1.
The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object.
v
t
Which one of the following graphs best represents the variation with time t of the acceleration a
of the object?
A.
a
0
C.
B.
0
0
0
t
a
D.
0
t
a
0
t
0
t
a
0
(1)
2.
A stone is thrown at an angle to the horizontal. Ignoring air resistance, the horizontal component
of the initial velocity of the stone determines the value of
A.
range only.
B.
maximum height only.
C.
range and maximum height.
D.
range and time of flight.
(1)
1
3.
The graph below shows how a quantity y varies with time t for a falling object.
y
0
0
t
Which one of the following quantities could be represented by y?
A.
Speed when air resistance is negligible
B.
Speed when air resistance is not negligible
C.
Distance moved from rest when air resistance is negligible
D.
Distance moved from rest when air resistance is not negligible
(1)
4.
A particle moves from a point P to a point Q in a time T. Which one of the following correctly
defines both the average velocity and average acceleration of the particle?
Average velocity
Average acceleration
A.
displacement of Q and P
T
change in speed from Q to P
T
B.
displacement of Q and P
T
change in velocity from Q to P
T
C.
distance between Q and P
T
change in speed from Q to P
T
D.
distance between Q and P
T
change in velocity from Q to P
T
(1)
2
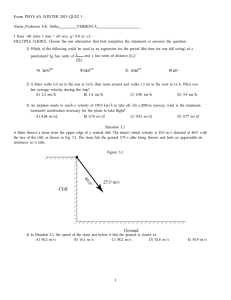
5.
Two stones, X and Y, of different mass are dropped from the top of a cliff. Stone Y is dropped a
short time after stone X. Air resistance is negligible.
Whilst the stones are falling, the distance between them will
A.
decrease if the mass of Y is greater than the mass of X.
B.
increase if the mass of X is greater than the mass of Y.
C.
decrease whether the mass of X is greater or less than the mass of Y.
D.
increase whether the mass of X is greater or less than the mass of Y.
(1)
6.
The diagram below shows the trajectory of a ball thrown into the air. There is no air resistance.
trajectory of ball
A
X
B
C
D
Which arrow gives the direction of the resultant force on the ball at the point X?
A.
A
B.
B
C.
C
D.
D
(1)
3
7.
A body starting from rest moves along a straight-line under the action of a constant force. After
travelling a distance d the speed of the body is v.
initial position
v
d
The speed of the body when it has travelled a distance
A.
v
.
4
B.
v
.
2
C.
D.
v
2
d
from its initial position is
2
.
v
2 2
.
(1)
4
8.
A stone is thrown with speed v from the top of a cliff of height H, as shown below.
h
v
cliff
H
sea
The stone is thrown at an angle to the horizontal so that it rises to a height h above the top of the
cliff before falling into the sea. The acceleration of free fall is g. Air resistance is negligible.
Which one of the following expressions gives correctly the speed of the stone as it hits the sea?
A.
v+
(2 gh )
B.
v+
(2 gH )
C.
(2 g {h + H })
D.
(v
2
+ 2 gH
)
(1)
5
9.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the ground. The graph shows the variation with time t
of the vertical displacement d of the ball.
Which of the following gives the final displacement after time T and the average speed between
time t = 0 m aand time t = T?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Displacement
Average speed
0
0
0
2D
T
2D
2D
T
2D
0
(1)
6
10.
A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. Air resistance is negligible. Which of the
following diagrams best represents the subsequent path of the ball?
A.
B.
C.
D.
(1)
7
11.
The graph below shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of an object from t = 0 to
t = T.
a
0
0
T
t
The shaded area under the graph represents change in
A.
displacement.
B.
velocity.
C.
momentum.
D.
kinetic energy.
(1)
8
12.
The graph below shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of a spaceship.
a
0
0
T
t
The spaceship is at rest at t = 0.
The shaded area represents
A.
the distance travelled by the spaceship between t = 0 and t = T.
B.
the speed of the spaceship at t = T.
C.
the rate at which the speed of the spaceship changes between t = 0 and t = T.
D.
the rate at which the acceleration changes between t = 0 and t = T.
(1)
9
13.
A car accelerates uniformly from rest. It then continues at constant speed before the brakes are
applied, bringing the car to rest.
Which of the following graphs best shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of the
car?
A.
a
0
B.
0
t
0
t
0
t
a
0
D.
t
a
0
C.
0
a
0
(1)
10
14.
A stone is thrown from the top of a cliff with speed v at an angle θ above the horizontal, as
shown.
cliff
Air resistance is negligible and the acceleration of free fall is g.
