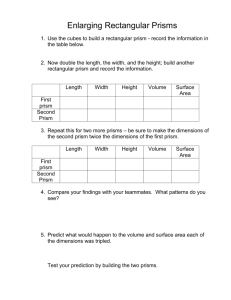
12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples Prisms Go to Surface Area or Volume . A prism is a solid object with: identical ends flat faces and the same cross section all along its length ! A cross section is the shape made by cutting straight across an object. The cross section of this object is a triangle ... .. it has the same cross section all along its length ... ... so it's a triangular prism. ▶ © 2015 MathsIsFun.com v0.77 Try drawing a shape on a piece of paper (using straight lines) https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 1/8 12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples Then imagine it extending up from the sheet of paper ... ... that's a prism ! No Curves! A prism is a polyhedron , which means all faces are flat! No curved sides. For example, a cylinder is not a prism, because it has curved sides. Bases Bases The ends of a prism are parallel and each one is called a base. Parallel Sides Parall el The side faces of a prism are parallelograms https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 2/8 12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples (4-sided shapes with opposite sides parallel) These are all Prisms: Square Prism: Cross-Section: Cube: Cross-Section: (yes, a cube is a prism, because it is a square all along its length) (Also see Rectangular Prisms ) Triangular Prism: Cross-Section: Pentagonal Prism: Cross-Section: https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 3/8 12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples and more! Example: This hexagonal ice crystal. It looks like a hexagon, but because it has some thickness it is actually a hexagonal prism! Photograph by NASA / Alexey Kljatov. Regular vs Irregular Prisms All the previous examples are Regular Prisms, because the cross section is regular (in other words it is a shape with equal edge lengths, and equal angles.) Here is an example of an Irregular Prism: Irregular Pentagonal Prism: Cross-Section It is "irregular" because the cross-section is not "regular" in shape. Right vs Oblique Prism When the two ends are perfectly aligned it is a Right Prism otherwise it is an Oblique Prism: https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 4/8 12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples Right Oblique Surface Area of a Prism Surface Area = Length 2 × Base Area + Base Perimeter × Length Area of Base Perimeter of Base Example: What is the surface area of a prism where the base area is 25 m2, the base perimeter is 24 m, and the length is 12 m: Surface Area = 2 × Base Area + Base Perimeter × Length = 2 × 25 m2 + 24 m × 12 m = 50 m2 + 288 m2 = 338 m2 (Note: we have an Area Calculation Tool ) https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 5/8 12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples Volume of a Prism The Volume of a prism is the area of one end times the length of the prism. Volume = Base Area × Length Example: What is the volume of a prism where the Length Area of Base base area is 25 m2 and which is 12 m long: Volume = Area × Length Perimeter of Base = 25 m2 × 12 m = 300 m3 Play with it here. The formula also works when it "leans over" (oblique) but remember that the height is at right angles to the base: Oblique Prism Volume = 8 × 7.2 × 15 ≈ 864 © 2018 MathsIsFun.com v0.622 And this is why: https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 6/8 12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples The stack can lean over, but still has the same volume More About The Side Faces The side faces of a prism are parallelograms (4-sided shape with opposites sides parallel) A prism can lean to one side, making it an oblique prism, but the two ends are still parallel, and the side faces are still parallelograms! But if the two ends are not parallel it is not a prism. Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 Question 9 Question 10 https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 7/8 12/18/2019 Prisms with Examples Copyright © 2017 MathsIsFun.com https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prisms.html 8/8