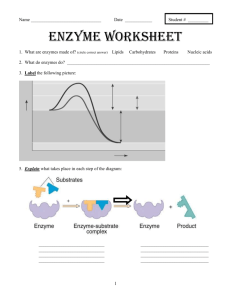
Fungal Protease Isolation & Characterization: A Research Study
advertisement
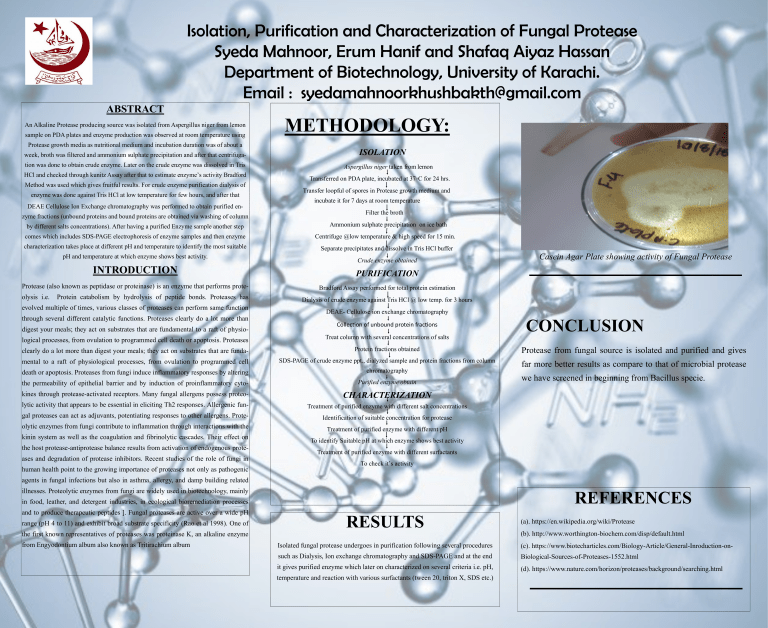
Isolation, Purification and Characterization of Fungal Protease Syeda Mahnoor, Erum Hanif and Shafaq Aiyaz Hassan Department of Biotechnology, University of Karachi. Email : syedamahnoorkhushbakth@gmail.com ABSTRACT An Alkaline Protease producing source was isolated from Aspergillus niger from lemon sample on PDA plates and enzyme production was observed at room temperature using Protease growth media as nutritional medium and incubation duration was of about a week, broth was filtered and ammonium sulphate precipitation and after that centrifugation was done to obtain crude enzyme. Later on the crude enzyme was dissolved in Tris HCl and checked through kunitz Assay after that to estimate enzyme’s activity Bradford Method was used which gives fruitful results. For crude enzyme purification dialysis of enzyme was done against Tris HCl at low temperature for few hours, and after that DEAE Cellulose Ion Exchange chromatography was performed to obtain purified enzyme fractions (unbound proteins and bound proteins are obtained via washing of column by different salts concentrations). After having a purified Enzyme sample another step METHODOLOGY: ISOLATION Aspergillus niger taken from lemon Transferred on PDA plate, incubated at 37◦C for 24 hrs. Transfer loopful of spores in Protease growth medium and incubate it for 7 days at room temperature Filter the broth Ammonium sulphate precipitation on ice bath comes which includes SDS-PAGE electrophoresis of enzyme samples and then enzyme Centrifuge @low temperature & high speed for 15 min. characterization takes place at different pH and temperature to identify the most suitable Separate precipitates and dissolve in Tris HCl buffer pH and temperature at which enzyme shows best activity. Crude enzyme obtained INTRODUCTION PURIFICATION Protease (also known as peptidase or proteinase) is an enzyme that performs prote- Bradford Assay performed for total protein estimation olysis i.e. Protein catabolism by hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Proteases has evolved multiple of times, various classes of proteases can perform same function through several different catalytic functions. Proteases clearly do a lot more than digest your meals; they act on substrates that are fundamental to a raft of physio- Casein Agar Plate showing activity of Fungal Protease Dialysis of crude enzyme against Tris HCl @ low temp. for 3 hours DEAE- Cellulose ion exchange chromatography Collection of unbound protein fractions CONCLUSION logical processes, from ovulation to programmed cell death or apoptosis. Proteases Treat column with several concentrations of salts clearly do a lot more than digest your meals; they act on substrates that are funda- Protein fractions obtained Protease from fungal source is isolated and purified and gives mental to a raft of physiological processes, from ovulation to programmed cell SDS-PAGE of crude enzyme ppt., dialyzed sample and protein fractions from column death or apoptosis. Proteases from fungi induce inflammatory responses by altering chromatography far more better results as compare to that of microbial protease the permeability of epithelial barrier and by induction of proinflammatory cyto- Purified enzyme obtain kines through protease-activated receptors. Many fungal allergens possess proteo- CHARACTERIZATION lytic activity that appears to be essential in eliciting Th2 responses. Allergenic fun- Treatment of purified enzyme with different salt concentrations gal proteases can act as adjuvants, potentiating responses to other allergens. Prote- Identification of suitable concentration for protease olytic enzymes from fungi contribute to inflammation through interactions with the Treatment of purified enzyme with different pH kinin system as well as the coagulation and fibrinolytic cascades. Their effect on the host protease-antiprotease balance results from activation of endogenous proteases and degradation of protease inhibitors. Recent studies of the role of fungi in human health point to the growing importance of proteases not only as pathogenic we have screened in beginning from Bacillus specie. To identify Suitable pH at which enzyme shows best activity Treatment of purified enzyme with different surfactants To check it’s activity agents in fungal infections but also in asthma, allergy, and damp building related illnesses. Proteolytic enzymes from fungi are widely used in biotechnology, mainly REFERENCES in food, leather, and detergent industries, in ecological bioremediation processes and to produce therapeutic peptides ]. Fungal proteases are active over a wide pH range (pH 4 to 11) and exhibit broad substrate specificity (Rao et al 1998). One of the first known representatives of proteases was proteinase K, an alkaline enzyme from Engyodontium album also known as Tritirachium album RESULTS (a). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protease (b). http://www.worthington-biochem.com/disp/default.html Isolated fungal protease undergoes in purification following several procedures (c). https://www.biotecharticles.com/Biology-Article/General-Inroduction-on- such as Dialysis, Ion exchange chromatography and SDS-PAGE and at the end Biological-Sources-of-Proteases-1552.html it gives purified enzyme which later on characterized on several criteria i.e. pH, (d). https://www.nature.com/horizon/proteases/background/searching.html temperature and reaction with various surfactants (tween 20, triton X, SDS etc.)