What is the horizontal velocity of the stone a time t after the stone has been thrown?
A.
v sinθ
B.
v sinθ – gt
C.
v cosθ
D.
v cosθ – gt
(1)
15.
Which one of the following is a correct definition of displacement?
A.
Distance from a fixed point
B.
Distance moved from a fixed point
C.
Distance from a fixed point in a given direction
D.
Distance moved in a given direction
(1)
11
16.
An object is falling, in air, towards the Earth’s surface.
What changes occur in the acceleration and in the velocity of the object as it approaches
terminal velocity?
acceleration
velocity
A.
decreases to zero
increases continuously
B.
decreases to zero
increases to a constant value
C.
constant
increases to a constant value
D.
constant
increases continuously
(1)
17.
A ball, initially at rest, takes time t to fall through a vertical distance h. If air resistance is
ignored, the time taken for the ball to fall from rest through a vertical distance 9h is
A.
3t.
B.
5t.
C.
9t.
D.
10t.
(1)
18.
The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object.
v
0
0
t
12
The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents
A.
the average velocity of the object.
B.
the displacement of the object.
C.
the impulse acting on the object.
D.
the work done on the object.
(1)
19.
Two identical metal spheres are held above the ground as shown.
spheres
(not to scale)
ground
The separation between them is small compared to their distance above the ground. When the
spheres are released, the separation of the spheres will
A.
remain constant.
B.
decrease continuously.
C.
increase continuously.
D.
increase initially and then remain constant.
(1)
13
20.
The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object moving along a straight
line.
v
0
0
t
Which graph shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of the object?
a
A. a
0
C.
B.
0
0
t
t
a
a
0
0
D.
0
0
t
0
t
(1)
14
21.
A raindrop falling through air reaches a terminal velocity before hitting the ground. At terminal
velocity, the frictional force on the raindrop is
A.
zero.
B.
less than the weight of the raindrop.
C.
greater than the weight of the raindrop.
D.
equal to the weight of the raindrop.
(1)
22.
The graph below shows the variation with time of the distance moved by a car along a straight
road. During which time interval does the car have its greatest acceleration?
distance
moved
A
B
C
D
time
(1)
15
23.
A stone X is thrown vertically upwards with speed v from the top of a building. At the same
time, a second stone Y is thrown vertically downwards with the same speed v as shown.
v
X
Y
v
Building
Air resistance is negligible. Which one of the following statements is true about the speeds with
which the stones hit the ground at the base of the building?
A.
The speed of stone X is greater than that of stone Y.
B.
The speed of stone Y is greater than that of stone X.
C.
The speed of stone X is equal to that of stone Y.
D.
Any statement about the speeds depends on the height of the building.
(1)
24.
A small steel ball falls from rest through a distance of 3 m. When calculating the time of fall, air
resistance can be ignored because
A.
air is less dense than steel.
B.
air resistance increases with the speed of the ball.
C.
the air is not moving.
D.
air resistance is much less than the weight of the ball.
(1)
16
25.
The graph below shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of a body moving in a
straight-line.
a
0
0
t1
t2
t
The shaded area represents
A.
the change in velocity from t1 to t2.
B.
the velocity at t2.
C.
the average velocity between t1 and t2.
D.
the velocity at t1.
(1)
17
26.
A particle is projected horizontally with speed v from a height H. It lands a horizontal distance
R from the point of launch as shown in the diagram below.
v
H
R
A second particle is projected horizontally from the same height with speed 2v. Neglecting air
resistance the horizontal distance travelled by this particle is
A.
B.
R.
2R.
C.
2R.
D.
4R.
(1)
27.
Juan is standing on the platform at a railway station. A train passes through the station with
speed 20 m s–1 in the direction shown measured relative to the platform. Carmen is walking
along one of the carriages of the train with a speed of 2.0 m s–1 measured relative to the carriage
in the direction shown. Velocity is measured as positive in the direction shown on the diagram.
Carmen
2.0 ms –1
20 ms –1
Juan
platform
velocity measured as a
positive in this direction
18
The velocity of Carmen relative to Juan is
A.
–22 m s–1.
B.
–18 m s–1.
C.
+18 m s–1.
D.
+22 m s–1.
(1)
28.
The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object.
v
0
0
t
19
Which one of the following graphs shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of the
object?
A.
0
C.
B.
a
0
0
t
D.
a
a
t
0
a
0
0
0
0
t
t
(1)
20
29.
