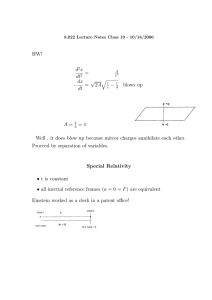
Fundamentals M15 GAS TURBINE ENGINE M15.18 Auxiliary Power Units (APUs) EASA Part-66 CAT A M15.18_A E Rev.-ID: 1APR2013 Author: DaC For Training Purposes Only ELTT Release: Jul. 10, 2013 Training Manual For training purposes and internal use only. E Copyright by Lufthansa Technical Training (LTT). LTT is the owner of all rights to training documents and training software. Any use outside the training measures, especially reproduction and/or copying of training documents and software − also extracts there of − in any format at all (photocopying, using electronic systems or with the aid of other methods) is prohibited. Passing on training material and training software to third parties for the purpose of reproduction and/or copying is prohibited without the express written consent of LTT. Copyright endorsements, trademarks or brands may not be removed. A tape or video recording of training courses or similar services is only permissible with the written consent of LTT. In other respects, legal requirements, especially under copyright and criminal law, apply. Lufthansa Technical Training Dept HAM US Lufthansa Base Hamburg Weg beim Jäger 193 22335 Hamburg Germany Tel: +49 (0)40 5070 2520 Fax: +49 (0)40 5070 4746 E-Mail: Customer-Service@LTT.DLH.DE www.Lufthansa-Technical-Training.com Revision Identification: S The date given in the column ”Revision” on the face of this cover is binding for the complete Training Manual. S Dates and author’s ID, which may be given at the base of the individual pages, are for information about the latest revision of that page(s) only. S The LTT production process ensures that the Training Manual contains a complete set of all necessary pages in the latest finalized revision. M15 GAS TURBINE ENGINE M15.18 AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS FRA US/O-5 DaC May 21, 2013 ATA DOC Page 1 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 PURPOSE Auxiliary Power Unit The auxiliary power unit is a small gas turbine engine on the aircraft, which supplies pneumatic bleed air and electrical power for the different aircraft systems. This gas turbine engine is often called the APU. It is mainly used on the ground when the aircraft engines are not running. On modern twin-engine aircraft the APU must also provide bleed air and electrical power in flight as a back-up source in case of engine bleed air and/or engine AC generator failure. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|APU Purpose|L1|A/B1 Page 2 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 1 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) 01|APU Purpose|L1|A/B1 Page 3 Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 APU Sections We can split the APU into 3 main sections: S the power section S the bleed section S the accessory gearbox section. The power section of the APU drives the compressor and the gearbox. This gearbox drives all APU accessories like S the fuel pump S the oil pumps S the cooling fan S the AC−generator FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! On very large APUs you may even find 2 AC−generators on the gearbox. HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 02|APU Sections|L1|A/B1 Page 4 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 2 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Main Sections 02|APU Sections|L1|A/B1 Page 5 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 APU Main Components The bleed section of the APU must make sure that sufficient bleed air is supplied to the aircraft pneumatic system. On most modern APUs you will find a separate compressor for this task. This compressor is usually called the ”load compressor”. As on all gas turbine engines, the power section has S a compressor S a combustion chamber S and a turbine. The compressor of the power section is mainly used to provide the air for the combustion. It can be either a single stage or a multiple stage compressor. On some APUs this compressor must also provide the bleed air for the aircraft pneumatic system. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 03|APU Main Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 6 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 3 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Sections 03|APU Main Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 7 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 APU Main Components cont. On APUs you will usually find centrifugal flow compressors. These compressors have good performance, a long lifetime, and they are resistant against foreign object damage known as F O D (pronounce as F. O. D.). FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 04|APU Main Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 8 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 4 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Sections 04|APU Main Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 9 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 APU Main Components cont. The combustion chamber of a modern APU is usually an annular type, but on older APUs you may also find can−type combustion chambers. The third main component of the APU power section is the turbine. You will find centrifugal turbines on small APUs or axial turbines with 2 or more stages on large APUs. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 05|APU Main Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 10 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 5 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Main Components 05|APU Main Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 11 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 APU Bleed Air Supply The APU must supply sufficient bleed air for the aircraft pneumatic system. The air pressure is usually 30 to 45 psi. There are 2 different methods of APU bleed air supply: S One uses the compressor of the power section and S the other one uses an individual load compressor. APUs with load compressors are very fuel efficient. This is because the load compressors can be switched off if bleed load is not required by the aircraft. This means that EGT limits are not reached so easy because no air is taken from the combustor. This improves the lifetime of the APU. The air flow into the load compressor is controlled by variable inlet guide vanes. These inlet guide vanes work like a modulating and shut−off valve. They can move into any position between open and closed. This is another advantage because the airflow can be changed on demand from the pneumatic system. