Macromolecules in Food: Tests & Functions - High School Biology

Friday, 9/1
1.) What are the monomers of proteins?
2.) What are the polymers of nucleotides?
3.) Previously, we discussed lactose intolerance and the role of lactase. Lactase helps speed up the chemical reaction of breaking down lactose. Knowing the function of lactase, what type of macromolecule is it?
Today:
1.) Turn in “Properties of Water” Booklet
2.)“There’s What In My Food?” (discussion of the types of tests for detecting macromolecules in food samples)
Homework:
1.) “Vitruvian Man” packet due by TUES., 9/5
2.) “Macromolecule” quiz WED/THURS., 9/6 & 9/7
3.) Enzyme Foldable (assign on 9/5) due MON., 9/11
4.) Unit 1 Test (multiple-choice portion) TUES., 9/12
5.) Unit 1 Test (FRQ) WED/THURS, 9/13 & 9/14
Word of the Day
Moratorium (noun)
A temporary pause or suspension of activity
“Because of the deadly virus, many people are calling for a
moratorium on flights from West
Africa.”
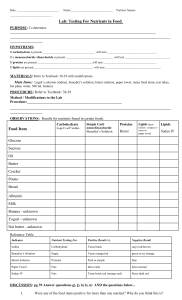
There’s WHAT In My Food?!
Three of the four types of macromolecules we have discussed can be found on food nutrition labels…
Look at the label to the left. 3 of the 4 macromolecules can be found in foods.
The 3 biochemical molecules found on a nutrition label are:
1____________________
2____________________
3____________________
You know that carbohydrates…
1.) Are a source of energy
2.) Provide structure and support
What kinds of foods are rich in carbohydrates?
CARBOHYDRATES
CARBOHYDRATES
THERE ARE 2 TYPES OF
CARBOHYDRATES
Complex (Polysaccharides)
• White rice; white bread; pasta (and other foods) made with white flour; apple juice; orange juice; candy; soda; etc.
• Whole grain foods like oatmeal, whole wheat bread, & whole wheat pasta; fresh fruits & vegetables
• Filled with FIBER
TESTING FOR THE PRESENCE OF
COMPLEX CARBS (STARCH)
• To your food sample, you add iodine solution (Lugol’s reagent)
• If the test is positive and complex carbs are present , the sample will turn from gold-brown to dark purple/black
• If the test is negative and complex carbs are absent, the sample will remain gold-brown
TESTING FOR THE PRESENCE OF SIMPLE
SUGARS (GLUCOSE)
• To your food sample, you add Benedict’s solution
• YOU THEN MUST HEAT THE SAMPLE
• If the test is positive and simple sugars are present , the sample will turn from blue to brick-red/orange
• If the test is negative and simple sugars are absent, the sample will remain blue
Negative Positive Positive
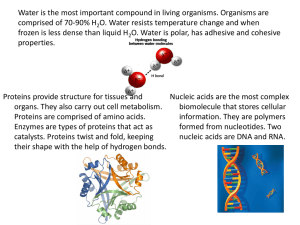
You know that proteins…
1.) Play a role in transport (hemoglobin)
2.) Provide regulation (hormones like insulin)
3.) Help us move (muscles)
4.) Provide structure and support
(membranes, hair, nails)
5.) Function as enzymes
What kinds of foods are rich in protein?
PROTEINS
TESTING FOR THE PRESENCE OF
PROTEINS
• To your food sample, you add Biuret solution
• If the test is positive and proteins are present , the sample will turn from blue to lavender/purple
• If the test is negative and proteins are absent, the sample will remain blue
You know that lipids…
1.) Store the most energy (long-term energy storage)
2.) Protect against heat loss (insulation)
3.) Protect against water loss
4.) Act as chemical messengers (steroid hormones)
5.) Are a major component of cell membranes
LIPIDS
TESTING FOR THE PRESENCE OF LIPIDS:
2 TYPES OF TESTS
• To your food sample, you add Sudan III (or IV) stain ( a fat soluble dye) and a small amount of water
• If the test is positive and lipids are present , the dye stains the lipids bright red-orange and forms two layers (oil and water)
• If the test is negative and lipids are absent , the sample remains brick-red and forms only one layer (just water)
2
nd
Lipid Test: The “Paper Bag” Test
• Place a drop of your food sample on a paper bag
• If the test is positive and lipids are present , the sample will leave a translucent (light can pass through) spot on the bag
• If the test is negative and lipids are absent, the sample will dry completely and be opaque (cannot see through it)
Left: Water
Right: Vegetable Oil
Graphic Organizer: Complete the handout with your group
INDICATOR MACROMOLECULE NEGATIVE
TEST
POSITIVE TEST
Benedict’s Solution
Iodine Solution
Biuret Solution
Sudan III Solution
Paper Bag Test
LET’S PRACTICE!
Students conducted an investigation using Biuret reagent to determine the presence of proteins in different foods. The results are shown in the table below.
