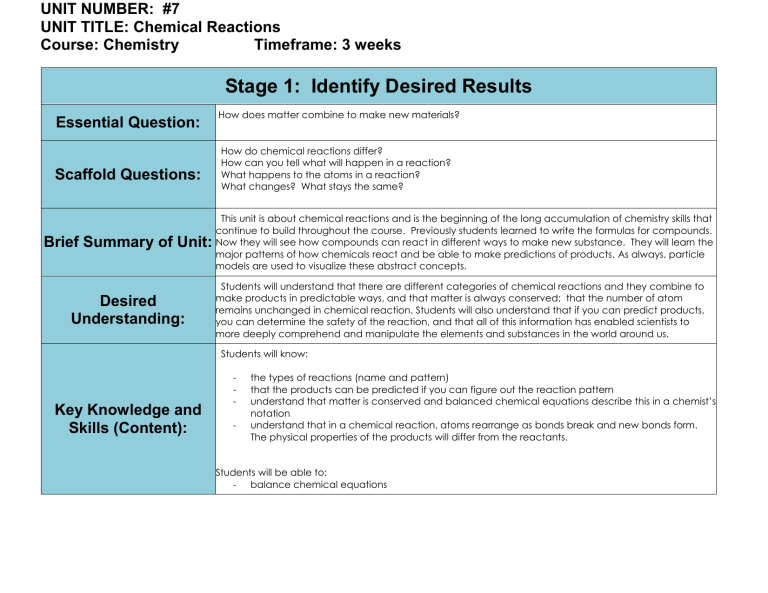
UNIT NUMBER: #7 UNIT TITLE: Chemical Reactions Course: Chemistry Timeframe: 3 weeks Stage 1: Identify Desired Results Essential Question: Scaffold Questions: Brief Summary of Unit: Desired Understanding: How does matter combine to make new materials? How do chemical reactions differ? How can you tell what will happen in a reaction? What happens to the atoms in a reaction? What changes? What stays the same? This unit is about chemical reactions and is the beginning of the long accumulation of chemistry skills that continue to build throughout the course. Previously students learned to write the formulas for compounds. Now they will see how compounds can react in different ways to make new substance. They will learn the major patterns of how chemicals react and be able to make predictions of products. As always, particle models are used to visualize these abstract concepts. Students will understand that there are different categories of chemical reactions and they combine to make products in predictable ways, and that matter is always conserved; that the number of atom remains unchanged in chemical reaction. Students will also understand that if you can predict products, you can determine the safety of the reaction, and that all of this information has enabled scientists to more deeply comprehend and manipulate the elements and substances in the world around us. Students will know: Key Knowledge and Skills (Content): - the types of reactions (name and pattern) that the products can be predicted if you can figure out the reaction pattern understand that matter is conserved and balanced chemical equations describe this in a chemist’s notation understand that in a chemical reaction, atoms rearrange as bonds break and new bonds form. The physical properties of the products will differ from the reactants. Students will be able to: - balance chemical equations UNIT NUMBER: #7 UNIT TITLE: Chemical Reactions Course: Chemistry Timeframe: 3 weeks - write formula equations from word equations identify reaction type, particularly synthesis w/oxygen and combustion create an activity series of metals based upon lab data predict the products of synthesis, single replacement, double replacement and decomposition reactions determine if equations are accurate representations draw particle models of simple reactions HS-PS1-2. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties. State Science Standards HS-PS1-7. Use mathematical representations to support the claim that atoms, and therefore mass, are conserved during a chemical reaction. HS. PS1-4 Develop a model to illustrate that the release or absorption of energy from a chemical reaction system depends upon the changes in total bond energy. State Standards Reading RST.9-10.7 Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form (e.g., a table or chart) and translate information expressed visually or mathematically (e.g., in an equation) into words. (HS-PS1-1) State Standards Writing WHST.9-12.5 Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. (HS-PS1-2) Alignment to the Vision of High Quality Instruction in Science (How do the instructional targets in this unit align to the district’s vision of high quality instruction?) Students will engage in the following scientific practices: - Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking - Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions - Developing and Using Models Stage 2: Determine Acceptable Evidence UNIT NUMBER: #7 UNIT TITLE: Chemical Reactions Course: Chemistry Timeframe: 3 weeks (How will students demonstrate their attainment of the desired understanding?) Students will need to write equations to describe real world reactions and also draw particle models of reactions. science.chemistry.unit7.PerfTask Performance Task HS-PS1-2. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties. HS-PS1-7. Use mathematical representations to support the claim that atoms, and therefore mass, are conserved during a chemical reaction. Degree of Competence/Criteria (How will we evaluate quality student work in the performance task? How will we determine that students can use their learning independently?) Key (How will we know if students can demonstrate mastery of the unit’s content, skills, and common core state standards?) science.chemistry.unit7.contTest Other Evidence (Content-Centered) Key HS-PS1-2. Construct and revise an explanation for the outcome of a simple chemical reaction based on the outermost electron states of atoms, trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties. HS-PS1-7. Use mathematical representations to support the claim that atoms, and therefore mass, are conserved during a chemical reaction. UNIT NUMBER: #7 UNIT TITLE: Chemical Reactions Course: Chemistry Timeframe: 3 weeks Student Self-Reflection Students will reflect around science.chemistry.unit7.StudentRefl and Self-Regulation (Student-Centered) System-Centered Competence Performance assessment uses question stems that are in this format