Genetics: Incomplete Dominance, Multiple Alleles, Mutations
advertisement

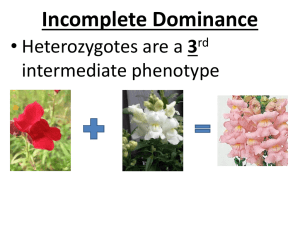
GENETICS Chapter 11, Section 2 Incomplete Dominance Neither allele seems dominant Result is an intermediate phenotype When the offspring of two homozygous parents show intermediate phenotype Example: A red flower and a white flower are crossed. The result is a pink flower. Nothing is dominant. Multiple Alleles A trait that is controlled by more than two alleles is controlled by this. Produce more than three phenotypes of that trait Blood type produces four phenotypes (A blood, B blood, AB blood, and O blood) Alleles are A, B, and O. O is recessive to both A and B A and B are both dominant Possible genotypes: AA, AO, BB, BO, AB, OO Polygenic Inheritance Occurs when a group of gene pairs acts together to produce a trait. More than one gene contributes to the phenotype Many alleles, examples: eye color, skin color, height, weight, intelligence, behavior Traits vary over a wide range Environment plays an important role in the expression of traits controlled by this Impact of Environment Your environment plays a role in how some of your genes are expressed or whether they are expressed at all. Environmental influences can be external or internal. You might be able to influence their expression by the decisions you make. We will discuss examples. Mutations Errors in the DNA when it is copied inside of a cell—changes in genes Not all mutations are harmful Possible causes: X-rays, sunlight, chemicals Problems can also occur if the incorrect number of chromosomes is inherited because of mistakes in the process of meiosis. Example—Down’s syndrome results when three copies of chromosome 21 are produced Recessive Genetic Disorders Disorders caused by recessive genes Cystic fibrosis—thick mucus builds up in the lungs and it is hard to breathe, also hard to digest food because mucus reduces the flow of substances necessary for digestion Sex Determination Dad determines the sex of the child Alleles for females: XX Alleles for males: XY Each parent gives one allele and a mom can only give an X. Sex-Linked Disorders Sex-linked gene—an allele inherited on a sex chromosome Example: color blindness caused by a trait on the X chromosome Males are colorblind if their X has the trait Females are colorblind if BOTH of their X’s has the trait.