Substance
Honey
Color after adding Biuret reagent
Blue
Cottage Cheese Purple/Lavender
Potato
Water
Dark Blue
Light Blue
According to the data, which foods tested by the students contained proteins?
A. Honey & Potato
B. Potato & Chicken Broth
C. Cottage Cheese & Water
D. Cottage Cheese & Yogurt
Chicken Broth Dark Purple
Yogurt Light Purple
Work quietly in your groups to read this scenario and answer the questions:
You come across an unrecognizable mass of food on the sidewalk.
Before you eat it, you decide to analyze the nutrients in it to see if it is a wise dietary choice. Here are the results of your 4 tests:
Sudan IV
Positive
Benedict’s Solution
Negative
Iodine
Negative
Biuret Solution
Positive
1.) Is it likely that this food came from a green plant? Why or why not? (Hint: Think about the three major macromolecules/nutrients in
different types of food)
2.) Does this food contain the simple sugar glucose? How can you tell?
3.) Could “acts as an insulator” and/or “acts as an enzyme” be the function of any of the molecules in this food? Explain your reasoning.
Answers
1.) Is it likely that this food came from a green plant? Why or why not? (Hint: Think about the three major macromolecules/nutrients
in different types of food) No. Plants contain carbohydrates, especially complex carbs such as polysaccharides (cellulose).
However, the Iodine test was negative for complex carbs.
2.) Does this food contain the simple sugar glucose? How can you tell? No, it does not contain glucose. The Benedict’s test was negative.
3.) Could “acts as an insulator” and/or “acts as an enzyme” be the function of any of the molecules in this food? Explain your reasoning.
Yes, because the Sudan IV test was positive (lipids were present, and they are insulators) and the Biuret test was positive (proteins were present, and many proteins are enzymes).
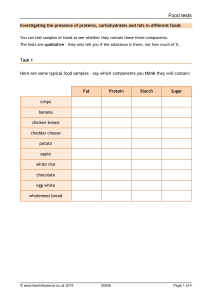
Working again in your groups, look at the chart below. Think about which macromolecules might be present in each of the food samples, and therefore, which of the five tests might be positive for each sample.
Food
Sample
Oatmeal
Benedict’s Biuret Iodine Sudan III/IV Paper Bag
Test
Egg Whites
Apple Juice
Milk
Peanut Butter
French Fries
Pepperoni
Pizza
Water
Answers
Food
Sample
Oatmeal
Egg Whites
Apple Juice
2% Milk
Peanut Butter
French Fries
Pepperoni
Pizza
Water
Benedict’s Biuret Iodine Sudan III/IV Paper Bag
Test
Work quietly in your groups to read and answer these questions.
1.) Which of the following is not a function of polysaccharides?
A.) Energy Source
B.) Energy Storage
C.) Structural Support
D.) Storage of Genetic Information
2.) Which of the following statements is false?
A.) A wax is a lipid
B.) Starch is a lipid
C.) Saturated fats are solid at room temperature
D.) Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature
Answers
1.) Which of the following is not a function of polysaccharides?
A.) Energy Source
B.) Energy Storage
C.) Structural Support
D.) Storage of Genetic Information
2.) Which of the following statements is false?
A.) A wax is a lipid
B.) Starch is a lipid
C.) Saturated fats are solid at room temperature
D.) Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature
3.) Which of the following molecules stores hereditary information?
A.) ATP
B.) DNA
C.) Protein
D.) Carbohydrates
4.) What is the name of the molecule in plants that stores sugars?
A.) Starch
B.) Protein
C.) Cellulose
D.) Glycogen
Answers
3.) Which of the following molecules stores hereditary information?
A.) ATP
B.) DNA
C.) Protein
D.) Carbohydrates
4.) What is the name of the molecule in plants that stores sugars?
A.) Starch
B.) Protein
C.) Cellulose
D.) Glycogen
5.) The “tails” of phospholipids position themselves away from water. Which of the following describes this characteristic of phospholipids?
A.) Polar
B.) Adhesive
C.) Hydrophilic
D.) Hydrophobic
6.) Complete the following analogy.
Simple sugars : Carbohydrates :: Amino Acids : ?
A.) Lipids
B.) Proteins
C.) Nucleic Acids
D.) Amino Groups
Answers
5.) The “tails” of phospholipids position themselves away from water. Which of the following describes this characteristic of phospholipids?
A.) Polar
B.) Adhesive
C.) Hydrophilic
D.) Hydrophobic
6.) Complete the following analogy.
Simple sugars : Carbohydrates :: Amino Acids : ?
A.) Lipids
B.) Proteins
C.) Nucleic Acids
D.) Amino Groups
7.) Name at least two of the five functional groups we talked about.
Bonus points if you tell me the atoms that compose each and/or in what macromolecules they are found.
Answers
Functional Group
Hydroxyl
Carboxyl
Carbonyl
Amino
Phosphate
Atoms
-OH
-COOH
-CO
-NH
2
-PO
4
Found In…
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Proteins
DNA (and ATP)