3.3 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance - Lect-converted
advertisement

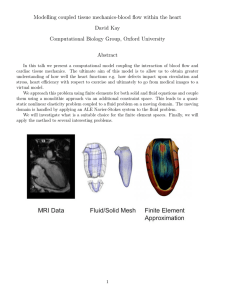
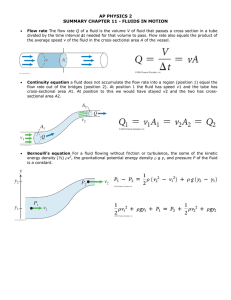
2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II Lecture #16: Fluid and Electrolyte Balance To Do: Tell if each of these is part of or refers to the intracellular (I) or the extracellular fluid compartment E). Lymph Cytoplasm Plasma Interstitial fluid Contains most of the body’s water Fluid located between tissue cells Transports substances in body Provides medium for chemical reactions to occur Answer the following: If you urinate more than you drink, you are in: a) positive water balance; b) negative water balance Obligatory water loss is: a) the amount of water we lose after vigorous exercise as sweat; b) loss that results in a negative water balance; c) the minimum amount of water lost each day. Other than urine, most water is lost through the: a) skin; b) lungs; c) sweat; d) feces. To Do: For each of the following statements, decide which direction fluid would tend to move. Use these choices: B = into the blood I = into the interstitial fluid C = into the cells Lower than normal sodium levels. Low blood pressure. Higher than normal sodium levels. Lower than normal levels of plasma proteins. High blood pressure. Higher than normal levels of plasma proteins. To Do: Mark whether each of these occurs when the plasma is too dilute (D) or too concentrated (C). Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus are stimulated. Vagus nerve causes feelings of thirst. Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus are inhibited. Feelings of thirst decrease. ADH secretion decreases. Water output decreases (more reabsorption) ADH secretion increases. Water output increases (less reabsorption) 1 4 To Do: Indicate whether each of the following would occur when fluid volume is too high (H) or too low (L). Hypovolemic shock Decreased angiotensin II levels High blood pressure Increased aldosterone secretion Decreased renin secretion Decreased aldosterone secretion Increased renin secretion Increased reabsorption of sodium Increased angiotensin II levels Decreased reabsorption of sodium If ADH is present, what effect will the absorbed fluid have on plasma concentration? a) it will make it more dilute b) it will make it more concentrated c) it will not change it REVIEW OF FLUID BALANCE – Answer the following questions: Fluid balance means that: a) the total volume of fluid is normal; b) the distribution of fluid in the various compartments is normal; c) both a and b To maintain fluid balance, output must input. a) be greater than; b) equal; c) be less than Movement between the plasma and interstitial fluid is controlled by: a) osmotic pressure b) hydrostatic pressure; c) both a and b Movement between interstitial fluid and intracellular fluid is controlled by: a) osmotic pressure b) hydrostatic pressure; c) both a and b The hormone that maintains the correct fluid volume is: a) aldosterone; b) ADH; c) angiotensin The hormone that maintains the correct fluid concentration is: a) aldosterone; b) ADH; c) angiotensin Eating salty potato chips without a drink would stimulate release of: a) aldosterone; b) ADH Dehydration due to evaporation of water vapor from the lungs would stimulate release of: a) aldosterone; b) ADH 4 5 To Do: Complete the following: Write the symbols for Na+, K+, Cl-, HPO4-2, Ca+2, and Mg+2 either inside or outside the cell to show where most is found. Which two fluid compartments are most similar in terns of the amounts of electrolytes found there? a) extracellular and intracellular b) interstitial and intracellular c) plasma and interstitial Edema could be caused by: a) lots of salt; b) too much potassium; c) too little sodium True or False: A change in the amount of fluid in a compartment could cause an electrolyte imbalance. Match the electrolytes with the statements below. Choices: Na+, K+, Cl-, 4HPO -2, Ca+2, and Mg+2. Forms bones & teeth, needed for blood clotting Helps maintain blood pressure Maintains electrical potential of cells Forms gastric acid, helps transport O2 and CO2 To Do: Match the statements with the imbalance they apply to. (Letters match the sections above) b. Simple water depletion c. Salt depletion d. Salt poisoning e. Abnormal sodium retention Taking a salt tablet without drinking sufficient water. Dehydration resulting from loss of water vapor through the lungs. The kidneys reabsorb too much salt and water due to high levels of aldosterone. A person with diarrhea drinks plenty of water, but doesn’t eat anything. Too little fluid is in the cells and too much is in the plasma and interstitial fluid; the fluid throughout the body has too much salt. The cells remain normal and the fluid concentration is fine, but there is too much fluid in the plasma and interstitial compartment. Fluid throughout the body is too dilute; the cells have too much water while the plasma and interstitial fluid have too little. Both the cells and the plasma and interstitial fluid have too little fluid; all the body’s fluids are too concentrated. 