the price, the more would be the elasticity of demand. For, when the price is relatively large, a further rise in price would have a considerable dampening effect on demand and a fall in price would have an encouraging effect on demand. Elasticity of demand will be high at higher level of the price of the commodity and low at lower level of price. Time allotted for consumption -When people can’t afford the existing solution of a problem, they manage to come up with a cheaper solution in the long run. A cliché but a good example is the gas prices. A lot of people drive to work. Suppose there is a sharp increase in gas prices. They have to keep going to work, therefore they can’t react to the price change quickly. But in the long run, people will start moving into nearer places to their work and walk there. Therefore, in the long run, elasticity increases. Commodity whose consumption can be put off experiences elastic demand whereas the commodity whose consumption cannot be postponed, like medicine, has inelastic demand. COMPLEMENTERIES Postponement of consumption - Commodity whose consumption can be put off experiences elastic demand whereas the commodity whose consumption cannot be postponed, like medicine, has inelastic demand.