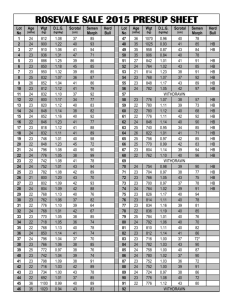
Breeding Soundness Evaluation (BSE) • BSE is an attempt to measure the bull’s potential to cause conception. • The BSE aims to identify bulls which are satisfactory (not necessarily those which are superior) • Through BSE fertility of bull can not be estimated • Fertility is a complex trait which is influenced by both male and female traits as well as by extraneous factors(e.g. nutrition, environment, disease etc). • The BSE is a relatively quick and simple screening procedure which does not comprehensively assess all aspects of male fertility Significance • BSE is a relatively quick and economic procedure for screening bulls prior to sale or use. • Its objective is to establish a baseline, above which bulls could be regarded as satisfactory potential breeders. • It is simple, repeatable and unambiguous test to judge the breeding capacity male animal. • However, the BSE should not substitute for professional judgment or common sense. • In the BSE, bulls are placed into the categories of satisfactory, unsatisfactory and deferred. • The process is most effective in identifying bulls at the lower end of the potential fertility spectrum. Procedure BSE • 1. Physical examination. • 2. Reproductive examination (including measurement of scrotal circumference). • 3. Collection and examination of semen. • 4. Libido/serving capacity test. Physical exam • Physical health • General body condition, teeth, eyes, etc. • Medical history : vaccination, previous health etc. • Managemental history: feed, housing, previous use Physical Exam Skin Physical Exam Permanent ID Physical Exam Permanent ID Physical Exam Eyes Physical Exam Eyes Physical Exam Teeth Musculoskeletal disease • Joints • Laminitis • Scars around coronary band • Interdigital growths • Footrot • Hoof Cracks Interdigital Fibroma Rear Limb conformation Locomotion--Critical. Sickle Hocked Cow Hocked Post Legged Crooked Legs/Feet Rear Limbs confirmation • Libido & mating ability are directly related to leg problems. • Relationship of hip joint with stifle, hock and pastern joints • from side (Post legged, Camped behind & Sickle hock) • from behind (Bow leggedness or base narrow & Toed-out stance or base wide) Post legs Examination of Underline External Exam of Penis & Prepuce • Incomplete Extension • Frenulum • Hair Rings • Fibropapillomas (Warts) • Prolapse of Prepuce • Lacerations • Adhesions Prepuce and sheeth Eversion, adhesions and pendulous Penis • • • • • • Ventral or lateral deviation Injury cockscrew penis adhesions persistent penile frenulum tumors Penile Hair Ring Persistent Frenulum Penile Fibropapilloma Secrotum/Tesits • Scrotum/Testis = Testis held too close to the body, unilateral hypoplasia, scrotal hernia, • incomplete descent of testis (cryptorchidism-bilateral or unilateral also called minorchidism), testicular degeneration & rotation of tesis > 40 • Normal conformation of scrotum = elongated, rounded, rotation ≤ 40 with distinct cleavage • Epididymis = Hypoplasia, aplasia, Inflammation, tumour, abscess & spermatic granuloma Visual Exam of Scrotum • Scrotal Conformation • Evidence of Injury • Skin Lesions Palpation of Scrotum • Ensure there are two testes • Free & Moveable • Tone • Symmetry • Epididymis Atrophied Left Testicle Scrotal Circumference • Indicates Fertility & Puberty • Ensure Both Testicles are In Scrotum • Cradle Scrotal Neck • Place Tape at Largest Diameter • Pull until Skin Indents Scrotal Circumference Tape Proper Tape Placement Incorrect Hand Placement • • • • • • • • • • • • • Scrotal circumference (SC) It is indicative of semen quality, quantity and pathological lesions Bulls with < 30 cm SC should not be used for breeding. Holstein-Friesian bulls = Sc is 32-36 cm at 1 year of age and it may exceed 40 cm at the age pf 2 -3 years in excellent cases. Buffalo bulls = SC is 27, 28, 29, 29, 30 and 34 cm at the age of 2-3, 3-4, 4-5, 5-6, 6-7 and 7-8 years, respectively. ↑ SC of bull = early puberty in daughters ↓ SC of bull = delayed puberty, irregular estrous cycles and delayed conception in daughters Pathological lesions of small testis = Testicular hypoplasia & testicular degeneration Pathological lesions of large testis = Obstructive lesions in the head of epididymis and Orchitis Society for Theriogenology Semen evaluation • Motility • Viability • Concentration • Plasma membrane integrity • Acrosome integrity • Morphological abnormalities • DNA integrity Libido testing • Reaction time • Length of time taken for a bull to respond/mount to a given stimulus (exposed to cow in estrus or dummy) For further reading • https://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/animals-and-livestock/beefcattle/breeding/bull-selection/structural-soundness