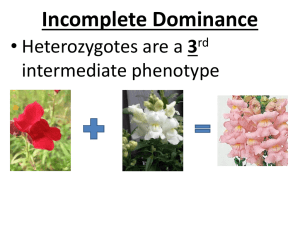
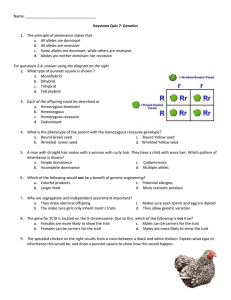
Unit 3 Lesson 1 Lesson Quiz Name: Date: Quiz: Inheritance Read each question. Circle the letter of the correct answer. 1. Look at the diagram shown. 4. A botanist crosses a pea plant that produces smooth seeds with a pea plant that produces wrinkled seeds. The resulting plants all produce smooth seeds. What can be determined from the results of the experiment? A. Smooth shape and wrinkled shape are both recessive traits. B. Smooth shape and wrinkled shape are both dominant traits. C. Smooth shape is a dominant trait, and wrinkled shape is a recessive trait. D. Smooth shape is a recessive trait, and wrinkled shape is a dominant trait. Which of these gives the correct ratio for the offspring predicted by the diagram? 5. The diagram shows several structures located within a cell. A. 2 BB : 1 Bb B. 1 BB : 1 BB C. 1 BB : 1 Bb D. 1 BB : 2 Bb 2. Alleles carry the codes for producing which of these types of large molecules? A. lipids B. proteins C. nucleic acids D. carbohydrates Which statement best describes the relationship among the structures? 3. A scientist crossed a white-flowered plant with a blue-flowered plant. Which of these outcomes would show that blue flower color is dominant to white flower color? A. Structures B and C are located IN Structure A and code for inherited traits. B. Structures B and C come together to form a new organisms during fertilization. A. All of the second generation is blue. C. Structure A is a small part of Structures C and B, and codes for a single inherited trait. B. All of the second generation is white. C. One-fourth of the second generation is blue. D. Structure C is located within Structure B, which is located within Structure A, and all three code for different versions of the same trait. D. One-fourth of the second generation is white. Lesson Quiz © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 1 Module B • Assessment Guide Unit 3 Lesson 1 Lesson Quiz Name: Date: 6. The diagram shows a cross that is similar to one of Mendel’s pea plant crosses. What is the dominant phenotype of the offspring in the cross shown? A. Ff B. FF C. blue D. white 7. Look at the diagram shown. The alleles for the parents are missing. The parents in the diagram have which of these alleles? A. DD and Dd B. Dd and Dd C. Dd and dd D. DD and dd Lesson Quiz © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 2 Module B • Assessment Guide Unit 3 Lesson 1 Lesson Quiz Name: Date: Read each statement. Write your answer on the lines. 8. Jake made a chart to trace the traits of straight and curly hair in his family. The lines on the chart show relationships. Parents are connected by a horizontal line while vertical lines lead to their offspring. A shaded circle or square in Jake’s chart represents a person with straight hair. Predict if the straight hair is controlled by a dominant allele or a recessive allele? (Hint – If straight hair is a dominant allele , it should be present in ALL generations of the family) 9. A pair of fruit flies reproduces and has one thousand offspring. All one thousand of the offspring have the alleles gg. What is the most likely combination of alleles for each parent? Lesson Quiz © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 3 Module B • Assessment Guide Unit 3 Lesson 1 Lesson Quiz Name: Date: 10. The diagram shows a Punnett square made to predict the earlobe shape of the offspring of two parents. The capital A stands for the trait of free-hanging earlobes, and the lowercase a stands for the trait of attached earlobes. Write the genotype of each offspring. What will be the phenotype of each offspring? Is the trait of free-hanging earlobes dominant or recessive? What is the expected ratio of free-hanging earlobes to attached earlobes in the offspring? Lesson Quiz © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company 4 Module B • Assessment Guide