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 06|APU Bleed Air Sup|L1|A/B1 Page 12 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 6 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Load Compressor 06|APU Bleed Air Sup|L1|A/B1 Page 13 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 APU Electrical Power Supply Another major task of the APU is to provide electrical power as a back−up source for the aircraft. This electrical power supply comes from generators which are driven via the APU gearbox. Most APUs have 1 generator which is the same type as the engine generators. You may also find 2 generators on very large APUs. Engine driven generators need a constant speed drive to run at a fixed speed if the electrical network requires a constant frequency. APU generators do not need a constant speed drive because the APU is always controlled to a constant speed by the APU fuel control unit. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 07|APU Elec Pwr Sup|L1|A/B1 Page 14 EASA PART-66 M15 Purpose M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 7 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Generators 07|APU Elec Pwr Sup|L1|A/B1 Page 15 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 APU INSTALLATION APU Compartments The APU compartment is located in the aircraft tail section. The tail cone is attached to the fuselage structure and arranged as a support and fairing for the APU. The APU and its components are enclosed by compartments: The equipment compartment, the APU compartment and on some aircraft there is also a muffler compartment. The APU equipment compartment houses the APU equipment like, for example: S the air−intake actuator, S the APU fire extinguisher bottle, S the fuel supply line and S the bleed air duct. The APU compartment houses the APU. It is entirely fire proof and serves as a fire compartment. The APU fire walls prevent any possible fire propagation to the fuselage. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|Introduction|L1|A/B1 Page 16 Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Fire Wall Figure 8 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Compartments 01|Introduction|L1|A/B1 Page 17 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 APU Access Doors The APU doors give access for servicing and maintenance. There are usually 2 doors located on the bottom of the rear fuselage. On small aircraft there is only 1 door. Latches in the lower inboard edge of the access door hold and secure the doors closed. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 03|APU Access Doors|L1|A/B1 Page 18 Lufthansa Technical Training FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 Access Door Latch Figure 9 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Access Doors 03|APU Access Doors|L1|A/B1 Page 19 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 APU Mounts There are 3 APU mounts that support the APU. The mounts are named the right aft mount, the left aft mount, and the forward mount. On large aircraft most APU mounts are connected by APU mount links. APU mount links are rods or tubes that transmit the forces from the mounts to the aircraft structural points. 3 mounts support the APU. 1 mount is always a fixed mount for strength and stability. The other 2 mounts are flexible because they must permit limited movement for thermal expansion. All 3 mounts transmit vertical loads and forces from the APU to the aircraft structure. 2 mounts transmit axial loads and forces from the APU to the aircraft structure. Only 1 mount transmits lateral loads and forces from the APU to the aircraft structure. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 05|APU Mounts|L1|A/B1 Page 20 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 10 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Forces Transmitted by APU Mounts 05|APU Mounts|L1|A/B1 Page 21 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 APU Air Intake System The major components of the air intake system are: S the air intake door, S the air intake door actuator, S the air intake nose and S the air inlet duct. The air intake door is also named the air intake flap. It can be a lower intake door which you typically find on Airbus aircraft. The APU air intake can also be on the right hand upper side of the fuselage which is typical for Boeing aircraft. The APU air intake door supplies air to the APU, or it closes off the APU air inlet if the APU is not running. The door also prevents birds and debris from entering the APU inlet and reduces aerodynamic drag in flight. The air inlet door is operated by an electrical actuator. The APU air intake door actuator is normally driven by 28 volt DC power. In addition all actuators have a manual override to open the air intake door if the electrical motor does not operate. A door position switch monitors the position of the APU air intake door. This makes sure that the APU can only run if the air intake door is open. The door actuator rod transmits the actuator movement to the air intake door. The actuator rod extends to open the air intake door or the actuator rod retracts to close it. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 09|APU Air Intake System|L1|A/B1 Page 22 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Installation M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 11 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Air Intake System 09|APU Air Intake System|L1|A/B1 Page 23 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 APU CONTROLS APU Start - Activation The APU supplies the AC generator with a constant speed. This constant speed demand makes it very easy for APU control to be automatic. An electronic APU control unit controls the APU in 3 separate operating modes. S The start mode controls the APU from start activation until it has reached 100 % speed. S The Normal Speed Mode keeps the APU at 100 % speed regardless of load changes. S The APU shut−down mode monitors and controls APU shut−down. