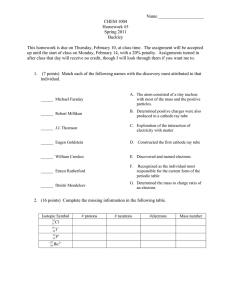
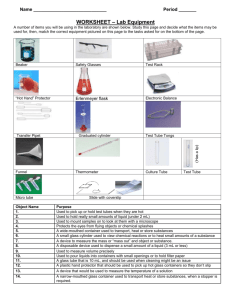
Electrolysis Introduction: Electrolysis is the electro-chemical process in which an electric current is passed between two electrodes through an ionized solution (electrolyte) to deposit positive ions (anions) on the negative electrode (cathode) and negative ions (cations) on the positive electrode (anode) that is a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from naturally occurring sources such as ores. It also plays a major role in the purification of metals and decomposition of compounds like water, as well as to obtain elements that are too chemically reactive to be found free in nature. Materials and Equipment: (good for 1 setup) 1 small container (plastic cup) tap water (at least 500 ml) vinegar (enough to fill 1 container) 25 grams of rock salt 2 pcs. of thumbtacks 1 pc. 9-volt battery matchstick 2 test tubes rubber bands stirring rod Procedure: 1. Prepare the remaining equipment required for the experiment. Make sure that the containers are clean and dry before use and being filled by fluids. 2. On your plastic container, insert 2 thumbtacks with relative length from each other unto the container. Ensure that the water won’t leak out at the bottom. 3. Fill the plastic container with ¾ water and ¼ vinegar with 25 grams of rock salt. Ensure before filling the container, the solution is properly stirred and mixed. 4. Using the rubber band and test tube, ensure a setup of which the position of the test tube filled with water on top of the thumbtacks is in properly placed while the reaction is taking place. 5. Connect the battery into the thumbtacks (Determine the anode and the cathode.) 6. For each process, take a step by step documentation. Observe the amount of gas formed in the reaction from the anode and cathode. Take time. 7. After a few minutes or until one test tube is filled with gas. Take the setup, disconnect the battery and light up both test tube without releasing the gas inside with the matchstick and observe what happened to the anode test tube and cathode test tube. Result and Discussion: Data Analysis: 1. Write a balanced reaction for each of the experiment including the combustion inside the test tube. 2. Why does more gas form in one test tube than in the other? 3. What should the ratio of hydrogen gas volume be to oxygen gas volume? 4. How many mL of gas did you actually collect? Hydrogen? Oxygen? Does this volume match your ratio? 5. Which gas was in the tube with the positive and which gas was in the tube with the negative? How do you know which was Hydrogen and which was oxygen? 6. How could this be used in a real world application? Research this topic of water electrolysis and see if there are any real world applications to the decomposition of water.