
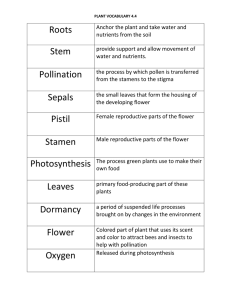
Plant Vocabulary 1. angiosperms - grouping of flower-producing, seed-bearing vascular plants. The reproductive structures are flowers in which the ovules are enclosed in an ovary. 2. anther - The part of the stamen where pollen is produced; a male flower part 3. auxin - a plant hormone that promotes root formation and bud growth; also responsible for plant tropisms such as phototropism and gravitropism 4. bryophytes - a grouping of land plants that do NOT have true vascular tissue and are nonvascular plants 5. cotyledon - seed leaf within the embryo of a seed. Flowering plants whose embryos have a single cotyledon are grouped as monocots; embryos with two cotyledons are grouped as dicots 6. cross-pollination - the pollination of a flower or plant with pollen from another flower or plant. 7. cuticle - outermost waxy layer on the top of a leaf which prevents water loss 8. dermal tissue - A layer of cells covering the outer parts of a plant, much like our skin, which protects the plant; these tissue cells secretes a waxy layer called the cuticle that inhibits water loss. 9. dicot - a flowering plant (angiosperm) that has a pair of leaves, or cotyledons, in the embryo of the seed. Most common garden plants, shrubs and trees, and broad-leafed flowering plants are in this subgrouping 10. ethylene gas - plant hormone that stimulates fruits to ripen 11. fertilization - the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism; in plants a seed may be formed as a result 12. fibrous root system - thin, moderately branching roots growing from the stem; root system found in monocot plants and ferns 13. filament - the thin part of a stamen that supports the anther; a male flower part 14. Flower/reproductive parts - flowers are the reproductive structures of Angiosperms; the flower parts are divided into male (stamen and anther) or female (stigma, style, and ovary). 15. fruit - the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) formed from the ovary after flowering 16. gibberelins - plant hormones that cause the roots, stems, and leaves to elongate (get longer) 17. grana or granum (singular) - the stack of thylakoids within the chloroplast of plant cells; grana contain chlorophyll and are the location of photosynthesis 18. gravitropism/geotropism - a change in the growth of a plant in response to gravity; roots grow in the direction of gravitation pull (positive response); stems grow away from gravitational pull (negative tropism) 19. ground tissue - The cells within a plant below the dermal tissue and around the vascular tissue whose function is to conduct photosynthesis and store water and glucose. 20. guard cells - specialized cells which control the opening and closing of stomata on a leaf 21. gymnosperms - grouping of seed-producing, vascular plants that includes conifers (pine and spruce trees), cycads, and ginkgos. The term "gymnosperm" has Greek language roots and means "naked seeds". 22. leaf - a plant structure whose primary function is to provide food for the plant through photosynthesis 23. light dependent reaction - the first part of photosynthesis where solar (light) energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP, which are used in the second part of photosynthesis; occurs in the granum and requires water (H2O) 24. light independent reactions (Calvin Cycle) - the second part of photosynthesis in which sugars are made from carbon dioxide. Also known as the Calvin cycle, this part of photosynthesis does not require light; occurs in the stroma 25. monocot - a sub-category of the angiosperm (flower plants) grouping; a flowering plant having one cotyledon or seed-leaf in the embryo. Grass and corn plants are monocot examples. 26. mycorrhizae - Mutualistic relationship between a fungus and the roots of the plant. The relationship mutualistic because the plant gains increased absorption of water and minerals from the soil and the fungus gets food (glucose) from the cells in the roots. 27. ovary - the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located at the base of the flower; a female flower part 28. ovule - the female reproductive structure that develops into a seed in a seed-bearing plant 29. phloem - vascular tissue that moves sugars (glucose) from the leaves to other parts of the plant. 30. photosynthesis - the process by which plants and other organisms which contain chlorophyll use sunlight to synthesize glucose (food) from water and carbon dioxide. The chemical formula is shown in the picture. 31. phototropism - tendency of plants to grow toward a source of light through the elongation of cells located on the opposite side of the stem 32. pistil - the female reproductive part of a flower. The pistil, centrally located, typically consists the ovary, a style, arising from the ovary, and a pollenreceptive tip, the stigma, variously shaped and often sticky 33. pollen - a powdery substance produced at the anther with contains male plant gametes (sperm cells). 34. pollination - a process in which pollen is transferred to the female reproductive organs of seed plants, thereby enabling fertilization and reproduction to occur 35. pteridophytes - grouping of primitive vascular plants such as ferns which do not produce seeds. 36. reaction - a response to something that happens; plant tropisms are a reaction to light, water, and gravity 37. root - the part of a plant which absorbs water and anchors the plant 38. root hairs - hair-like extensions which grow off of roots and which increase the surface area for greater water absorption 39. sepal - a part of the flower that are usually green, and function as protection for the flower in bud, and as support for the petals when in bloom. 40. sporangia - an enclosure in which spores are formed on the underside of fern fronds. See image. 41. stamen - the male fertilizing organ of a flower consisting of a pollencontaining anther and a filament 42. stem - main body or stalk of a plant that supports the leaves; contains vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) which transport water and food (glucose) up and down the stem. 43. stigma - The pollen-receptive surface of a pistil, usually sticky; it is located at the top of the style where deposited pollen enters the pistil 44. stimulus - a change in an organism's surroundings that causes the organism to react; examples are light, touch, temperature 45. stoma - a stoma (plural stomata) is a pore, or opening, found on the underside of leaves that is used to control gas exchange (CO2 in, O2 out) stoma/stomata - opening on the underside of a leaf which allows for gases to enter and exit the leaf. Oxygen exits and carbon dioxide enters a leaf through this opening 46. style - a long, slender stalk that connects the stigma and the ovary tap 47. root system - root system containing a central, large root; the main root is larger in diameter than the secondary roots. 48. thigmotropism - A directional growth of a plant in response to touch. 49. transpiration - the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers tropism A (directional) growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimulus; made possible by plant hormones 50. vacuole - vesicle (container) within the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosed by a membrane and typically containing fluids 51. vascular tissue - the tissues which move water and food (glucose) through the plant. Made up of phloem which moves glucose food and xylem moves water and minerals 52. xylem - the type of vascular tissue that conducts (moves) water and minerals from the roots upward through the stem to the leaves



![Plant Review Leaf Terminology 1. This leaf is [ lobed / unlobed ]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015513249_1-facb2ec0ce63e86d5e5176f641280e9a-300x300.png)