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|APU Start−Act|L1|A/B1 Page 24 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 12 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Operating Modes 01|APU Start−Act|L1|A/B1 Page 25 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 APU Start - Activation cont. The start mode is always activated manually by switches on the overhead panel in the cockpit. The control switches look different on different aircraft types, but they have the same function. On an Airbus there are 2 individual switches, S the APU master switch, and S the APU start switch. On Boeing aircraft there is only 1 APU switch with an additional start position. This switch serves as a master switch and as a start switch. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 02|APU Start−Act|L1|A/B1 Page 26 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 13 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Start Mode 02|APU Start−Act|L1|A/B1 Page 27 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 APU Start - Activation cont. 2 actions are necessary to start the APU: S Start initiation and S Start activation. Start initiation means that electrical power is supplied to the APU control unit. When the master switch is set to ON, the APU control unit is supplied with electrical power and first performs a pre-start test. This pre-start test makes sure that the APU control unit itself operates properly and that all important sensor signals are available. The APU control unit tests the electrical circuits and the condition of the sensors, for example the APU speed sensor, the exhaust gas temperature probes, the low oil pressure switch, and the oil temperature sensor. When the pre-start test is successfully performed, the APU air inlet door is commanded to open, the APU fuel supply is prepared, the fuel shut-off valve is opened, and the APU fuel boost pump is switched on. When the master switch is on, the APU indication is available in the cockpit. The speed indicator and the EGT indicator show zero and the air inlet door is open. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 03|APU Start−Act|L1|A/B1 Page 28 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 14 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Start Initiation 03|APU Start−Act|L1|A/B1 Page 29 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 Normal Operation Control After the APU reaches its operational speed the control becomes very simple. The APU control unit must now only make sure that the speed for the generator drive remains constant at 100% and that no excessive EGT is reached. The APU control unit uses 2 signals for constant speed control. S These are the APU speed signal, and S the torque motor signal. The APU control unit maintains a constant speed by comparing the actual APU speed with the necessary speed. It then changes the torque motor signal to change the fuel metering. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 07|Normal Ops Ctrl|L1|A/B1 Page 30 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 15 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Normal Speed Mode 07|Normal Ops Ctrl|L1|A/B1 Page 31 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 Normal APU Shut-Down There are 3 different ways to shut−down the APU. S The normal way is to manually turn off the APU master switch. S Automatic shut−down is activated by the APU control unit because of malfunctions in important APU components. S An emergency shut−down is activated, for example, by the fire switch or by an alternate emergency shut−down switch. The 3 shut−down methods differ in the components which initiate the shut−down. They also differ in the time that it takes to stop the APU. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 11|Nor APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 32 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 16 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Different APU Shut-Downs 11|Nor APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 33 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 Normal APU Shut-Down cont. When the master switch is set to OFF, the APU is prepared for a safe shut-down. This means that the APU is only allowed to shut-down after it has operated for a sufficient time without pneumatic or electric load. This cool-down period differs between zero and 120 s and can be changed by maintenance on some APUs, if necessary. When the cool-down period has passed, the control unit closes off the fuel supply to the combustion chamber so that the APU comes to a stop. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 12|Nor APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 34 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 17 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Normal APU Shut-Down 12|Nor APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 35 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 Automatic APU Shut-Down Automatic shut-down is always activated by the APU control unit. It can be activated in any operational mode. This protects the APU from damage if operating limits are exceeded or important APU components are defective. In automatic shut-down the stop command is activated immediately without any cool-down period. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 13|Auto APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 36 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 18 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Automatic APU Shut-Down 13|Auto APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 37 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 Emergency APU Shut-Down In case of an APU emergency shut-down the APU must be switched off immediately without any cooling-down period. This emergency shut-down is usually initiated by switches on the aircraft like the APU fire switch or external emergency shut-down switches. