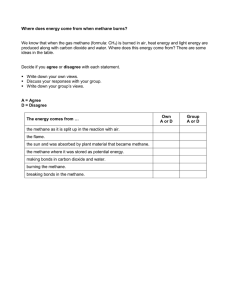
Name Date Heat of Combustion Lab Directions: In this activity, you will use experimental data obtained from a bomb calorimeter to calculate the molar heat of methane, CH 4 a hydrocarbon. You will then compare the experimental results with the actual molar heat of combustion of methane and calculate the percent error. 1. You may recall that the products of the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon are water vapor and carbon dioxide gas. Write the balanced equation showing the combustion of methane. Do not forget to include the states of matter of the reactants and the products. Hint: Methane is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. To begin the experiment, 1.11g of methane CH 4 is burned in a bomb calorimeter containing 1000 grams of water. The initial temperature of water is 24.85oC. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g oC. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 695 J/ oC . After the reaction the final temperature of the water is 35.65oC. 2. Calculate the change in temperature, ΔT 3. Using the formula q water = m • c • ΔT ,calculate the heat absorbed by the water 4. Using the formula q cal = Ccal • ΔT ,calculate the heat absorbed by the calorimeter. © 2016 Connections Education LLC. All rights reserved. 5. The total heat absorbed by the water and the calorimeter can be calculated by adding the heat calculated in steps 3 and 4. The amount of heat released by the reaction is equal to the amount of heat absorbed with the negative sign as this is an exothermic reaction. Using the formula ∆H = - (q cal + q water ) , calculate the total heat of combustion. 6. Evaluate the information contained in this calculation and complete the following sentence: This calculation shows that burning ____________ grams of methane [takes in/gives off] ______________ energy. 7. The molar mass of methane is 16.04 g/mol. Calculate the number of moles of methane burned in the experiment. 8. What is the experimental molar heat of combustion? 9. The accepted value for the heat of combustion of methane is -890 KJ/mol . Explain why the experimental data might differ from the theoretical value. = 10. Give the formula % error theoretical value − experimental value ×100% , theoretical value calculate the percent error for the experiment. © 2016 Connections Education LLC. All rights reserved. 2