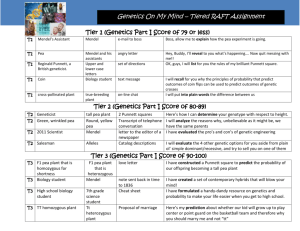
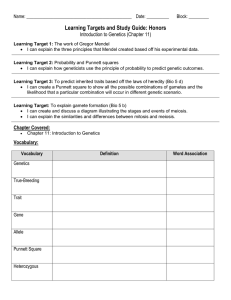
Cornell Notes Name: ___________________________________ Class: _________________ Period: ________ Topic: Genetics Date: ____________________________ Essential Question: Who is the Father of Genetics and what was his contribution to the understanding of genetics? Questions/Main Ideas: Who is Gregor Mendel? Notes: _____________________ was an Austrian monk born in 1822. His parents were peasants with a background in agriculture. Mendel was an expert botanist. Called “The Father of Genetics” because he was one of the first to study ____________of____________________________. What did Mendel study? Mendel used ________ ________________ to perform his studies. He kept ____________ ________________ of his pea plants among many______________________. Using_________________, he was able to predict the outcome of his experiments. New and exciting _______________were established! Why peas? 1. The male and female parts of the pea plant are enclosed inside the same flower, so it is easy to _________________ ________________. 2. The peas are easy to grow, and they grow___________. They also produce lots of_______________. 3. Each character of garden peas comes in 2 clearly ______________ ____________. For example, they either have purple or white flowers, or their stems are either long or short. Which characteristics did he study? Mendel studied the following pea characteristics: 1.flower __________2. flower ___________3. ___________color 4. seed_________ 5. __________ shape 6. pod _______7. stem length Mendel’s Experiments The P generation consists of the first two true-bred individuals that are crossed. The P stands for Parental. The offspring of the P generation is called the______ ____________. F stands for filial, which means “son” or “daughter”. Mendel's experiments allowed the F1 generation to________________________________ which creates the_______ _________________, or the second filial generation. In the F1 generation all white flowers had disappeared, but in the F2 generation, some had come back! The ratio seen in the F2 generation was 3:1, 3 purple flowers for each white flower. Who is Reginald Punnett? Mr. Punnett (1875-1967) attended the University of Cambridge and earned a degree in zoology. Afterwards he worked at the University as an assistant studying livestock. Farmers already knew that when they bred two animals, the offspring received characteristics from each parent (though they did not know of genes nor DNA). However, Punnett was determined to prove that ___________________________________________ among livestock. He charted out experiments using what he called a__________________. In pea plants, round peas are dominant and wrinkled peas are recessive. Using the steps, cross a plant heterozygous for pea shape and a homozygous dominant pea plant. Step 1) Determine the parental cross: ______ x _______ Step 2) Set up Punnett square with parental crosses (outside the box). Step 3) Fill in the Punnett Square to determine genotypes among offspring (inside the box). Step 4) Determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios among offspring. GENOTYPIC RATIO _____% are homozygous dominant _____% are heterozygous PHENOTYPIC RATIO _____% are round Summary: