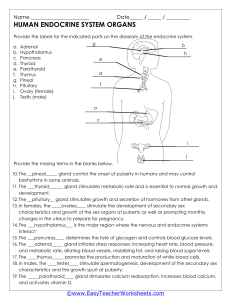
2.7.2015 Histology of the Endocrine Glands Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy, KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction • Endocrine tissue is made up of cells that produce secretions which are poured directly into blood. • Endocrine cells lie in close apposition to blood capillaries or sinusoids. • Secretions of endocrine cells are called hormones. • Hormones travel through blood to target cells and influence their function. The Endocrine Glands (Ductless glands) • Pituitary (hypophysis) – Anterior pituitary – Posterior pituitary • Adrenal gland (suprarenal) – Adrenal cortex – Adrenal medulla • Thyroid gland – Follicles – Parafollicular cells • Parathyroid gland The Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) a The Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) • “Master endocrine gland”. • Parts: Adenohypophysis (Anterior Pituitary): consist of pars distalis, pars intermedia & pars tuberalis. Neurohypophysis (Posterior Pituitary): consist of pars nervosa, infundibular stalk & median eminence. Adenohypophysis Pars Distalis: • Cells are arranged as irregular cords in between thin-walled fenestrated sinusoids. • Consists of 2 major group of cells: chromophils & chromophobes. • Chromophils are of 2 types: basophils & acidophils. Pars Intermedia: • • • • Poorly developed in humans. Consists mainly of basophils. Presence of colloid filled vesicles. Some cells produce melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH). Pars Tuberalis: • Consists of chromophilic (mostly basophilic) & chromophobic cells. Neurohypophysis Consists of: • Numerous non-myelinated nerve fibres • Supporting cells (pituicytes) • Sinusoids Produce 2 hormones: • Oxytocin • Vasopressin Herring bodies: collection of secretory granules at the terminal portion of axonal processing. Posterior Pituitary Hypophysis (Mallory-Azan & orange G. stain) Cells and hormones of the anterior pituitary LM staining Cell type Acidophil Somatotrophs Hormone Releasing (+) or inhibiting (-) horm. Growth hormone (GH) = somatotropin GHRH (+) Somatostatin (-) Acidophil Mammotrophs Prolactin (PRL) = lactotrophs [Dopamine (-) estrogen (+)] Basophil Thyrotrophs TRH (+) Basophil Gonadotrophs Luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH); both = gonadotropin Basophil (human) Corticotrophs Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) = thyrotropin GnRH (+) Adrenocorticotropin CRH (+) (ACTH) = corticotropin Hypophysis (H&E stain) Pars distalis (Azan stain) Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary (trichrome stain) Anterior pituitary (H&E stain) Basophil Posterior Pituitary • Hormones – Antidiuretic hormone (ADH = arginine vasopressin) – Oxytocin • Neurosecretion – Hormones synthesized as part of larger proteins (neurophysins) in neuron cell bodies of hypothalamus. – Transported in axons to pars nervosa (hormone cleaved from neurophysin). – Hormone secreted from axon terminals into capillaries. • Pituicytes – Specialized glia of pars nervosa. Pars intermedia, between anterior and posterior pituitary Anterior Posterior (Poorly developed and of doubtful function in humans) Intermedia Rathke's pouch Pars intermedia (rat pituitary) THYROID GLAND Microscopic structure • The gland is surrounded by a thin fibrous capsule. • Septa from the capsule extend into the gland & divide it into lobules. • Lobules are made up of spherical masses called follicles. • Follicle has a cavity filled with homogenous material called colloid. • Follicular cells are normally cuboidal in shape. • Secrete 2 hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) & tetraiodothyronine (T4) or thyroxine. Microscopic structure (contd…..) Parafollicular cells (C-cells): • Embedded within a follicle or lie between follicles. • Singly or in groups. • Cells are polyhedral with oval eccentric nucleus and cytoplasm contains secretory granules. • Light staining cells. • Secrete hormone calcitonin. Parathyroid Gland • Small ovoid bodies (4 in no.) embedded in the connective tissue capsule on the posterior surface of thyroid gland. • Consists of 2 types of cells: Chief cells (principal cells): more numerous, polygonal, round centrally located nucleus & mildly eosinophilic cytoplasm, secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH). Oxyphil cells: larger in shape, deep acidophilic cytoplasm. Parathyroid Gland (H&E stain) Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland) Microscopic structure (low power) • The gland is covered by connective tissue capsule. capsule cortex • Capsule sends septa inside the gland. • 2 parts: Cortex Medulla medulla Microscopic structure (low power) Zona glomerulosa Cortex Zona fasciculata Zona reticularis Medulla Mineralocorticoid (aldosterone) Glucocorticoids (cortisol) Androgen (dehydroepiandrosterone) & Estrogen Catecholamines (epinephrine & norepinephrine) Adrenal Cortex 3 layers: • Zona Glomerulosa: cells are arranged as rounded clusters separated by thin connective tissue. Cells are columnar with dark staining nuclei and acidophilic cytoplasm. • Zona Fasciculata: thick zone, large pale staining polyhedral cells arranged into parallel columns 1-2 cell thick. • Zona Reticularis: small rounded deep staining cells arranged in branching & anastomosing cords. Adrenal Medulla • Cells are large, epitheloid & arranged in groups. • Cells are closely related to sinusoidal capillaries. • Cytoplasm is light basophilic with H&E stain. • Chromaffin reaction: Tissue fixation with potassium bichromate shows fine brown granules in the cells of medulla. Capsule Cortex Medulla References 1. diFiore’s Atlas of Histology with functional Correlations, 12th Edition. 2. Textbook of Human Histology. Inderbir Singh, 1st Edition. 3. Textbook of Histology. GP Pal, 3rd Edition. MCQ Q1. The supportive cells in pars nervosa are known as: a. Chromophils b. Chromophobes c. Herring bodies d. Pituicytes MCQ Q2. Parafollicular cells is a specific feature of: a. Pituitary b. Thyroid c. Parathyroid d. Suprarenal MCQ Q3. The epithelial lining of thyroid follicles in resting phase is: a. b. c. d. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Transitional MCQ Q4. Increased amount of lipid droplets are found in cells of which zone of adrenal gland? a. Zona glomerulosa b. Zona fasciculata c. Zona reticularis d. All of the above MCQ Q5. Chromaffin reaction is depicted by which endocrine gland? a. Pituitary b. Thyroid c. Parathyroid d. Suprarenal



![Histology of the Endocrine Glands [PPT]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009540792_1-dcb524b76ce5a611a6272fa9c8392dd4-300x300.png)