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 15|Emg APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 38 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 19 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Emergency APU Shut-Down 15|Emg APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 39 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 Emergency APU Shut-Down cont. The external emergency shut-down switches are in areas of the aircraft where they are easily accessible to the ground personnel, for example: S at the nose landing gear, S in the main wheel well, S or on the refuelling station depending on aircraft type or size. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 16|Emg APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 40 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 20 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 External Emergency Shut-Down Switches 16|Emg APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 41 EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 Emergency APU Shut-Down cont. An automatic APU emergency shut-down is activated in a fire condition when the aircraft is on ground. On modern aircraft types the APU fire is then extinguished automatically by a special fire extinguishing system. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 17|Emg APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 42 Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 APU Controls M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Fire Extinguisher Bottle Figure 21 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Automatic Fire Shut-Down 17|Emg APU Shut−Dwn|L1|A/B1 Page 43 EASA PART-66 M15 Primary APU Fuel System M15.18 PRIMARY APU FUEL SYSTEM Organization The primary fuel system of the APU is also named the low pressure fuel system. This system starts at the fuel tanks and ends at the fuel control unit of the APU. The secondary fuel system, which is also named the high pressure fuel system, starts at the fuel control unit and ends at the fuel nozzles on the combustion chamber. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|Organization|L1|A/B1 Page 44 EASA PART-66 M15 Primary APU Fuel System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 22 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Primary APU Fuel System 01|Organization|L1|A/B1 Page 45 EASA PART-66 M15 Primary APU Fuel System M15.18 Operation The APU fuel feed system has a separate APU fuel boost pump, but there are also 2 tank boost pumps in each tank. The APU fuel boost pump is needed to give positive fuel supply if the tank boost pumps are not available. This positive fuel pressure in the APU fuel feed line is very important to prevent cavitation at the high pressure fuel pump of the APU. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 03|Operation|L1|A/B1 Page 46 EASA PART-66 M15 Primary APU Fuel System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 23 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Primary APU Fuel Supply 03|Operation|L1|A/B1 Page 47 EASA PART-66 M15 Primary APU Fuel System M15.18 Operation cont. On Airbus aircraft you also find a control push button on the inner firewall of the APU compartment. This push button is named the APU fuel line vent switch. If you push the vent push button the APU fuel boost pump is started and the APU fuel shut-off valve opens. The vent push button bypasses the APU master switch. This is an advantage for maintenance because they can purge the APU fuel feed line without a person in the cockpit. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 06|Operation|L1|A/B1 Page 48 EASA PART-66 M15 Primary APU Fuel System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 24 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Fuel Line Vent Push button 06|Operation|L1|A/B1 Page 49 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 AIR SYSTEM Introduction The APU air system is divided into two sub-systems, S the cooling air system and S the bleed air system. The bleed air system has three main tasks; S bleed supply, S surge protection, and S if the APU has a load compressor, load compressor control. The bleed supply system controls the supply of the APU bleed air to the aircraft pneumatic system. The surge protection system prevents any surge condition of the APU compressors. If the APU has a load compressor this system also belongs to the air bleed system. The load compressor control system controls the amount of air going over the load compressor to meet the bleed demand of the aircraft pneumatic system. The control system also prevents surging. The other sub-system of the APU air system is the APU cooling system. This system uses air from the APU air intake to cool the APU, the APU compartment, and air cooled components like the oil cooler or the AC generator. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|Introduction|L1|A/B1 Page 50 Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Air Intake Figure 25 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Bleed Air System 01|Introduction|L1|A/B1 Page 51 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 Load Compressor Control System Introduction Many APUs have a load compressor system because it reduces the fuel consumption of the APU. In most operating conditions the APUs can supply electrical power and pneumatic bleed air at the same time, but this is not always necessary. If only one power source is needed, the other one can be switched off. When the APU bleed is switched off, the EGT decreases. