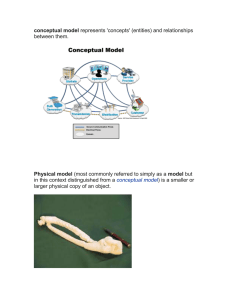
Week 6 summary Low-Fidelity Prototyping are useful because they tend to be simple, cheap, and quick to produce. And does not look very much like the final product and does not provide the same functionality. ● Storyboarding ● Sketching ● Wizard of Oz High-fidelity prototype looks like the final product and/or provides more functionality than a low-fidelity prototype, High-fidelity prototypes can be developed by modifying and integrating existing components – both hardware and software. conceptualizing the design the benefits: ● Orientation: enabling the design team to ask specific kinds of questions about how the conceptual model will be understood by the targeted users. ● Open-mindedness: preventing the design team from becoming narrowly focused early on. ● Common ground: allowing the design team to establish a set of common terms that all can understand and agree upon, reducing the chance of misunderstandings and confusion arising later on. conceptual model provides a working strategy and a framework of general concepts and their interrelations. The core components are: ● Metaphors and analogies that convey to people how to understand what a product is for and how to use it for an activity (e.g. browsing, bookmarking). ● The concepts that people are exposed to through the product, including the task– domain objects they create and manipulate, their attributes, and the operations that can be performed on them (e.g. saving, revisiting, organizing). ● The relationships between those concepts (e.g. whether one object contains another, the relative importance of actions to others, and whether an object is part of another). ● The mappings between the concepts and the user experience the product is designed to support or invoke (e.g. one can revisit through looking at a list of visited sites, most-frequently visited, or saved websites). The classics include the desktop, spreadsheet and the web. Metaphors are considered to be a central component of a conceptual model. Key guiding principles of conceptual design are: 1. Keep an open mind but never forget the users and their context. 2. Discuss ideas with other stakeholders as much as possible. 3. Use prototyping to get rapid feedback. 4. Iterate, iterate, and iterate. Conceptual design and concrete design are closely related. The difference between them is rather a matter of changing emphasis: during design, conceptual issues will sometimes be highlighted and at other times, concrete detail will be stressed. Concrete design also deals with issues related to user characteristics and context, and two aspects that have drawn particular attention for concrete design are accessibility and national culture. Scenarios 1. As a basis for the overall design. 2. For technical implementation. 3. As a means of cooperation within design teams. 4. As a means of cooperation across professional boundaries, i.e. as a basis of communication in a multidisciplinary team. two kinds of resource: physical computing kits and software development kits (SDKs). Physical computing is concerned with how to build and code prototypes and devices using electronics. A software development kit (SDK) is a package of programming tools and components that supports the development of applications for a specific platform, e.g. for iOS on iPad, iPhone, and iPod touch, for the Kinect device, and for the Windows phone. SDK: program tools and components API : inputs and outputs