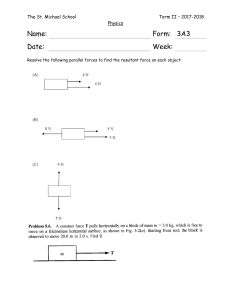
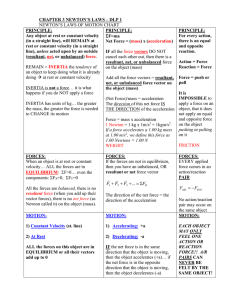
Newton’s nd 2 Law Thursday, 19 March 2020 Newton’s nd 2 Law: Starter On the Starter WS, determine the Resultant Force and Direction in each case. (02:06:55) 4 minutes Answers. A. 6 N Right B. 0 N C. 5 N Left D. 10 N Left E. 10 N Right F. 0 N G. 7 N Left H. 100 N Right Newton’s nd 2 Law: Lesson Objectives Understand and apply Newton’s 2nd Law of motion. Newton’s nd 2 Law: Learning Outcomes 1. Be able to determine which of Newton’s laws to apply (balanced vs unbalanced forces). 2. Be able to restate Newton’s 2nd law and how force, mass and acceleration are related. 3. Be able to apply Newton’s 2nd law. Balanced Forces: Newton’s st 1 Law Recall Newton’s 1st Law An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. The first law will apply when the forces are balanced From the starter WS determine where Newton’s 1st Law applies (02:06:55) 1 minute B and F Newton’s nd 2 Law: Resultant Force The second law states that the acceleration of an object depends on the Resultant Force acting upon the object and the Mass of the object. Newton’s 2nd Law applies to Unbalanced Forces (when there is a Resultant Force). From the Starter WS determine where Newton’s 2nd Law applies (02:06:55) 2 minutes A C D E G H Newton’s nd 2 Law: Equation Acceleration = Force ÷ Mass Example: Force = 30 N, Mass = 10 kg Acceleration = 30 N ÷ 10 kg = 3 m/s² From the Starter WS calculate the acceleration in each case (02:06:55) 6 mins Force = Mass X Acceleration Mass = Force ÷ Acceleration Units: mass – kg (kilograms) F – Newtons (N) Acceleration – m/s² (meters per second squared) 4N 10N Resultant Force = 6 N Calculate acceleration = F/m 15N 25N Resultant Force = 10 N Calculate acceleration = F/m a = 10 N/2 kg = 5m/s² 5N Resultant Force = 0 N Calculate acceleration = F/m a = 0 N/1 kg = 0 m/s² 5N Resultant Force = 7 N Calculate acceleration = F/m a = 7 N/14 kg = 0.5 m/s² 500 N Resultant Force = 100 N Calculate acceleration = F/m a = 100 N/50 kg = 2 m/s² a = 6 N/6 kg = 1 m/s² Mass = 6 kg 10N Mass = 2 kg 10N Resultant Force = 0 N Calculate acceleration = F/m 5N a = 0 N/10 kg = 0 m/s² Mass = 10 kg 10N Mass = 1 kg 5N Resultant Force = 5 N Calculate acceleration = F/m 12N a = 5 N/2.5 kg = 2 m/s² Mass = 2.5 kg 15N Mass = 5 kg Mass = 14 kg 5N Resultant Force = 10 N Calculate acceleration = F/m a = 10 N/ 5 kg = 2 m/s² 400 N Mass = 50 kg Newton’s nd 2 Law: Word Problems (02:06:55) 5 mins 5 minutes End Newton’s 1st Law st 1 and nd 2 Laws Summary 2nd Law A Resultant Force = 4N E 10N 15N 25N Direction Mass = 6 kg Direction Mass = 2 kg B Resultant Force = 10N F Resultant Force = 5N 10N 5N Direction Mass = 10 kg C 10N Direction Mass = 1 kg 5N Resultant Force = G Resultant Force = 12N 5N Direction Mass = 2.5 kg Direction Mass = 14 kg D Resultant Force = 15N 5N H Resultant Force = 400 N Direction Mass = 5 kg Resultant Force = 500 N Direction Mass = 50 kg Resultant Force = 6 N Right 4N 10N Mass = 6 kg 15N 25N Mass = 2 kg Resultant Force = 0 N 10N Resultant Force = 0 N 5N 10N Mass = 10 kg 10N 5N Mass = 1 kg 5N Resultant Force = 5 N Left Resultant Force = 7 N Left 12N Mass = 2.5 kg 5N Mass = 14 kg Resultant Force = 10 N Left 15N Mass = 5 kg Resultant Force = 10 N Right 5N Resultant Force = 100 N Right 400 N Mass = 50 kg 500 N A. Resultant Force = 6 N E. Mass = 6 kg Newton’s Law: 2ND Mass = 2 kg Newton’s Law: 2ND B. Resultant Force = 0 N F. Resultant Force = 0 N 4N 10N 10N 15N 5N 10N 25N Resultant Force = 10 N 5N Mass = 10 kg Newton’s Law: 1ST Mass = 1 kg Newton’s Law: 1ST C. Resultant Force = 5 N G. Resultant Force = 7 N 10N 5N 12N 5N Mass = 2.5 kg Newton’s Law: 2ND Mass = 14 kg Newton’s Law: 2ND D. Resultant Force = 10 N H. Resultant Force = 100 N 15N 5N 400 N Newton’s Law: 2ND Mass = 5 kg 500 N Newton’s Law: 2ND Mass = 50 kg