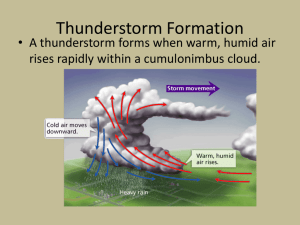
Weather Test Review Sheet Sea Breezes occur during the day time as land heats up faster than water. Air rises from the land and the wind blows from the sea to replace it. Land breezes occur at night as land cools off faster than water. Air rises from the water and cool air from the land blows toward the water to replace it. Ozone in the stratosphere helps protect us from UV radiation from the sun. Ozone in the troposphere is a pollutant which makes it harder to breathe. The Earth spinning produces the Coriolis Effect. This deflects wind to the right in the northern hemisphere and wind to the left in the southern hemisphere. Winds flow clockwise around high pressures in the northern hemisphere and counterclockwise around low pressures. It is the opposite in the southern hemisphere. Trade winds are easterly winds that blow in-between 30 degrees latitude and the equator. They help bring precipitation to Hawaii. The westerlies are the main winds that bring storms to Utah. Condensation nuclei are small dust or pollen particles that are found in the air that water vapor condenses onto to form tiny water droplets. Clouds form as air rises and cools and expands and reaches the dew point. The dew point is the temperature that the air has to cool off to in order to for condensation to occur (dew or cloud to form) Humid air is lighter than dry air. Air is forced to rise in the following ways: - Wind blowing into a mountain. - Along a front such as a cold front. - Hot/humid air. - Cold Air Aloft (Lake Effect) El Nino occurs in the ocean when warm water off the coast of southeast Asia moves toward South America. This changes the weather patterns and brings moisture to normally dry areas and drought to normally wet areas. Hurricanes develop over water that is 80 degrees or warmer. A tropical depression forms first and then when wind speeds reach 39 miles per hour, it is called a tropical storm. When wind speeds reach 74 miles per hour they are called hurricanes, cyclones, or typhoons depending on where they occur. Hurricane season in the northern hemisphere goes from June through November. Hurricanes usually produce a foot or more of rain. The “eye” of the hurricane usually has calm or very light winds. The strongest winds occur just outside the eye in the eye wall. Hurricane Katrina caused lots of damage to the New Orleans area back in 2005. Hurricane Harvey moved very slowly and brought over 3 feet of rain to Texas. A storm surge forms when hurricane winds bring higher ocean water to the land. This causes destructive flooding along the coast. Tornadoes often form in supercell thunderstorms. These are very powerful storms. Tornadoes often form when two different air masses collide. Tornado season is during the spring and early summer. Tornadoes are classified by wind speed. EF0 tornadoes are the weakest and EF5 are the strongest and most destructive. Tornadoes occur in “tornado alley” in the Midwest part of the United States. A tornado destroyed much of the town of Joplin, Missouri. As warm moist air rises it produces cumulus and then cumulonimbus clouds. A thunderstorm forms. Rain forms as cloud droplets come together to form bigger drops or when supercooled droplets freeze onto ice particles which melt on the way down. Hail as water droplets freeze onto ice particles. Powerful updrafts lift the hail and grows layer by layer until it is too heavy for the updrafts and falls down. Lightning forms when clouds become charged from friction from updrafts and downdrafts. This removes electrons and causes charged particles. Lightning can reach 50,000 degrees Fahrenheit. (5 times hotter than the surface of the sun) Thunder is produced when superheated air rapidly expands and contracts. Cold fronts form as cold air digs underneath warm air forcing the warm air to rise. Heavy precipitation often occurs from a cold front. Warm fronts form as warm air advances. The warm air moves over the cold air. Light steady precipitation often happens from this. Stationary fronts occur as air masses are modified and the front stalls. An anemometer is used to measure wind speed. The cups move faster with a stronger wind. A barometer is used to measure air pressure. The air pressure presses down on the mercury causing it to rise up in the tube. A hygrometer is an instrument used to measure humidity. The relative humidity is the percentage of how saturated the air is.