Distance and Displacement Worksheet
advertisement
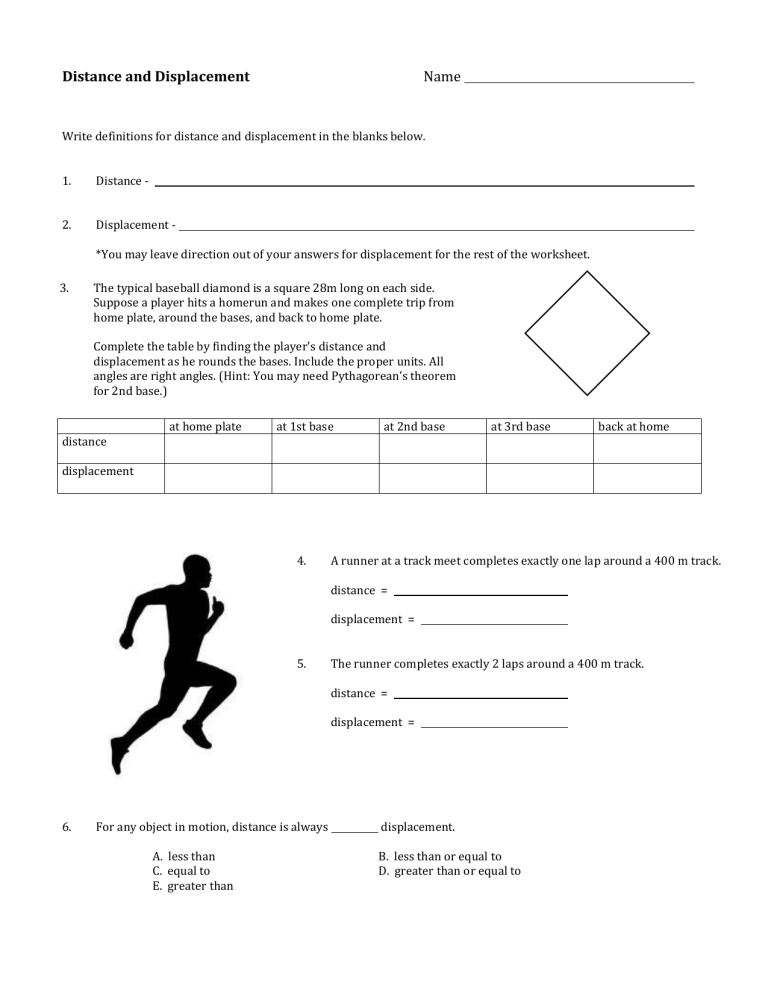
Distance and Displacement Name Write definitions for distance and displacement in the blanks below. 1. Distance - 2. Displacement *You may leave direction out of your answers for displacement for the rest of the worksheet. 3. The typical baseball diamond is a square 28m long on each side. Suppose a player hits a homerun and makes one complete trip from home plate, around the bases, and back to home plate. Complete the table by finding the player's distance and displacement as he rounds the bases. Include the proper units. All angles are right angles. (Hint: You may need Pythagorean’s theorem for 2nd base.) at home plate at 1st base at 2nd base at 3rd base back at home distance displacement 4. A runner at a track meet completes exactly one lap around a 400 m track. distance = displacement = 5. The runner completes exactly 2 laps around a 400 m track. distance = displacement = 6. For any object in motion, distance is always A. less than C. equal to E. greater than displacement. B. less than or equal to D. greater than or equal to 7. A swimmer swims a half lap, moving from the left end to the right end of a pool that is 50 meters long. distance = displacement = <8. 50 meters long -> A swimmer swims an entire lap, moving from the left end to the right end and back again to the left end in a pool that is 50 meters long. distance = displacement = <- 50 meters long -> Distance and Displacement Name Write definitions for distance and displacement in the blanks below. 1. Distance - (Answers will vary.) The total length of the path taken 2. Displacement - (Answers will vary.) The difference between the final and initial positions, including direction *You may leave direction out of your answers for displacement for the rest of the worksheet. 3. The typical baseball diamond is a square 90 ft long on each side. Suppose a player hits a homerun and makes one complete trip from home plate, around the bases, and back to home plate. Complete the table by finding the player's distance and displacement as he rounds the bases. Include the proper units. All angles are right angles. (Hint: You may need Pythagorean’s theorem for 2nd base.) distance at home plate 0 ft at 1st base 90 ft at 2nd base 180 ft at 3rd base 270 ft back at home 360 ft displacement 0 ft 90 ft 127.3 ft 90 ft 0 ft 4. 5. 6. For any object in motion, distance is always A. less than C. equal to E. greater than (over) A runner at a track meet completes exactly one lap around a 400 m track. distance = 400 m displacement = 0m The runner completes exactly 2 laps around a 400 m track. distance = 800 m displacement = 0m D displacement. B. less than or equal to D. greater than or equal to 7. 8. A bug walks exactly halfway around the edge of a circular cupcake with a diameter of 5.00 cm. distance = 7.85 cm displacement = 5.00 cm A swimmer swims a half lap, moving from the left end to the right end of a pool that is 50 meters long. distance = 50 m displacement = 9. 50 m A swimmer swims an entire lap, moving from the left end to the right end and back again to the left end in a pool that is 50 meters long. distance = 100 m displacement = 10. For a typical day in your life, from the time you get out of bed in the morning to the time you climb back into your bed at night, estimate the following: distance = 11. 0m (Answers will vary.) displacement = Think of the total distance you have covered in your lifetime. Is it possible for you to move in some direction to reduce this distance to zero? 0m No 12. If so, where would you go? If not, why not? (Answers will vary.) No matter what direction you move, distance is always being added to your lifetime total. 13. Is it possible for you to make your lifetime displacement equal to zero? 14. If so, where would you go? If not, why not? (Answers will vary.) You could return to the place of your birth. Yes