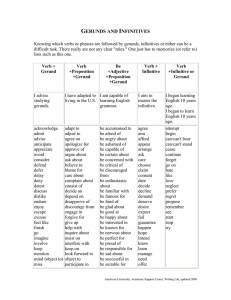
Gerund What is a gerund? • The Gerund is non-finite form of the verb which can have the force of a verb as well as that of a noun • Non-finite Verbs • A non-finite verb (also known as a verbal) is the term used to describe a verb that is not showing tense. In other words, it’s a verb form that does not act like a verb (or, at least, the type of verb you need to form a sentence). Therefore, a non-finite verb is never the main verb in a sentence. (That's a finite verb.) There are three types of non-finite verbs: gerunds (e.g., baking, singing). • infinitives (e.g., to bake, to sing). • participles (e.g., baking/baked, singing/sung). The Forms of the Gerund Present Perfect Active reading having read Passive being read having been read The Tense and Voice Distinctions of the Gerund • The Present Gerund denotes an action simultaneous with that expressed by the main verb. • I think of making you a present • He continued writing his letter. The Tense and Voice Distinctions of the Gerund • The Perfect Gerund denotes an action prior (before)to the action expressed by the main verb. • They reported having taken part in the competition. The Present Gerund can denote a prior action: • After the verbs to remember, to forgive, to excuse, to thank • Eg. Thank you for helping me. • I remember posting the letters. The Present Gerund can denote a prior action: • After the prepositions on and after • Eg. On reaching the end of the street we turned towards the river. • After catching a few fish, we prepared a good breakfast The Voice Distinctions • After the verbs to want, to need, to require, to deserve and the adjective worth we use the active gerund (though the meaning is passive) • My watch needs repairing • The film is worth seeing The Functions of the Gerund As the subject of a sentence Eg. Dancing was Mary’s hobby. as an object: Eg. He likes teaching English The Functions of the Gerund As an attribute (with preposition): Eg. It’s the best way of explaining this grammar rule An adverbial modifier: Eg. She dressed without making a sound The Functions of the Gerund As part of a compound verbal predicate: Eg. Let’s begin reading the text The Gerund is used after: Accuse of Apologize for Approve of Blame smb. for Congratulate on Prefer to Thank for Think of The Gerund is used after: Consist in Count on Depend on Hear of Inform of Insist on Prevent from Succeed in The Gerund is used after: Admit Avoid Consider Delay Deny Enjoy Escape Excuse The Gerund is used after: Fail Fancy Finish Forgive Imagine Include Postpone Stop The Gerund is used after phrasal verbs Burst out Give up Go on Leave off (stop) Keep on Put off (delay) Verbs used with the Gerund and the Infinitive To like To prefer To hate To begin To start To remember To forget To regret Verbs used with the Gerund and the Infinitive To stop To cease To continue To try To be afraid of To go on Remember+ a gerund To talk about a memory Example: I remember about posting the letter Remember+ to infinitive To talk about something someone needs to do Example: Remember to post the letter!