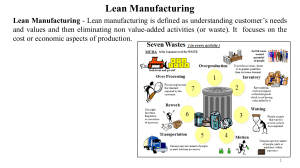
Operations Management Producing Goods and Services IGCSE BUSINESS STUDIES Definitions • Production – Process of adding value to a product (using four factors of production – land, labour, capital and enterprise) to satisfy customer needs and wants. • Productivity – How a business measures it’s efficiency Calculating Productivity Productivity could mean using fewer inputs to produce the same amount of output. Or using the same amount of input to produce a greater amount of output Increasing Productivity Ways to improve productivity • Improving layout of factory so production becomes faster and more efficient • Training workers so they can be more productive • Using automation Benefits of increasing efficiency/productivity • Lower cost per unit • Less employees needed (reduce labour cost) • Reduces overall costs. Holding Stocks Why do businesses hold stock? • Businesses keep stocks for a variety of reasons, for example, factories keep raw material inventory to make sure there are enough materials for production while a shop might hold stock to ensure that products are available to customers. Too much stock • Money wasted on storage cost • Depreciation cost • Shelf life (items may reach best before date before being sold) • Money could’ve been used on something else Not enough stock • Opportunity lost (profit could be made if product sold) Stock Control Chart Buffer stock is inventory to deal with sudden customer demands for a product or in case supplies doesn’t get delivered on time. Defining Lean Production Lean Production is a term for techniques used by businesses to cut down waste and increase efficiency. Common wastes in businesses • Overproduction – Producing too many products which then costs the business money to keep the product in storage. (and may get damaged/expires etc..) • Waiting – Goods not being processed • Transporting – Materials being moved around the factory inefficiently • Over-processing – e.g. using advanced machine to do simple tasks • Defects- production of faulty products which can’t be sold. How Lean Production reduces cost Costs can be reduced by lean production Benefits of lean production • Less storage of raw materials (e..g no need for refrigeration costs, warehouse etc…) • Less defects in production (broken products don’t get produced) • Better use of equipment • Speeding up production by cutting out unnecessary tasks • Less money tied up in stock Lean Production via Kaizen Kaizen means continuous improvement by eliminating waste: • Workers meet regularly to discuss problems and possible solutions • In this way, wastage is reduced and efficiency is improved • Factory floors are usually rearranged so that the flow of production from one activity to the next is improved. Lean Production via JIT Just-in-time (JIT) production focuses on: • Focus on reducing the need to hold stocks of raw material or parts that are needed (This reduces storage costs) • Raw materials are delivered just in time by suppliers for production • Reliable suppliers are needed for this to work As example, fruit might get delivered to for processing 30 minutes before production starts, this means that the factory won’t have to spend money on expensive refrigerators to store fruit before it gets produced and produced into cans. Lean Production via cell production Cell production is where: • The production line is divided into separate teams of workers, each makes a part of the finished production • Motivation is improved due to the variety of tasks and the worker belonging to a team Video Presentation Methods of Production JOB PRODUCTION Job Production is where each product is different and made to specific instructions by the consumer. e.g. tailor made suits, customizable birthday/wedding cakes Advantages of Job production • Workers have more varied job (They won’t become bored) • Higher price can be charged for product • Product meets requirements of the customer Disadvantages of Job production • Costs of production are high because skilled labour is used • Product takes a long time to produce • Products are made to order so any errors may be expensive for the company to fix Methods of Production BATCH PRODUCTION Baitch production s similar products are made in batches (e.g. batch of white shirts then another batch of green shirts are made) Advantages of Batch production • Gives more variety of jobs to workers • Production can be easily changed from one product to another • Gives consumers a variety of products (e.g. many colour shirts) Disadvantages of Batch production • Expensive to produce goods • Machines have to be reset when changing from one batch to another which slows down production (e.g. change colour of shirts from white to green dye) • Warehouse space is needed to store products Methods of Production FLOW PRODUCTION Flow production (Mass production) is where large quantities of identical products are produced on a continuous basis Advantages of Flow production • Goods are produced quickly and cheaply (economies of scale) • Increased efficiency through use of machinery • Less labour is needed (machines do the work) • Automated production line means production can operate overnight Disadvantages of Flow production • Very boring for workers (same product over and over) • Starting costs are high (expensive machines, big factory etc…) • If a machine breaks down the whole production line may stop • Expensive storage costs as they are lots of products Methods of Production WHAT PRODUCTION? Factors affecting which method of production to use • The nature of the product – Unique products will require job production. • Size of the market – Products with small number of customers mean job or batch production is used. Products with large amount of consumers = flow production should be used. • The nature of demand – Small and infrequent demand by customers means job or batch production will be used. • The size of the business – Small businesses tend to operate using job and batch production while large business may use flow production. Technology effects Improvements in technology can help reduce costs and improve product quality • Automation – Production by equipment which are controlled by computers. • Mechanisation – Production by machine operated by workers (human) • Computer aided design (CAD) – 3D drawing software to design new products • Electronic point of sale – Used at checkouts where stock records are automatically adjusted as an item barcode is scanned when it is sold. e.g. supermarket stock • Electronic funds transfer at point of sale (EFTPOS) – Cash registers connected to bank (Customer’s card is swiped and money is transferred right away from customer’s bank account Technology good or bad? Advantages of technology • Higher productivity • Improved motivation as boring jobs are now done by machines • Better quality products are produced • Faster communication • Improved flow of information for managers Disadvantages of technology • Higher unemployment as machines replace human labour • Technology is expensive • Technology becomes outdated very quickly and may needs to be upgraded often Video Presentation