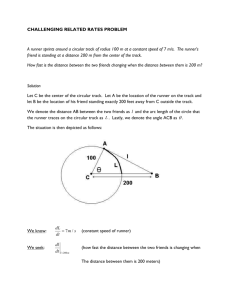
___________ ___________ ___________ __________ _____________ __________ _____________ ____________________ ____________________ HEAT FLOW THERMAL ENERGY Heat flows from _______ to _______. Thermal Energy is ____ dependent on _____________; it is _____________ on the number of _____________ in the substance. _______ / _______ ___________________ Help! _______ / _______ ______________ _______________ NOTE: the cup has a ________ temperature & higher __________ _________; however, it has _____ particles, so its thermal energy is _______! _______________ __________ __________ __________ FREEZING MELTING EVAPORATION VOCABULARY Heat: _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ Temperature: ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Thermal Energy: ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Sublime: __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Deposition: ________________________________________________________________________________________________ Melting: ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ Melting Point: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Freezing: __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Evaporation: _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Boiling Point: ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Condensation: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ GRAPHING DISTANCE (meters) KEY Runner 1 Runner 2 Graphing Basics: • • • Highlight the “x-axis” in pink Highlight the “y-axis” in blue Circle any points in which one runner passed the other runner (Hint: this is where the two runners “paths” cross) TIME (seconds) Graphing Interpretation: • What distance did Runner 1 start at?: ________________________ • What distance did Runner 2 start at?: ________________________ • What distance did Runner 1 end at?: ________________________ • What distance did Runner 2 end at?: ________________________ • Which runner stopped the furthest distance from the starting line?: ________________________ (Hint: the starting point is always zero) • Which runner had the biggest head start?: ________________________ • How much of a head start did that runner have? ________________________ • Which runner ran the most milage? ________________________ SOLID LIQUID HIGHER ATTRACTION GAS INCREASES DECREASES LOWER ATTRACTION TEMPERATURE DECREASES INCREASES KINETIC ENERGY HEAT FLOW Heat flows from HOT to COLD. THERMAL ENERGY Thermal Energy is NOT dependent on TEMPERATURE; it is DEPENDENT on the number of PARTICLES in the substance. HIGH / HOT Help! CUP OF HOT WATER NOTE: the cup has a higher temperature & higher kinetic energy; however, it has less particles, so its thermal energy is less! LOW / COLD ICEBERG MELTING POINT BOILING POINT SOLID LIQUID GAS FREEZING MELTING EVAPORATION VOCABULARY Heat: thermal energy transferred from a warmer object to a cooler one Temperature: a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance Thermal Energy: the total energy related to the motion of the atoms and molecules in an object or sample of matter Sublime: to change state from a solid to a gas Deposition: to change state from a gas to a solid Melting: to change state from a solid to a liquid Melting Point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid as thermal energy is added to it Freezing: to change state from a liquid to a solid Evaporation: to change state from a liquid to a gas at the surface of the liquid Boiling Point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas as thermal energy is added to it Condensation: to change state from a gas to a liquid GRAPHING DISTANCE (meters) KEY Runner 1 Runner 2 Graphing Basics: • • • Highlight the “x-axis” in pink Highlight the “y-axis” in blue Circle any points in which one runner passed the other runner (Hint: this is where the two runners “paths” cross) TIME (seconds) Graphing Interpretation: • What distance did Runner 1 start at?: 25 meters • What distance did Runner 2 start at?: 23 meters • What distance did Runner 1 end at?: 42 meters • What distance did Runner 2 end at?: 41 meters • Which runner stopped the furthest distance from the starting line?: Runner 1 (Hint: the starting point is always zero) • Which runner had the biggest head start?: Runner 1 • How much of a head start did that runner have? 25 meters • Which runner ran the most milage? Runner 2 (R1: 17 meters, R2: 18 meters)