Peter and Susan both stand on the edge of a vertical cliff.
V (Peter)
V (Susan)
Sea
Susan throws a stone vertically downwards and, at the same time, Peter throws a stone vertically
upwards. The speed V with which both stones are thrown is the same. Neglecting air resistance,
which one of the following statements is true?
A.
The stone thrown by Susan will hit the sea with a greater speed than the stone thrown by
Peter.
B.
Both stones will hit the sea with the same speed no matter what the height of the cliff.
C.
In order to determine which stone hits the sea first, the height of the cliff must be known.
D.
In order to determine which stone hits the sea first both the height of the cliff and the
mass of each stone must be known.
(1)
21
30.
An object has initial speed u and acceleration a. After travelling a distance s, its final speed is v.
The quantities u, v, a and s are related by the expression
v2 = u2 + 2as.
Which of the following includes the two conditions necessary for the equation to apply?
A.
a has constant direction
u and v are in the same direction
B.
a has constant direction
a, u and v are in the same direction
C.
a has constant magnitude
a has constant direction
D.
a has constant magnitude
u and v are in the same direction
(1)
31.
Which one of the following is a true statement concerning the vertical component of the
velocity and the acceleration of a projectile when it is at its maximum height? (The acceleration
of free fall is g.)
Vertical component of velocity
Acceleration
A.
maximum
zero
B.
maximum
g
C.
zero
zero
D.
zero
g
(1)
22
32.
A ball is dropped from rest at time t = 0 on to a horizontal surface from which it rebounds. The
graph shows the variation of time t with speed v of the ball.
v
A
C
0
0
B
D
t
Which one of the following best represents the point at which the ball just loses contact with the
surface after the first bounce?
A.
A
B.
B
C.
C
D.
D
(1)
23
33.
The graph shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of an object.
20
15
10
a / ms
–2
5
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
t/s
The object is at rest at time t = 0.
Which of the following is the velocity of the object at time t = 6.0 s?
A.
0.50 m s–1.
B.
2.0 m s–1.
C.
36 m s–1.
D.
72 m s–1.
(1)
24
34.
A car is heading due East at a speed of 10 m s−1. A bird is flying due North at a speed of
4 m s−1, as shown below.
N
W
4ms
E
–1
S
Car
Bird
10 m s –1
Which one of the following vectors represents the velocity of the bird relative to a person in the
car?
A.
B.
C.
D.
(1)
35.
A ball is released from rest near the surface of the Moon. Which one of the following quantities
increases at a constant rate?
A.
Only distance fallen
B.
Only speed
C.
Only speed and distance fallen
D.
Only speed and acceleration
(1)
25
36.
A ball rolls off a horizontal table with velocity v. It lands on the ground a time T later at a
distance D from the foot of the table as shown in the diagram below. Air resistance is negligible.
v
table
D
A second heavier ball rolls off the table with velocity v. Which one of the following is correct
for the heavier ball?
Time to land
Distance from table
A.
T
D
B.
T
less than D
C.
less than T
D
D.
less than T
less than D
(1)
37.
A stone is thrown horizontally from the top of a high cliff. Assuming air resistance is negligible,
what is the effect of gravitational force on the horizontal and on the vertical components of the
velocity of the stone?
Vertical component of velocity
Horizontal component of velocity
A.
increases to a constant value
stays constant
B.
increases continuously
stays constant
C.
increases to a constant value
decreases to zero
D.
increases continuously
decreases to zero
(1)
26
38.
A sailing boat is moving with constant velocity v to the right parallel to the dock.
Sailor Hulot, up on the mast, drops his telescope at the moment he is opposite Lucie who is
standing on the dock. Which one of the following best shows the path of the falling telescope as
seen by Lucie?
A.
B.
C.
D.
(1)
39.
The diagram below shows the path of a projectile in the absence of air resistance.
Vertical
position
Horizontal position
27
Which one of the following diagrams best represents the path of the projectile under the same
initial conditions when the air resistance is taken into account? (The path in absence of air
resistance is shown for comparison as a dotted line.)
A.
B.
Vertical
position
Vertical
position
Horizontal position
C.
Horizontal position
D.
Vertical
position
Vertical
position
Horizontal position
Horizontal position
(1)
40.
An athlete runs round a circular track at constant speed. Which one of the following graphs best
represents the variation with time t of the magnitude d of the displacement of the athlete from
the starting position during one lap of the track?
A. d
0
B. d
0
t
C. d
0
0
0
t
0
t
D. d
0
t
0
(1)
28