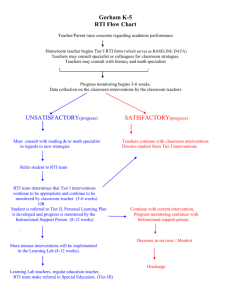
Response to Intervention Module #1: Teaching and Learning Presented by: Brent Johnson Instructional Director Agenda 1 Overview of Response to Intervention Purpose and Components of RTI 4 Teacher Methodology of RTI Practices Tell Us About Yourself! What is your name? What is your role? (i.e. Teacher/grade, principal, coach, etc.) How long have you been in education? Who is Brent Johnson? Instructional Director for NAEP Special Education Teacher for Gwinnett County Public Schools and Atlanta Public Schools 2013-2017 B.S. Educational Studies from Bethune-Cookman University Master of Arts in Teaching in Special Education from Georgia College and State University Education Specialist in Media with a concentration in Instructional Technology from the University of West Georgia National Academic Educational Partners NAEP GETS RESULTS National Academic Educational Partners Our Track Record • NAEP has implemented its solutions all over the nation with proven results and increased student achievement data. Our People • Our people have lived educational reform. Let our proven practitioners become your greatest resource and accelerate your student outcomes. Customization • No educational challenge is the same. NAEP customizes its solutions to optimize your RESULTS. True Collaboration • With NAEP, you are NEVER ALONE. We don't simply deliver a solution, we implement it WITH you side-by-side. “An intervention without progress monitoring is just an activity.” ― Warren Bemis Activity: 3 minutes •What does this quote mean to you? •Turn and talk with a peer to discuss it. •Prepare to share with the group. Objectives Participants will be able to.. 1 Analyze the RTI model and gain an understanding of each tier. 2 Understand the benefits of RTI and potential barriers to student success. 3 Define the RTI framework and key vocabulary associated with RTI. 1 8 What were the district RTI report findings? Areas of strength 1.Evidence of a RTI leadership team. 2.Implementation of an evidencebased universal screener (DIBELS). 3.Conversation held around data points used to identify at-risk students. 4.Leadership team is in place and each member has various roles within the school. Areas for improvement 1.RTI 101: Common understanding of RTI framework. 2.Common RTI Language 3.Clear understanding of differentiation vs. evidence-based interventions. 4.Knowledge of fidelity of interventions. 5.Infrastructure for supporting RTI (Defined role of the RTI team members). NAEP Professional Development Schedule Overview Needs Ensuring Assessment Equal Access Completed 2/13-2/17 Teaching and Learning Whole Group: 2/27-3/3 First Individual Coaching Session: 3/13-3/17 Second Individual Coaching Session: 3/27-3/31 Ensuring Equal Access Whole Group: 4/10-4/14 First Individual Coaching Session: 4/24-4/28 Second Individual Coaching Session: 5/8-5/12 Assessment Assessments s Whole Group: TBD First Individual Coaching Session: TBD Second Individual Coaching Session: TBD 2017 Calendar Case Study #1 Read Case Study #1 (Handout #1) H1a What are Jean Paul’s challenges? Jean Paul is an 8th grade student at D.W. Rogers Elementary School. He emigrated from Haiti when he was in the second grade. Jean Paul currently reads on a 3rd grade reading level. He has difficulty comprehending text on his grade level unless the text is read to him. Jean Paul also has difficulty solving multistep word problems and complains that he doesn’t understand what he is supposed to do to solve the problems. Jean Paul does not complete assignments and does not turn in homework. Jean Paul hasn’t received any support outside of some differentiation from his teacher. He is currently on track to receive a failing grade in reading and math. What could be some barriers to his success? 12 Case Study #2 Read Case Study #2 (Handout #1) H1b What differences do you see in the supports he received compared to Case Study #1? What process do you use to support struggling students like Alexander? Alexander is a 4th grader at Mary Mcleod Bethune Elementary School. Alexander is currently reading on a 1st grade reading level according to the recent STAR report. Alexander’s teacher, Ms. Clark, noticed that he takes several minutes to start assignments, does not like to read aloud, and has challenges reading his sight words. During her student centers, She pulls Alexander with a small group of other struggling students or independently to provide him more intensive instruction. She uses her pretest and posttest data to make decisions about her small group or individual instruction. She reports her findings to her assistant principal and academic coach to get support with Alexander. 13 The Purpose of “Look Fors” Self-Assessment & Progress Monitoring • Teachers are able to selfassess the implementation of newly acquired competencies with fidelity and a real-life understanding of what needs to change in the classroom. This presentation will consist of a set of important information that is a connection to the RTI district report. Consistent Teacher Vocabulary Skill Transfer & Support Allocation • Teachers can speak to each other with real, applicable, and consistent practitioner vocabulary ensuring that department and district wide efforts are aligned. • District and school-site supervisors will have a calibrated perspective on whether the professional development and skills transferred therein has actually transferred into the classroom allowing for optimal allocation of additional support when necessary. Each of these Look Fors were identified as areas of growth on the report. A magnifying glass on a slide means that this is a Look For. 14 Key “Look For” for This Session Key Look For 3.3) All staff understand that RTI is a framework to prevent all students, including students with disabilities, from having academic problems. Activity: Barriers to Success Let’s have a RTI talk! Select a low performing student in your class. Consider all of the student’s areas of weakness and strengths. Think about all of the strategies you have used to support that student. Share the details of that student with a partner. Your partner will listen and come up with some reasons that could serve as barriers to their success. 