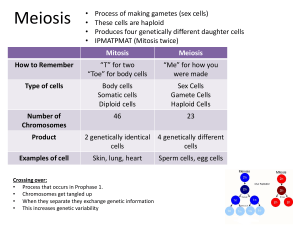
1st Quarter Final Study Guide 1. What is the purpose of mitosis? 2. What is mitosis NOT used for? 3. After which stage does cytokinesis occur? 4. What type of cells result after meiosis? 5. What number of chromosomes will result after mitosis? 6. What number of chromosomes result after meiosis? 7. What type of cell undergo meiosis? 8. What is the cell called after meiosis creates it? 9. If a gamete mother cell contains 6 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will a normal body cell contain? 10. Asexually reproducing organisms produce offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parents. What type of cell division are the offspring a product of? 11. Which type of cells would be more similar to each other a body cell or gamete cell? 12. What are the nitrogen bases in a DNA molecule and how do they pair with each other? 13. Which scientists are credited with discovering the physical structure of DNA? 14. What does phenotype refer to? 15. What does genotype refer to? 16. If a plant that has a purple flower has a parent that has a white flower, what is its genotype? (assume that purple is dominant) 17. Who is the Father of Genetics? 18. What is another name for traits affected by the environment or are a result of learning or training? 19. The allele that masks the effects of the other is ________________________ and the masked allele is _______________________________ 20. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross is called a ? 21. What would be the results of a genetic cross between parents that have TT and Tt? 22. If the results of a genetic cross were BB, BB, Bb, bb what would be the probability of getting a homozygous tall? Note that T is dominant (tall) and t is recessive (short) answer in percents 23. What are alleles? 24. What term means “same alleles”? 25. A man with AB blood type is married to a woman with AB blood. What type will their children be and in what percent of each? 26. A woman with type A blood type, genotype AO, is married to a man with type B blood type, genotype BO. What blood type would their children have? 27. What are all the possible blood types in the ABO blood type system? 28. Which blood type is the universal blood donor? 29. Which blood type can be donated to someone who’s blood type is unknown? 30. Lauren wants to know which location in her apartment is best for growing African violets. She has three African violets. She puts one on the balcony, one by the kitchen window, and one on the mantel in the living room. Each plant has the same size pot and the same soil, and Lauren gives each plant the same amount of water. The 2 variables: 1. location of plants 2. how the plants grow Which one is the independent variable (IV)? 31. Does heating a cup of water allow it to dissolve more sugar? The 2 variables: 1. water temperature 2. amount of dissolved sugar What is the dependent variable (DV)? 32. The changes that occur in an experiment that are directly caused by the experimenter (you) are called? 33. How many independent variables can be tested in a controlled experiment? 34. All the things in an experiment that must be the same to make it fair are called? 35. A scientist who wants to study the affects of fertilizer on plants sets up an experiment. Plant A gets no fertilizer, Plant B gets 5 mg. of fertilizer each day, and Plant C gets 10mg. of fertilizer each day. Which plant is the control group? 1st Quarter Final Study Guide ANSWER KEY 1. What is the purpose of mitosis? Growth and Repair 2. What is mitosis NOT used for? Sexual Reproduction 3. After which stage does cytokinesis occur? Telophase 4. What type of cells result after meiosis? 4 non-identical cells 5. What number of chromosomes will result after mitosis? The same number as before 6. What number of chromosomes result after meiosis? Half the normal body cells 7. What type of cell undergo meiosis? Sex cell 8. What is the cell called after meiosis creates it? Gamete 9. If a gamete mother cell contains 6 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will a normal body cell contain? 12 10. Asexually reproducing organisms produce offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parents. What type of cell division are the offspring a product of? Mitosis 11. Which type of cells would be more similar to each other a body cell or gamete cell? Body cell 12. What are the nitrogen bases in a DNA molecule and how do they pair with each other? A-T C-G 13. Which scientists are credited with discovering the physical structure of DNA? Watson and Crick 14. What does phenotype refer to? Physical appearance 15. What does genotype refer to? The genetic coding 16. If a plant that has a purple flower has a parent that has a white flower, what is its genotype? (assume that purple is dominant) Heterozygous or Pp 17. Who is the Father of Genetics? Gregor Mendel 18. What is another name for traits affected by the environment or are a result of learning or training? Acquired 19. The allele that masks the effects of the other is Dominant and the masked allele is Recessive 20. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross is called a ? Punnett Square 21. What would be the results of a genetic cross between parents that have TT and Tt? TT or Tt 22. If the results of a genetic cross were BB, BB, Bb, bb what would be the probability of getting a homozygous tall? Note that T is dominant (tall) and t is recessive (short) answer in percents 50% 23. What are alleles? Different forms of a gene 24. What term means “same alleles”? Homozygous 25. A man with AB blood type is married to a woman with AB blood. What type will their children be and in what percent of each? 25% Type A; 25% Type B; 50% Type AB 26. A woman with type A blood type, genotype AO, is married to a man with type B blood type, genotype BO. What blood type would their children have? AB; A; B; or O 27. What are all the possible blood types in the ABO blood type system? AB; A; B; or O 28. Which blood type is the universal blood donor? O 29. Which blood type can be donated to someone who’s blood type is unknown? O 30. Lauren wants to know which location in her apartment is best for growing African violets. She has three African violets. She puts one on the balcony, one by the kitchen window, and one on the mantel in the living room. Each plant has the same size pot and the same soil, and Lauren gives each plant the same amount of water. The 2 variables: 1. location of plants 2. how the plants grow Which one is the independent variable (IV)? Location of plants 31. Does heating a cup of water allow it to dissolve more sugar? The 2 variables: 1. water temperature 2. amount of dissolved sugar What is the dependent variable (DV)? The amount of sugar dissolved 32. The changes that occur in an experiment that are directly caused by the experimenter (you) are called? Independent Variable 33. How many independent variables can be tested in a controlled experiment? 1 34. All the things in an experiment that must be the same to make it fair are called? Controlled variables 35. A scientist who wants to study the affects of fertilizer on plants sets up an experiment. Plant A gets no fertilizer, Plant B gets 5 mg. of fertilizer each day, and Plant C gets 10mg. of fertilizer each day. Which plant is the control group? Plant A