5 6 Lecture #16: Fluid and Electrolyte Balance – Answer Key Page 2 - Tell if each of these is part of or refers to the intracellular (I) or the extracellular fluid compartment E). E Lymph I E I Cytoplasm E Plasma E Interstitial fluid Contains most of the body’s water E Fluid located between tissue cells Transports substances in body I Provides medium for chemical reactions to occur Answer the following: B If you urinate more than you drink, you are in: a) positive water balance; b) negative water balance C Obligatory water loss is: a) the amount of water we lose after vigorous exercise as sweat; b) loss that results in a negative water balance; c) the minimum amount of water lost each day. B Other than urine, most water is lost through the: a) skin; b) lungs; c) sweat; d) feces. Page 3 - For each of the following statements, decide which direction fluid would tend to move. Use these choices: B = into the blood I = into the interstitial fluid C Lower than normal sodium levels. I Higher than normal sodium levels. I High blood pressure. B C = into the cells Low blood pressure. I Lower than normal levels of plasma proteins. B Higher than normal levels of plasma proteins. Page 4 - Mark whether each of these occurs when the plasma is too dilute (D) or too concentrated (C). C Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus are stimulated. C Vagus nerve causes feelings of thirst. D Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus are inhibited. D Feelings of thirst decrease. D ADH secretion decreases. C Water output decreases (more reabsorption) C ADH secretion increases. D Water output increases (less reabsorption) Page 5 - Indicate whether each of the following would occur when fluid volume is too high (H) or too low (L). L Hypovolemic shock H Decreased angiotensin II levels H High blood pressure L Increased aldosterone secretion H Decreased renin secretion H Decreased aldosterone secretion L Increased renin secretion L L Increased angiotensin II levels H Decreased reabsorption of sodium Increased reabsorption of sodium C If ADH is present, what effect will the absorbed fluid have on plasma concentration? a) it will make it more dilute b) it will make it more concentrated c) it will not change it 6 7 Page 6 - REVIEW OF FLUID BALANCE – Answer the following questions: C Fluid balance means that: a) the total volume of fluid is normal; b) the distribution of fluid in the various compartments is normal; c) both a and b B To maintain fluid balance, output must input. a) be greater than; b) equal; c) be less than C Movement between the plasma and interstitial fluid is controlled by: a) osmotic pressure b) hydrostatic pressure; c) both a and b A Movement between interstitial fluid and intracellular fluid is controlled by: a) osmotic pressure b) hydrostatic pressure; c) both a and b A The hormone that maintains the correct fluid volume is: a) aldosterone; b) ADH; c) angiotensin B The hormone that maintains the correct fluid concentration is: a) aldosterone; b) ADH; c) angiotensin B Eating salty potato chips without a drink would stimulate release of: a) aldosterone; b) ADH B Dehydration due to evaporation of water vapor from the lungs would stimulate release of: a) aldosterone; b) ADH A Drinking a liter of water without eating food would cause more secretion of: a) aldosterone; b) ADH Page 9 - Complete the following: Write the symbols for Na+, K+, Cl-, HPO4-2, Ca+2, and Mg+2 either inside or outside the cell to show where most is found. Na+ Cl - Ca+2 K+ HPO4-2 Mg+2 C Which two fluid compartments are most similar in terns of the amounts of electrolytes found there? a) extracellular and intracellular b) interstitial and intracellular c) plasma and interstitial A Edema could be caused by: a) lots of salt; b) too much potassium; c) too little sodium T True or False: A change in the amount of fluid in a compartment could cause an electrolyte imbalance. Match the electrolytes with the statements below. Choices: Na+, K+, Cl-, 4HPO -2, Ca+2, and Mg+2. Ca+2 Forms bones & teeth, needed for blood clotting K+ Maintains electrical potential of cells Mg+2 Na+ Helps maintain blood pressure Cl- Forms gastric acid, helps transport O2 and CO2 HPO4-2 Part of ATP, forms a buffer system for pH Depressing ion found in chlorophyll 7 8 Page 11 - Match the statements with the imbalance they apply to. (Letters match the sections above) b. Simple water depletion c. Salt depletion d. Salt poisoning e. Abnormal sodium retention D Taking a salt tablet without drinking sufficient water. B Dehydration resulting from loss of water vapor through the lungs. E The kidneys reabsorb too much salt and water due to high levels of aldosterone. C A person with diarrhea drinks plenty of water, but doesn’t eat anything. D Too little fluid is in the cells and too much is in the plasma and interstitial fluid; the fluid throughout the body has too much salt. E The cells remain normal and the fluid concentration is fine, but there is too much fluid in the plasma and interstitial compartment. C Fluid throughout the body is too dilute; the cells have too much water while the plasma and interstitial fluid have too little. B Both the cells and the plasma and interstitial fluid have too little fluid; all the body’s fluids are too concentrated. 8