16 Individuals with Disabilities Act The Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004 (IDEA 2004) is a United States law that mandates equity, accountability and excellence in education for children with disabilities. This Act changes many sections of the statute to reflect new ideas around learning disabilities and the strategy called response to intervention or RTI. 17 What is RTI? H2 RTI is an assessment and intervention model that enables schools to deliver sound instructional methods to students who might otherwise “fall through the cracks.” A data-based method to determine the level of a student’s response to interventions that range from universal (those provided to all students, e.g., core reading program, core discipline program) to intensive individually delivered interventions. 18 Why Should Schools Use RTI? Nationally 30% of students do not graduate on time. Every year 1.3 million students do not graduate with their peers. That means every school day we lose 7,000 students. 68% of high school students graduate unprepared for college and 53% of college students enroll in remedial level courses. 19 Reason To Use RTI A national survey of school psychologists found that 75% of respondents endorsed RTI as a better method for identifying a reading disability. RTI can be used to identify students with learning disabilities (SLD) for special education services. RTI focuses on all students. Serves as an early intervention system. Uses data to drive decision making and teacher instruction. Limits overrepresentation in special education. 20 Speaking the Language How did the Lesson Design aid in the master of the objective? 21 The RTI Pyramid H3 The RTI Pyramid shows each tier, or level, of RTI. All students start in Tier 1. After receiving the Universal Screener, students either stay in Tier 1 or move to Tier 2 based on the findings of the universal screener. RTI Activity Your envelope contains the steps of the RTI process From your understanding of RTI put the steps in order Which steps do you feel you would need the most support in? Which steps do you feel you would need the most support in? 24 Implementation of RTI Create/Update the master schedule to reflect the dates for the universal screener, benchmarks, and other tests. Conduct screeners/benchmarks. Collect and interpret universal screener data. Group/tier students according to the data. Develop a monthly schedule for interventions for each tier. Identify research-based interventions to use to support students. Meet with Tier 2 students to give small group interventions. Progress monitor to determine the effectiveness of the intervention/instruction. Report findings to the RTI team. Brown-Chidsey, R. & Steege, M.W. (2011). Response to intervention: Principles and strategies for effective practice 2nd edition. 25 There are levels to this.. • All students receive tier 1 support • Evidence-based differentiated instruction in the general classroom setting • Guided by progress monitoring (benchmarks) • Implemented for minimum of 4 weeks Tier 1 Tier 2 ● Students experiencing academic and/or behavioral difficulties • Identified through progress monitoring data • Instruction that uses established intervention protocols (evidence-based, data driven) • Frequent progress monitoring • Tier 1 strategies continue • Implemented for minimum of 6 weeks • Students participating in the Student Support Team • Individualized assessment and interventions • More frequent progress monitoring • Tier 1 strategies continue • Time/intensity of supplemental instruction at Tier 2 increases • Implemented for a minimum of 8 weeks Tier 3 26 Scheduling After the universal screener, put your bottom 10% of students in Tier 2 Deliver Tier 1 and Tier 2 Interventions for 4 weeks before adjusting the intervention. Support your Tier 1 and Tier 2 students according to your schedule Progress monitor these students to determine the effectiveness of the intervention/instruction After collecting 8 data points, determine placement with the RTI team 27 RTI Support Using Differentiation vs. Using Evidence-Based Interventions Differentiation • Use of student centers: homogeneous/heterogeneous • Lessons planned for delivering instruction designed to meet individual student learning needs. • Multiple resources provided for instruction • Students are assessed in multiple ways • Multiple student learning styles are evident. Evidence-Based Interventions • Ongoing assessments and diagnostic tools given to determine learner needs. • Supported by expert opinion as appropriate for remediation of a deficit area. • Targeted assistance based on progress monitoring • Matches curricular materials and instructional level. • Delivered by a classroom teacher, interventionist, or other specialized teacher. • Delivered in a small group or intensive one on one segment. 28 Activity: Classroom Observation Video: 10 min, 56 sec. Answer questionnaire: 10 min. 5 minutes to share with a peer. 29 Modeling: Evidence-Based Interventions Reading Intervention: Paired Reading Activity (Tier 1 or 2) Organizational Intervention: Chunking (Tier 1, 2, or 3) 15 minutes Math Intervention: Number Talk (Tier 1) 30 Teacher Accountability Data Talks Progress Monitoring Delivery of Interventions Lesson Plans Common Assessments/ Planning Fidelity of Interventions Communication with the RTI Team Formative and Summative Assessments Data Wall 31 BRINGING IT ALL TOGETHER Next Steps: Teachers Put your students into homogeneous groups. Develop differentiated student centers for each group. Implement one strategy you plan to use to support their Tier 2 students. Begin having a common planning and creating common assessments. 33 Feedback Please complete the feedback forms before you leave. 34 BRENT JOHNSON BJOHNSON@NAEPARTNERS.ORG Activity: Case Study Tiering 5 minutes Review the sample STAR Math and STAR Reading reports Highlight the bottom 10% according to the data. Place the students into Tier 1 and Tier 2 groups based on the data. 36