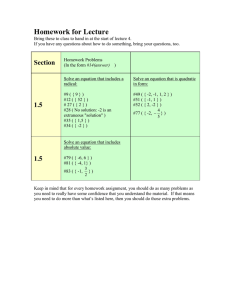
Content Standards: The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of quadratic equations, inequalities and functions, and rational algebraic equations. Performance Standards: The learner is able to investigate thoroughly mathematical relationships in various situations, formulate real-life problems involving quadratic equations, inequalities and functions, and rational algebraic equations and solve them using a variety of strategies. Learning Competency and Code: Solves Problems involving quadratic equations and rational algebraic equations (M9AL-le-1) Quarter: FIRST Week: 5th Day: 17 I. Objectives: At the end of 60 minutes, 85% of the learners are expected to: 1. Translate verbal phrases to mathematical expressions. 2. Give the equivalent equations for verbal statements involving quadratic equations. 3. Solve Number Problems involving quadratic equations.. II. Content: Subject Matter: Solving Problems involving quadratic equations. Integration: (Learning Area): Strategies: Learning through Discovery, Discussion, Interaction, paper and pencil activities Materials: Worksheets, chalk and chalk board, textbook References: *google: (Problem solving involving quadratic equations) *Math 9 Learners Material, pp. 174-183 * Advanced Algebra, Trigonometry and Statistics Math Ideas and life applications IV , pp. c. 2010 by ABIVA Publishing * Advanced algebra, Trigonometry and Statistics 2nd Edition, pp. 195-206 c. 2008 by Fernando Orines, et. Al. Phoenix Publishing House III. Learning Tasks: A. PRELIMINARIES; B. ELICIT: Answer the worksheets in just three (3) minutes. How does each of the following mathematical expression be read/written in English? 1. X + 3 6. (n-5)2 2 2. X 7. 10- d2 2 3. 3f 8. (m + n)2 2 4. k – d 9. x2+ y2 5. 2(n2+6) 10. m2- 9 C. ENGAGE: The teacher let the students give the answer by writing it on the board. Together, the students would then try to check whether the English phrases / interpretation they give is correct, letting them give the correct phrase if what they gave is wrong. Guide questions can be thrown by the teacher in cases the students cannot really give the correct English phrase. ANSWERS (Note, answers may vary, depending on how the sentence is being constructed; answers here are the nearest possible.) 1. sum of a number and 3. 2. square of a number 3. thrice the square of a number 4. a number decreased by a square of another number 5. twice the sum of the square of a number and six 6. the square of the difference of a number decreased by five 7. ten decreased by a square of a number 8. The square of the sum of two distinct numbers 9. The sum of the squares of two numbers. 10. the square of a number decreased by nine D. EXPLORE: Teacher: Ok, this time let’s try it on number problems: One positive integer is one-half the other and the sum of their squares is 80.What are these integers? The teacher would then give the students time to solve and then present their interpretation on the problem given. The students would are then given time to defend, discuss their answers in front. While the teacher would only listen to the student’s interaction, trying to take note important points for learning as well as the misconceptions if there’s anything that would arise. SOLUTION: Let x be the bigger number 𝑥 𝑥 2 + (2)2 = 80 𝑥2+ 𝑥2 4 = 80 4𝑥 2 + 𝑥 2 = 80 4 5𝑥 2 = 320 𝑥 2 = 64 X = ±8 ;note that the number we are looking for is a positive number, thus, we take x = 8. The smaller number is 8/2 = 4 Checking: 8 8 2 + ( )2 = 80 2 82 + 42 = 80 64 + 16 = 80 80=80 E. EXPLAIN The teacher would then give the important points jotted at the Explore stage, and let the students raise questions as well as letting the students answer questions/ parallel situations thrown by the teacher. F. ELABORATE The teacher would let the students enumerate the steps (in their own words) they found out earlier on how to solve Word problems involving quadratic equations, eventually supplying ideas , may there be cases students could not trace or there are steps not given/ left out. This list of steps would serve as their guide for the next activity. G. EXTEND The teacher let the students apply what they learned through the following activity. (Note: this is an Individual activity.) Solve the following number problems: 1. Find two consecutive positive integers having 145 as the sum of its squares. 2. Find two consecutive even integers whose product is 120. 3. Two Odd integers have 1023 when multiplied. What are these integers? Solutions: 1. Let x be the first positive number x + 1 be the second positive number x2 + (x+1)2 = 145 x2 + x2 +2x +1 = 145 x2 + x2 +2x +1-145 = 0 Checking: 2x2 +2x -144 = 0 82 + 92 = 145 2x2 +2x -144 = 0 64 + 81 = 145 2 145=145 2 x + x -72 = 0 (x-8)(x+9)=0 x-8 =0 ; x + 9 =0 x=8 ; x=-9 Since we are looking for two consecutive positive integer, we can only take 8 as our first number; -9 is the extraneous solution. x + 1 = 8 + 1 = 9. 2. Let x be the first positive even number x +2 be the second positive even number x ( x+2 ) = 120 x2 + 2x = 120 Checking: 2 x + 2x – 120 = 0 x ( x+2 ) = 120 (x +12)(x – 10) = 0 10(12) = 120 x + 12 = 0 ; x – 10 = 0 120 = 120 x = -12 ; x = 10 10 is the first positive even number; -12 is the extraneous solution. x + 2 = 10 + 2 = 12 12 is the second positive even number 3. Let x be the first odd integer x +2 be the second odd integer x ( x+2 ) = 1023 x2 + 2x = 1023 x2 + 2x – 1023 = 0 (x +33)(x – 31) = 0 x + 33 = 0 ; x – 31 = 0 x = -33 ; x = 31 Checking: x ( x+2 ) = 120 10(12) = 120 120 = 120 31 is the first odd integer; -33 is the extraneous solution. x + 2 = 31 + 2 = 33 33 is the second odd integer H. EVALUATE Evaluation is done by letting the students check their work, discussing the answers of the problems given. The teacher should be quick in trying to know what percentage of students got the correct answer/ solved the problem correctly to decide (Reflection) if re-teaching or giving another topic will be done next meeting. V. Assignment / Enrichment 1. Find two consecutive numbers whose product is 600. 2. Find two consecutive even numbers whose product is 80. 3. Two consecutive odd integers gives the product 2549 when multiplied. What are these integers? Reflection: A. No. of learners achieve 80%: ____ B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation: ___ C. Did the remedial lessons work? ___ D. No. of learners who have caught up the lesson: ___ E. No. of learners who continue to require remediation: ___ F. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? ___ G. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor help me solve? ___ H. What innovation or localized materials did I used/discover which I wish to share with other teacher? ___