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 05|Load Compr Ctrl Syst|L1|A/B1 Page 52 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 26 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Load Compressor 05|Load Compr Ctrl Syst|L1|A/B1 Page 53 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 Load Compressor Control System Introduction cont. The load compressor cannot be switched off, because it is fixed to the rotor shaft. The air inlet into the load compressor is closed off by the inlet guide vanes. This means that air cannot enter the load compressor. The main components of the load compressor system are: S the variable inlet guide vanes, S the inlet guide vane actuator with a mechanical transmission assembly, and S the APU control unit. The variable inlet guide vanes control the quantity of airflow into the load compressor. They can move to any position between open and closed. The inlet guide vane actuator moves the inlet guide vanes to the correct position. The actuator deflects the IGVs via a mechanical transmission. The APU control unit sends control signals to move the inlet guide vane actuator to the correct position. It also receives feedback signals about the true position of the actuator. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 06|Load Compr Ctrl Syst|L1|A/B1 Page 54 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 27 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Load Compressor Main Components 06|Load Compr Ctrl Syst|L1|A/B1 Page 55 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 Surge Protection Methods on APU’s APU compressors can surge, especially when bleed load changes. Compressor surging can be prevented by bleeding off the air that is blocking the compressor discharge. There are two surge protection methods used on APUs. The first method uses the anti-surge system. This system is installed on APUs, which do not have a load compressor. The anti-surge system has an anti−surge valve which always bleeds off air when surging is possible. The anti-surge valve is normally opened during flight to prevent surging. This method is not very fuel efficient because air is also bled off when there is no surging. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 10|Surge Prot Meth|L1|A/B1 Page 56 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 28 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU with Anti - Surge Valve 10|Surge Prot Meth|L1|A/B1 Page 57 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 Surge Protection Methods on APU’s cont. A better surge protection method is used on APUs with load compressors. Here a surge protection system monitors the airflow in the load compressor discharge duct and opens a surge control valve if the compressor surges. As a general rule we can say: The surge control valve opens if the airflow behind the load compressor decreases or stops. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 11|Surge Prot Meth|L1|A/B1 Page 58 EASA PART-66 M15 Air System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 29 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU with Surge Control Valve 11|Surge Prot Meth|L1|A/B1 Page 59 EASA PART-66 M15 Oil System M15.18 APU OIL SYSTEM Organization The oil system of a typical APU has the same main components and functions as all oil systems on gas turbine engines, but there are two differences on APU oil systems, which you do not find on engine oil systems. APU oil systems have a de-oiling valve which helps to improve the APU start sequence, and on many APUs the oil system is also used to cool the APU generator. An APU oil system always has: S a reservoir, S an oil supply pump, S an oil cooler, S an oil filter, S oil supply lines, and S oil scavenge lines. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|Organization|L1|A/B1 Page 60 EASA PART-66 M15 Oil System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 30 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Oil System Layout 01|Organization|L1|A/B1 Page 61 EASA PART-66 M15 Oil System M15.18 APU Oil Vent System Operation cont. The air/oil separator has vanes, which are mounted on a drive gear in the APU gearbox. As you can imagine it separates the air/oil mist by rotating action. Here you can see an enlarged view of the air/oil separator in the APU gearbox. The oil mist enters the separator from the left and is accelerated by the vanes on the separator. The rotation of the air/oil separator forces the oil to the gearbox and lets the air escape through the hollow drive shaft into an external pipe, which leads to the APU exhaust duct. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 09|APU OilVent Sys Ops|L1|A/B1 Page 62 EASA PART-66 M15 Oil System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 31 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Air / Oil Seperator 09|APU OilVent Sys Ops|L1|A/B1 Page 63 EASA PART-66 M15 Oil System M15.18 APU Generator Oil Cooling System Most modern APUs have oil cooled generators which use oil from the APU oil system for cooling purposes. You can see that these generators are connected to the APU oil supply system, but they usually have an independent oil scavenge system. The generator oil scavenge system has: S a scavenge pump which is usually installed in the APU gearbox, S a separate oil scavenge filter, and S a scavenge oil return line to the APU gearbox. The generator oil cooling system is closely monitored for malfunction. It has an oil temperature sensor installed in the APU generator. This sensor monitors the generator oil temperature and transmits it to the APU control unit. If the generator oil temperature becomes too high, the APU control unit initiates an automatic APU shut-down. The generator scavenge filter is equipped with a filter bypass valve and a differential pressure switch. