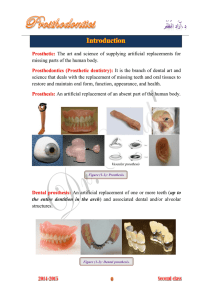
Introduction to pre-clinical complete denture Term Prosthesis Prosthetics Prosthodontics (Prosthetic Dentistry ) Dentulous Completely edentulous Partially edentulous Denture Complete denture Removable partial denture Fixed partial denture Single complete denture Immediate denture: Overdenture Obturator Implant prosthesis Support Retention Stability Dr. Wafaa Ibrahim Definition An artificial replacement of an absent part of the human body The art and science of supplying artificial replacement for missing parts of the human body. The branch of dentistry that deals with the replacement of missing dental and oral and craniofacial structures A condition in which complete set of natural teeth are present in the mouth. A condition in which the mouth is without teeth. A condition in which some of the natural teeth are lost An artificial substitute for missing natural teeth and adjacent tissues. A removable dental prosthesis that replaces the entire dentition and associated structures of the maxillae or mandible A partial denture that can be removed and placed in the mouth. A partial denture that is cemented to natural teeth or dental implants It is a denture that occludes against some or all natural teeth A complete or removable partial denture fabricated for replacement immediately following the removal of natural teeth A removable partial or complete denture that covers and rests on remaining natural teeth, roots or dental implants A prosthesis used to close a tissue opening(congenital or a acquired) A prosthesis that utilizes dental implants for retention, support and stability The resistance to displacement towards the basal tissue or underlying structures The quality inherent in the dental prosthesis acting to resist the forces of dislodgment along the path of placement away from the tissues. The quality of a removable dental prosthesis to resist displacement by functional horizontal stresses. Page 1 Introduction to pre-clinical complete denture Natural Versus Artificial Teeth: Natural teeth are firmly rooted in the bone of the jaw so they can incise, tear and finely grind food. • Artificial teeth rest on the oral mucosa and are held there by weak forces while subjected to powerful displacing forces, so, their efficiency as a masticatory apparatus is limited. Objectives of Complete Denture 1-Restoration of the masticatory function 2- Restoration of the normal appearance. • Loss of teeth agingfalling of lips and cheek • Loss of teeth resorption of alveolar bone 3- Correction of speech defects resulting from loss of natural teeth • Proper length and labiolingual position of the teeth 4- Preservation of alveolar bone & Tempromandibular joint • Restoration of chewing minimize the rate of alveolar atrophy 5- Satisfaction & comfort of the patient Ill fitting denture discomfort Surfaces of a complete denture 1- Polished surface: the outer (external) surface of the denture that carries the artificial teeth. It includes the facial, lingual, and palatal surfaces facing the cheeks, lips, and tongue. • Labial, buccal, and lingual surfaces of teeth are part of the polished surface. 2- Occlusal surface: the portion of the denture surface that makes contact with its antagonist (opposing occlusion). 3- Fitting surface: the surface that fits on the tissues. Also called basal surface, tissue surface, and impression surface Dr. Wafaa Ibrahim Page 2 Introduction to pre-clinical complete denture Components of a complete denture: 1. Artificial teeth 2. Denture base: the part of the denture that rests on the tissue foundation and to which artificial teeth are attached. – Retention and stability. – Carry and support teeth. – Represents oral mucosa. – Support lips and cheeks. a. Denture borders: the margin of the denture base at the junction between the polished and the impression surfaces. b. Denture flanges: the vertical extensions of the denture base that extend from the cervical margin of the teeth to the borders of the denture. •They are named according to their location as follows: - Buccal flange: related to cheeks and occupies buccal vestibule. - Labial flange: related to lips and occupies labial vestibule. - Lingual flange: portion of mandibular denture related to tongue and occupies lingual sulcus. c. Palatal portion: that portion of the maxillary denture related to the palate. Steps of C.D Construction: Dr. Wafaa Ibrahim Page 3
![other forms of removable partial denture [ppt]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009527564_1-3147e0c80cfc579c21cbc7c629e44157-300x300.png)