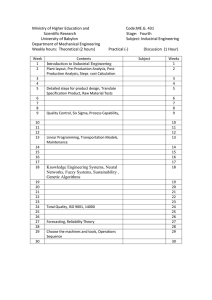
+
ISO 9000/9001
Software Process Improvement Initiative
Omer Azmon
Anna Brjezovskaia
VelimirLesikov
Eduardo Borjas
Darius Vincent Salim
+
Preview of ISO 9000/9001
What is ISO?
General Background
Who Uses ISO 9000/9001
Motivation for ISO 9000/9001
Goals for ISO 9001
Features of ISO 9001
Comparison With Other SPI Initiatives
Team Opinions
Q & A Session
+
What is ISO?
ISO stands for the “International Organization for
Standardization”.
Central Secretariat is located in Geneva, Switzerland.
A network of the national standards institutes of 162 countries with one member (one vote) per country.
A non-governmental organization that forms a bridge between the public and private sector.
Standards are developed by technical committees.
Certifications are performed by an independent third party registrar company accredited by a national accreditation body.
+
General Background
ISO 9000 describes fundamentals of quality management systems, which form the subject of the ISO 9000 family, and defines related terms.
ISO 9000 is 1 of the over 17,500 standards, which were published by the ISO. It first came out in 1987, the latest standard was published in 2005.
ISO 9001 specifies requirements for a quality management system. It first came out in 1994, the latest standard was published in 2008.
+
Who Uses ISO 9000/9001
ISO 9001 is used from certified companies, most of the time it involves two major positions in the company:
Consultant - that prepares the documentation
The company's management and staff to guarantee that the new system is properly documented and the documentation is properly implemented.
Used by small companies mainly because of a need from their corporate partners which are looking for better quality and standardizing methods.
+
Motivation for ISO 9000/9001
Started in England during WWII for quality management of weapons manufacturers
Into the 1970’s many organizations (Ford, British Ministry of
Defense) had their own quality management systems
The problem then became that there was no single standard for quality in England
From there it became first a British standard, then a
European standard, and ultimately an international standard
+
Goals for ISO 9001
ISO 9001:2008 specifies requirements for a quality management system where an organization:
needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently provide product that meets customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, and
aims to enhance customer satisfaction through the effective application of the system, including processes for continual improvement of the system and the assurance of conformity to customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements.
Source: International Organization for Standardization (http://www.iso.org)
+
Goals for ISO 9001
(continued)
Reduce waste and increase productivity
Improve employee awareness, morale and motivation
Raise profits
Improve marketing
Increase customer satisfaction
Create a more effective and efficient operation
Decreased variation, increased consistency and predictability of operations
+
Features of ISO 9001
Say It.
Document/define
Processes
Do It.
Implementation
Prove It.
Objective evidence (records, audits & responses)
Maintain It & Improve It!
Ongoing management commitment
Adequate resources
Continual improvement of the system
+
Features of ISO 9001
(continued)
1 Scope
2 Normative Reference
3 Terms and Definitions
4 Quality Management System
5 Management Responsibility
6 Resource Management
7 Product Realization
8 Measurement, Analysis and Improvement
+
Features of ISO 9001
Scope
Demonstrate consistent conformance to customer & regulatory requirements
Address customer satisfaction through:
Effective system
Based on continual improvement & preventive actions
Application
Define in quality manual
+
Features of ISO 9001
:
Normative Reference
“normative” means that it is included as an auditable requirement.
ISO 9000 Quality Management Systems - Fundamentals and Vocabulary
+
Features of ISO 9001
Terms and Definitions
ISO 9000:2000 Quality Management Systems -
Fundamentals and Vocabulary
Supplier Organization Customer
Product = Result of a process (Hardware, software, services)
+
Features of ISO 9001
Quality Management System
Establish, implement, document, maintain and continually improve the QMS processes.
Identify processes and sequence
Determine effectiveness
Monitor, measure, analyze, and implement actions
Documentation includes: procedures, quality policy, instructions, quality manual, data and records
Control of documents and records
+
Features of ISO 9001
Management Responsibility
Management Commitment
Customer Focus
Quality Policy
Business Planning and Objectives
Responsibility, Communication and Authority
Management Reviews
+
Features of ISO 9001
Resource Management
Provide Resources
Human Resources
Training, awareness & competency
Personnel assignment
Work Environment
Infrastructure
+
Features of ISO 9001
Product Realization
Planning for Product Realization
Customer-related Processes
(Product requirements & communication)
Purchasing
(Supplier evaluation, purchasing requirements, verification)
Design/Development
(Planning, inputs, outputs, reviews, verification, validation & change control)
+
Features of ISO 9001
Measurement, Analysis and Improvement
Monitoring, Planning, and Measurement
Customer satisfaction
Internal audits
Process & Product monitoring/measurement
Analysis of Data
Improvement
Constant Improvement
Preventive Action
Corrective Action
+
Comparison With Other SPI Initiatives
CMMI - ISO 9000 is more basic. The documentation involves fewer details and it has to be constantly improved for further product updates - in comparison to CMMI, where further process improvements are already covered when documentation and specifications are created.
Six Sigma - ISO 9000 is using documentation as continuous quality assurance, rather then data.
+
Team Opinions
Positives
Democratic
Internationally Used
Easy To Implement
Good Starting Point
If Used Correctly Will Lead To Consistent Quality Products
Negatives
Doesn’t Necessarily Lead To A Quality Product
Can Lead To Just An “Empty” Plaque On The Wall
Not Software Specific Like ISO/IEC 90003:2004
+
Question &
Answer Session
+