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 11|APU Gen Oil Cooling Sys|L1|A/B1 Page 64 EASA PART-66 M15 Oil System M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 32 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Generator Oil Cooling System 11|APU Gen Oil Cooling Sys|L1|A/B1 Page 65 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 IGNITION & STARTING Starting System Introduction The components which are necessary for an APU start are: S the APU control switches, S the APU control unit, S the APU starter motor, S the aircraft battery, S the APU starter lead which transmits the battery power to the APU starter motor, and S the APU start relay which connects or/and disconnects the battery power to the starter motor. You find the control switches for APU start in the cockpit. These switches are used to prepare and activate the APU start sequence or shut-down of the APU. The master switch supplies electrical power to the APU control unit which starts its power-up test. After a successful test it opens the APU fuel shut-off valve, and the APU fuel pump starts running if the fuel pressure is too low, and it opens the intake door. A signal from the start switch then activates the start sequence. You usually find the APU control unit in the tail section of the aircraft. The APU control unit receives the start signal from the start switch and closes the APU start relay. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|Start Sys Intro|L1|A/B1 Page 66 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 APU Air Intake Door FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 33 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Starting Preparation 01|Start Sys Intro|L1|A/B1 Page 67 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 Starting System Introduction cont. The APU start relay is usually installed in the electronic equipment compartment of the aircraft. It is closed by the APU control unit as long as the APU starter needs power from the aircraft battery. APUs are usually started by DC motors which you can find on the APU gearbox. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 02|Start Sys Intro|L1|A/B1 Page 68 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 34 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Starting Components 02|Start Sys Intro|L1|A/B1 Page 69 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 APU Starter Description The main components of a typical APU starter are the DC motor and the starter clutch. The starter motor is usually a brush type DC motor. It has: S a housing with a mounting flange, S two terminals for the power leads, S brushwear indicators, and S an electrical connector for feedback signals to the APU control unit. The brushwear indicators show if the brushes on the starter motor are worn out. These indicators are usually small inspection windows. Behind the windows there are indicator pins which show the length of the brushes. On most modern APUs you also find electrical brushwear sensors. These electrical sensors send signals to the APU control unit when the brushes reach their wear limits. On many APUs there is another signal which is send from the starter motor to the APU control unit. With this feedback signal the APU control unit knows how much voltage is available at the APU starter motor terminals. The voltage feedback signal is used for trouble shooting to find out which component has caused an APU start problem. For example, a slow APU start with a low voltage at the starter terminals indicates that the problem is in the starter power supply and NOT in the APU starter motor. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 03|APU Starter Descr|L1|/A/B1 Page 70 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 35 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Starter Main Components 03|APU Starter Descr|L1|/A/B1 Page 71 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 Start System Operation We will now look at a typical APU start procedure. When the APU start switch is activated the APU control unit energizes the starter relay. The starter relay closes and DC power from the aircraft battery is available at the APU starter motor. The starter motor drives the APU rotor. At starter cut-off speed the APU control unit opens the starter relay. This disconnects the battery from the APU starter motor. The APU continues to accelerate without starter support. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 06|Start Sys Ops|L1|A/B1 Page 72 Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Speed Sensor Figure 36 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Start System Operation 06|Start Sys Ops|L1|A/B1 Page 73 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 APU Starter Limitations The APU starter motor needs a very high current to accelerate the APU rotor. This means that the starter motor and also the battery become very hot, especially at the beginning of the start sequence. Therefore, after each APU start they must cool down sufficiently before you can use them again. You must be very careful during maintenance activities when you have to start the APU more frequently. There are three starter limitations that must always be observed during an APU start. These limitations are: S the starter duty time, S the starter cool down time, and S the starter duty cycle. The starter limitations make sure that the starter equipment does not get overstressed and overheated. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 07|APU Starter Limit|L1|A/B1 Page 74 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 37 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Starter Limitations 07|APU Starter Limit|L1|A/B1 Page 75 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 APU Ignition System Operation The main components of a typical APU ignition system are: S the APU control unit, S the ignition exciter, S the ignition leads, and S the igniter plugs. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 08|APU Ign Sys Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 76 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 38 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Ignition System Components 08|APU Ign Sys Comp|L1|A/B1 Page 77 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 APU Ignition System Operation cont. The APU ignition system is usually powered by direct current. The DC power supply for the ignition exciter comes from the APU control unit. The ignition exciter converts low voltage DC power into the high voltage for the igniter plugs. If you want more information on ignition exciter operation, refer to the Ignition lesson of Module M15.13. The ignition system is activated in parallel with the APU start system. On some APUs the ignition system is switched on by the APU speed signal, and on other APUs the ignition is switched on directly by the start command signal. When ignition is on, the fuel/air mixture in the combustion chamber ignites. The APU ignition is always switched off by the APU control unit if the APU reaches a sufficient speed. This happens either at starter cut-out speed or when the APU reaches operational speed. