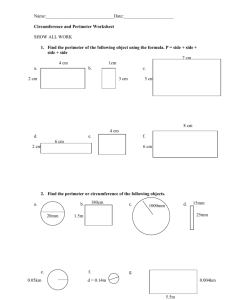
FINDING AREA, PERIMETER, AND CIRCUMFERENCE Area, perimeter, and circumference are all measures of two-dimensional shapes. These are things you can think of as flat: a football field, a piece of paper, or a pizza. You're probably not interested in how high they are, but you might want to know their: ● Perimeter or Circumference. This is the total length of a shape's outline. If you built a fence around its edge, how long would that fence be? If you walked around the edges of this area, how far would you have gone? The length of a straight-sided shape's outline is called its perimeter, and the length of a circle's outline is called its circumference. ● Area. This is the total amount of space inside a shape's outline. If you wanted to paint a wall or irrigate a circular field, how much space would you have to cover? Triangles 1. The perimeter of any triangle is the sum of its sides: a + b + c perimeter = a + b + c c a 5 3 b P=a+b+c P=3+5+4 P = 12 4 2. The area of any triangle is half its base times its height. area = 1/2 bh h 3 b 4 A = 1/2 bh A = 1/2 * 3 * 4 A = 1/2 * 12 A=6 It doesn't matter which of the triangle's short legs is the "base" and which is the "height": you get the same solution either way. h A = 1/2 bh A = 1/2 * 4 * 3 A=2*3 A=6 4 b 3 Squares 1. A square is a kind of rectangle, and the perimeter of any rectangle is the sum of its four sides. Since all sides of a square are the same, perimeter = 4s s P = 4s P=4*3 P = 12 3 s 3 2. The area of a square is equal to any one of its sides times any other: s * s . Since that's the same as s squared, area = s2 s A = s2 A = 32 A=3*3 A=9 3 s 3 Rectangles 1. The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of its four sides. Since a rectangle has two equal short sides (width, w ) and two equal long sides (length, l ), perimeter = 2l + 2w w 3 l 7 P = 2l + 2w P = (2 * 7) + (2 * 3) P = 14 + 6 P = 20 2. The area of a rectangle is equal to its length times its width. area = l * w w A=l*w A=3*7 A = 21 3 l 7 Parallelograms Like squares and rectangles, parallelograms are quadrilaterals: they have four sides and four interior angles. In a parallelogram those angles are not right angles, but the opposite sides must still be parallel to each other. 1. The perimeter of a parallelogram is the sum of its four sides. Since a parallelogram has two equal short sides (width, w ) and two equal long sides (length, l ), perimeter = 2l + 2w w P = 2l + 2w P = (2*5) + (2 * 4) P = 10 +8 P = 18 4 l 5 2. The area of a parallelogram is equal to its base (another name for length) times its height. Its height is not the same as its width: height is measured by a vertical line perpendicular (at right angles to) the base. area = b * h h A=b*h A=3*5 A = 15 3 b 5 Trapezoids A trapezoid is also a quadrilateral: it has four sides, but only two are parallel. 1. The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of its four sides. perimeter = a + b + c + d b a 2 c 4 3 d P=a+b+c+d P=2+3+4+5 P = 14 5 2. To find the area of a trapezoid, we use its two bases and its height: A = 1/2 (b 1 + b 2 ) * (h) area = 1/2 (b1 + b2) (h) b1 h 2 3 b2 5 A = 1/2 (2 + 5) * 3 A = 1/2 * 7 * 3 A = 1/2 * 21 A = 10.5 Circles To find a circle's circumference or area, you first need to know either its radius: r , the distance from its center to any point on its outer edge, or its diameter: d , the length of a straight line through the circle's center that touches any two points on the outer edge. A circle's radius is always exactly half its diameter. r d 1. The circumference of any circle equals two times its radius multiplied by pi (π, approximately 3.14). We can also say it equals pi times its diameter. circumference = 2 π r r OR πd 3 C=2 π*3 C=6* π C ≈ 18.84 Because 3.14 is only an approximate value for pi, we replace the "equals" sign (=) with the "approximately equals" sign ( ≈). For accuracy, some teachers prefer to use the symbol: the circumference of this circle is 6 π . 2. To find the area of a circle, square its radius and multiply the result by pi . area = πr 2 r 3 A = πr 2 A = 32 * π A = (3 * 3) * π A=9* π A = 9π or ≈ 28.26 Created Fall 2012 Pocatello REND 327 208-282-3662 ISU Math Center Student Success Center www.isu.edu/success/math Idaho Falls CHE 220 208-282-7925