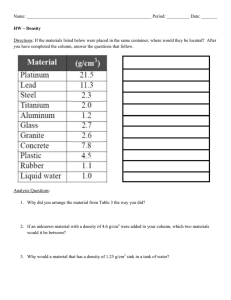
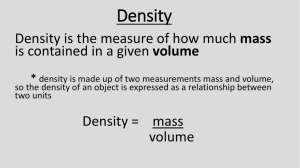DENSITY There are three phases of matter: solid liquid gas Density – how close together the molecules are Solids Molecules close together Liquids Molecules spread out further Gas Molecules spread far apart To determine density, you must divide the mass by the volume. Density = mass volume Mass is measured in grams using a triple beam balance… or a digital scale. We can determine the mass of the box using the digital scale. 750 g Some units for mass…. • grams (g) • kilograms (kg) • milligrams (mg) ….and conversion factors • 1000 g = 1 kg • 1000 mg = 1 g • 1 000 000 mg = 1 kg Volume of a regularly-shaped object can be measured using a ruler. Some units for volume…. • cubic centimeter (cm3) • milliliter (mL) • liter (L) ….and conversion factors • 1 cm3 = 1 mL • 1000 mL = 1 L If the object has smooth sides where a ruler can be used to measure the length, width, and height, it is considered regular-shaped. Volume = length x width x height 2 cm 5 cm 15 cm V=lxwxh V = 15 cm X 5 cm X 2 cm V = 150 3 cm Density = mass Volume m D V Density = mass Volume 750 g D 150 cm3 Density = mass Volume 750 g 5 g/cm3 150 cm3 Determine the volume of the cube. 3 cm V=lxwxh V = 3 cm X 3 cm X 3 cm V = 27 3 cm A piece of silver has a mass of 2800 grams and occupies a volume of 266 cm3. What is the density of silver? If a block of copper measures 2.00 cm x 4.00 cm x 5.00 cm and its mass is 356 grams, what is its density? Volume of a liquid is measured in mL using a graduated cylinder, beaker, or flask. Objects that do not have smooth sides to measure are called irregular-shaped. To measure the volume of these objects we use water displacement. Water is put into a graduated cylinder and the volume of the water is measured. 50 40 30 20 10 The object is placed in the graduated cylinder. 50 40 30 The volume of the water and the object is determined. 20 10 The first volume is subtracted from the second volume. 40 mL – 29 mL = 11 mL The volume of the object is 11mL. Density does not depend on the amount of the substance (intensive property). The density of the block is 16 g/cm3 If it is cut in half, what happens to the density? Density of block is 16 g/cm3 Density of block is 16 g/cm3 Buoyancy is the upward force of a fluid on an object. Another example of buoyancy is a hot air balloon. The air, a fluid, buoys the balloon. Some organisms use buoyancy to move. An example is the jellyfish. The density of water is 1g/mL. If an object with a density of less than 1g/mL is placed in the water, it will float. If an object with a density of greater than 1g/mL is placed in the water, it will sink. The density of the liquid determines if the material placed in it will float or sink. We can make a density column to demonstrate the different densities of materials. DENSITY Alcohol Oil Water COLUMN Can you give an estimation of the density of the alcohol and the oil? Density = 1g/mL DENSITY COLUMN Alcohol Oil Water Density = 1g/mL The density of the oil is less than 1 g/mL. The density of the alcohol is less than the density of the oil. DENSITY COLUMN Alcohol Density = .75 g/mL Oil Density = .96 g/mL Water Estimate the density of the piece of wood. The density Density = 1g/mL of wood is .8 g/cm3. DENSITY COLUMN Alcohol Density = .75 g/mL Oil Density = .96 g/mL Water Estimate the density of the piece of ice. The density Density = 1g/mLof ice is .9 g/cm3. Fluids can flow, but not all fluids flow quickly. Viscosity is defined as the resistance to flow. Some fluids move slowly. They have a high viscosity. Syrup pours slowly. It is very viscous. Glue is also viscous. Some fluids move quickly. They have a low viscosity. Water pours quickly. It is less viscous. We can compare viscosity by putting a drop of three different fluids on a board and then tilting the board. 1 2 3 Fluid #1 was the least viscous. Why? Which fluid was the most viscous? How could you tell? Being less viscous has its advantages!