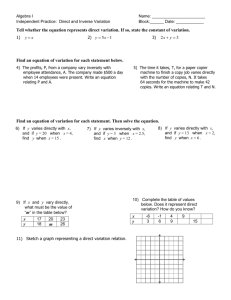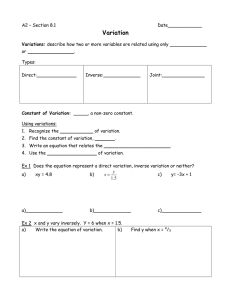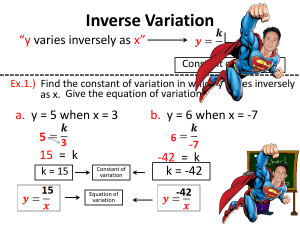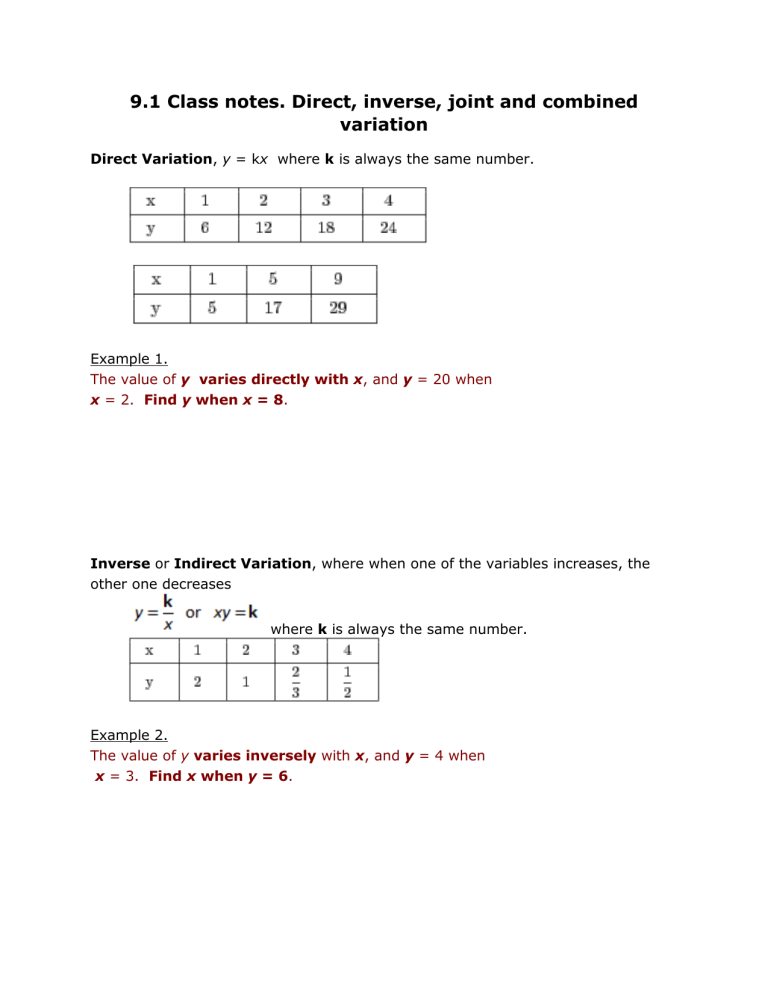
9.1 Class notes. Direct, inverse, joint and combined variation Direct Variation, y = kx where k is always the same number. Example 1. The value of y varies directly with x, and y = 20 when x = 2. Find y when x = 8. Inverse or Indirect Variation, where when one of the variables increases, the other one decreases where k is always the same number. Example 2. The value of y varies inversely with x, and y = 4 when x = 3. Find x when y = 6. Example 3. For the Choir fundraiser, the number of tickets Allie can buy is inversely proportional to the price of the tickets. She can afford 15 tickets that cost $5 each. How many tickets can Allie buy if each cost $3? Joint Variation, where more than two variables are related directly z=kxy Example 4 Supposed x varies jointly with y and the square root of z. When x = –18 and y = 2, then z = 9. Find y when x = 10 and z = 4. Combined Variation, which involves a combination of direct or joint variation, and indirect variation Example 5 y varies jointly as x and w and inversely as the square of z. Find the equation of variation when y = 100, x = 2, w = 4, and z = 20.