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 09|APU Ign Sys Ops|L1|A/B1 Page 78 EASA PART-66 M15 Ignition & Starting M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 39 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Ignition System Operation 09|APU Ign Sys Ops|L1|A/B1 Page 79 Lufthansa Technical Training FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 APU START & SHUT-DOWN APU Start Checklist Before you start the APU you must make sure that all safety checks are performed. These safety checks are carried out with an APU start checklist. We will now follow a typical checklist and look at each task step by step. We have already performed all checks that are necessary prior to energizing the electrical network on the aircraft. These checks make sure that no aircraft system is activated inadvertently after electrical power is put on. If all APU circuit breakers are closed, you can be sure that all electrical circuits for APU operation are supplied. The battery switches must always be in the ON position. You must also check the battery voltage. On this aircraft, for example, it must be more than 23V. The APU generator push button switch must be OFF to make sure that the APU generator is not connected to the aircraft electrical circuits by mistake. The fire warning test makes sure that the fire warning system operates properly. It also tests the electrical circuits to the squibs on the fire extinguisher bottle. If external power is available, the fire warning test is performed correctly if the aural fire warning sounds, the red light in the APU fire switch illuminates, and the squib and discharge lights in the agent push button illuminate. If external power is not available, only the red light in the APU fire switch and the squib and discharge lights in the agent push button illuminate. The APU bleed switch must be OFF to prevent the APU bleed valve opening and the cross-bleed valve selector is put to AUTO to make sure that the APU supplies the complete pneumatic system when the APU bleed switch is set to ON. One of these fuel boost pump switches must be put ON to supply fuel to the APU. HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 01|APU Start Checklist|L1|A/B1 Page 80 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 40 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Start Checklist 01|APU Start Checklist|L1|A/B1 Page 81 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 Start Indications Before you start the APU you must be familiar with the indications you will see during an APU start. The most important indications during APU start are: S the battery voltage, S the speed indication, and S the EGT indication. On some APUs you must also look at the oil quantity indication. The battery voltage is shown next to the battery switches. During APU start the decrease in battery voltage shows that the APU starter is accelerating the APU. The battery voltage first decreases, and then after starter cut-out it increases again. This shows that the starter motor draws energy from the battery. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 02|Start Indications|L1|A/B1 Page 82 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 41 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Start Indications 02|Start Indications|L1|A/B1 Page 83 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 Start Indications cont. The indications on the ECAM are only available if the AC power is switched ON. The increase in EGT indicates that the fuel supply to the combustion chamber is available, because the APU control unit opened the APU fuel solenoid valve. The fuel solenoid valve is usually opened by the speed signal in the APU start sequence at the same time that the ignition is switched on. During the APU start sequence you must make sure that the APU shows a smooth acceleration. The smooth acceleration indicates that the starter is operating properly and the fuel metering from the fuel control unit is correct. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 03|Start Indications|L1|A/B1 Page 84 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 42 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 Start Indications 03|Start Indications|L1|A/B1 Page 85 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 APU Shut-Down Checklist This condition shows an APU running with the APU bleed switch ON. We now go through the steps to shut-down this APU using the checklist. First set the APU bleed switch to OFF. Next set the APU master switch to OFF, but note that the APU will not shut down immediately. The APU shuts down when the master switch is set to OFF and the cool-down period is completed. Then all fuel pumps must be switched off. The following steps are now different from aircraft to aircraft. In this example you must also check that the batteries are OFF and that all circuit breakers are in the required condition. If there is an emergency, the quickest way to shut down the APU is to activate the fire switch. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 04|APU Shut−Down|L1|A/B1 Page 86 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 43 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Checklist 04|APU Shut−Down|L1|A/B1 Page 87 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 Start and Shut-Down Simulations Use the checklist for the APU start and shut-down tasks. Make sure that you do not overheat the APU starter motor. If you have reached the starter duty cycles, you must click on the clock symbol before you can do the next APU start. FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 05|APU Shut−Down|L1|A/B1 Page 88 EASA PART-66 M15 Start & Shut-Down M15.18 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY! Lufthansa Technical Training GAS TURBINE ENGINE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS Figure 44 HAM US/F-4 SwD 01.04.2008 APU Checklist 05|APU Shut−Down|L1|A/B1 Page 89 M15.18 A E TABLE OF CONTENTS M15 GAS TURBINE ENGINE . