Social Media, Collaboration, and Academic Performance in Malaysia
advertisement

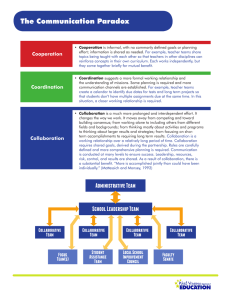
The Mediating effect of Collaborative learning in Student’s Academic Performance and the role of social media in private Universities of Malaysia Name: Mahazabeen Haque Shoilee ID: BGA 160005 Introduction The social media defines a group of internet-based applications that build on the ideological and technological basis of web. It helps people to minimize distances and makes easier for them to share information, files, pictures and videos. The questions are about the social media and its influence on academic performance and how it can be used effectively to improve student academic performance. Research Problems (Choney, S; 2010) &MehMood, S;& Taswir, t; 2013), (Kist, W; 2008), (Jacobsen & Forste, R; 2011), said that the use of social media is one of the key factors that can affect student's educational performance in a positive or negative way. Research Scope There are many parents and guardians who thought that students spend too much time on Facebook and other social media sites and do not have enough time to learn. Although parents are anxious about the regular use of social media, many students continue to take advantage of the site every day. The scope of the study will concentrate on the academic performance among the students in a private university of Kuala Lumpur, Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur Malaysia. Research Question Research Objectives Does the use of social media sites have any impact on student’s academic performance? To examine the impact of social media on academic performance among the students. How the social media impact to student’s academic performance through collaborative learning? To ascertain the impact of social media through collaborative learning to student’s academic performance. Literature Review Independent Variables Interaction with Peers Interaction with teachers (Frazier & Eighmy 2012; Hatch, 2012; Rocconi, 2011; Kuh, Cruce, Shoup, Kinzie, & Gonyea, 2008; Zhao & Kuh, 2004) suggests that planned and purposeful opportunities for peer engagement of college students impacts their learning throughout their college experience. To achieve success in education interaction with teachers is necessary because it produces better and more effective learning and may also be an essential way (Bannan,B; 2002 & Siau et al., 2006; Chou, C; 2003 & Siau et al., 2006). (Fewkes & McCabe, M; 2012 & Junco et al, R; 2012 & Top,E; 2012) said that social media promote cooperation and contribution to the relationship that can arise among students, also provides direct opportunities for curricular distribution. Some teachers or supervisors have found a number of methods to integrate social media into their lectures and curricula, while others do not want to use it (Fewkes & McCabe, 2012). Cont… Engagement Engagement is a social media context, which result in a learning environment characterized by greater collaboration and communication brought about by peer discussion and interaction (Heafner & Friedman, 2008; Jackson, 2011; Liu et al., 2011). (Astin; 2010) said engagement was defined as the amount of physical and mental energy a student spends on the academic experience. This theory of student engagement comes from the strength of a training practice that is proportional to anyone who talks to improve student engagement. Mediating Variable Collaborative Learning Collaborative learning is the interactions and connections between the students with the curricula. It emphasis on interaction among participants in education. (Shoshani, Y and Barun, H; 2007) said that social media supports collaborative learning to make a resource full learning. Collaborative learning consists of the interactions and connections between the students with the curricula. Collaborative learning is "an approach to decision-making that encourages systems thinking, joint learning, open communications, transparency, accountability, alternative dispute resolution, and appropriate change (Daniels & Walker, G; 1996). Cont… Dependent Variable Students’ Academic Performance Social media can be used by academics in different ways, as social networking sites were proposed as a means of communicating with students (Mack, D; 2007). According to (Madge et al, C; 2009), social media improves educational access and interaction and informs the learning gap informally between students and instructors. Conceptual Framework Theoretical Framework Self-regulation Theory Achievement Goal Theory Hypothesis H1: There is a significant relationship between Interactive with peers and Collaborative learning by using social media. H2: There is a significant relationship between Interactive with teachers and Collaborative learning by using social media. H3: There is a significant relationship between Engagement and Collaborative learning by using social media. H4: There is a significant relationship between Collaborative learning and students’ academic performance by using social media. H5: There is a significant relationship between Interactive with peers and students’ academic performance. H6: There is a significant relationship between Interactive with teachers and students’ academic performance. H7: There is a significant relationship between Engagement and students’ academic performance. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Research Design Population / Sample Quantitative research proposal is being adopted for this research. The targeted population on this survey will be the student’s one of the private University of Malaysia Kuala Lumpur. The quantitative methodology will used to evaluate the correlation between the independent variable (interaction), mediating variable (collaborative learning) and dependent variable (academic achievement of students). Sample Size With the 5% margin of the error and 95% confidence level, the sample size is calculated from the table 294. Data Collection Sampling Technique The primary data comes from the questionnaires. Non-probability sampling technique will be use. The secondary data is derived, concluded and summarized from previously published studies and articles related to the social media and academic achievements of the students. Cont… Measurement Scale Nominal and ordinal scales will be used for measurement scale. Instrument Design This research questionnaire consists of 4 sections Part A: Demographic information Part B: Independent Variables Part C: Mediating Variables Part D: Dependent Variable Data Analysis This study will use the Partial Least Squares (PLS) analysis technique (Smart PLS 3.0 software) to analyze and test the research model. Profile of Respondent Total respondent number was 300. The majority of age group was 23-27, 43.0%. Bachelor’s degree students response more, and it was 60.3%. Male respondents were 52.0%. And, local students was 61.3%. Convergent Validity Construct Validity Construct validity shows that whether the results that are achieved from the usage of the measures in the questionnaire fit the theories an the model and research design. According to Hair et al. (2010) values greater than 0.5 are considered as significance. Convergent validity shows that whether constructs and measures that must be related and correlated, are in fact related and correlated or not. According to Hair et al. (2010) values greater than 0.7 are considered as significance. Reliability Analysis AVE values should > 0.5 & CR values should greater than > 0.7. To confirm composite reliability, loadings, cross loadings, AVE values must be checked to remove items below than 0.5. Hypothesis H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H6 H7 Results of Path coefficients and hypothesis testing Relationship Standard Beta Standard Error interactivity with peers -> 0.151 0.067 collaborative learning interactivity with teachers -> 0.184 0.067 collaborative learning engagement -> collaborative 0.556 0.067 learning collaborative learning -> academic 0.524 0.054 performance interactivity with peers -> academic -0.016 0.062 performance interactivity with teachers -> 0.115 0.063 academic performance engagement -> academic 0.278 0.077 performance T-value Decision supported 2.289 supported 2.744 supported 3.635 supported 9.658 0.263 1.872 Not supported Not supported 8.247 R square R Square R Square Adjusted 0.701 0.697 0.669 0.666 student’s academic performance collaborative learning supported Findings Limitations The findings reveal that there is a positive significant and strong relationship between the use of social media and academic performance. Sample size was 300, which is not sufficient. Respondents reported that spending fewer hours a week can learn more on average, compared to non-users. The focus of this study is one of the privates University of Malaysia, therefore it cannot be generalized. Lastly, this study is a cross-sectional study and data was collected at one point of time