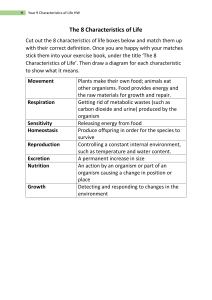
Do Now:List some processes that every living organism must do in order to survive r o w t h u t r i t i o n e p r o d u c t i o n e g u l a t i o n e s p i r a t i o n x c r e t i o n y n t h e s i s r a n s p o r t Process by which organisms increase in size and/or number of cells. ◦ One cell organism: Increases in the size of a single cell ◦ Multicellular organism: Increases in size and number of cells, accompanied by specialization or differentiation How an organism takes in nutrients from its environment and changes them into usable forms. These nutrients are used for growth, repair, energy, and maintenance. 2 types of nutrition: 1. Autotroph 2. Heterotroph 1. Autotrophic: CAN make its own food ◦ By photosynthesis ◦ 2. Water + Carbon Dioxide + light energy Glucose + Oxygen Heterotrophic: CANNOT make their own food. ◦ They must find it in their environment. ◦ Processes involved: 1. Ingestion: taking in food 2. Digestion: breaking down food 3. Egestion: elimination of indigestible food Cellular respiration: the release of stored chemical energy from food (nutrients). Energy produced is used for life processes. ◦ 2 types: 1. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen (O2) 2. Anaerobic respiration does NOT require O2 How an organism maintains a stable internal environment as the external environment constantly changes. Involves the coordination of various activities of an organism. 2 systems are involved: 1. Nervous system: carries electric impulses (messages) throughout the body by nerves 2. Endocrine system: carries liquid hormones (messages) through the blood. When an organism produces organisms of its own kind. **Necessary for survival of the species, NOT the individual** 2 types: 1. Asexual: only requires 1 parent. Offspring identical to parent 2. Sexual: requires 2 parents. Offspring not identical to either parent. Results in variation (key ingredient for evolution) Removal of metabolic waste products produced by an organism. If wastes accumulate, it can be harmful. ◦ “Building” or “to make bigger” ◦ Combining simple substances chemically to form a more complex substance ◦ This allows the organisms to replace or repair worn out parts and grow Delivery system Involves absorption (taking in) and __________________(circulation ) of nutrients. ◦ Simple organisms: materials enter the cell(s) directly from their environment ◦ Multicellular organisms: a circulatory system is needed. It transports materials to, and wastes away from the cells of the organisms. Example: blood METABOLISM: The sum of all chemical reactions (all 8 life functions) in an organism HOMEOSTASIS: Condition of maintaining a stable internal environment. Ex: regulating body temperature Smallest: Organelle…….. (nucleus) Cell…………….. (1 heart cell) Tissue…………. (50 heart cells) Organ…………. (the heart) Organ System…(the circulatory system) Largest: Organism……… (a human)