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 M15.18 AUXILIARY POWER UNITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 PURPOSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . AUXILIARY POWER UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU SECTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU MAIN COMPONENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU BLEED AIR SUPPLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU ELECTRICAL POWER SUPPLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 2 4 6 12 14 APU INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU COMPARTMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU ACCESS DOORS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU MOUNTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU AIR INTAKE SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 16 18 20 22 APU CONTROLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU START - ACTIVATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . NORMAL OPERATION CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . NORMAL APU SHUT-DOWN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . AUTOMATIC APU SHUT-DOWN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . EMERGENCY APU SHUT-DOWN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 24 30 32 36 38 PRIMARY APU FUEL SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ORGANIZATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 44 46 AIR SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . LOAD COMPRESSOR CONTROL SYSTEM INTRODUCTION SURGE PROTECTION METHODS ON APU’S . . . . . . . 50 50 52 56 APU OIL SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ORGANIZATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU GENERATOR OIL COOLING SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . 60 60 64 IGNITION & STARTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . STARTING SYSTEM INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU STARTER DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66 66 70 START SYSTEM OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU STARTER LIMITATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU IGNITION SYSTEM OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72 74 76 APU START & SHUT-DOWN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU START CHECKLIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . START INDICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU SHUT-DOWN CHECKLIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . START AND SHUT-DOWN SIMULATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . 80 80 82 86 88 Page i M15.18 A E TABLE OF CONTENTS Page ii M15.18 A E TABLE OF FIGURES Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Main Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Main Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Load Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Generators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Compartments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Access Doors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Forces Transmitted by APU Mounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Air Intake System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Start Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Start Initiation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Normal Speed Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Different APU Shut-Downs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Normal APU Shut-Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Automatic APU Shut-Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Emergency APU Shut-Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . External Emergency Shut-Down Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Automatic Fire Shut-Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Primary APU Fuel System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Primary APU Fuel Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Fuel Line Vent Push button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bleed Air System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Load Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Load Compressor Main Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU with Anti - Surge Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU with Surge Control Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Oil System Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Air / Oil Seperator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Generator Oil Cooling System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Starting Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Starting Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Starter Main Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69 71 Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure Figure 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 APU Start System Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Starter Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Ignition System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Ignition System Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Start Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Start Indications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Start Indications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . APU Checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89 Page i M15.18 A E TABLE OF FIGURES Page ii M15.18 A E TABLE OF FIGURES Page iii M15.18 A E TABLE OF FIGURES Page iv