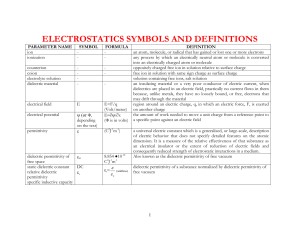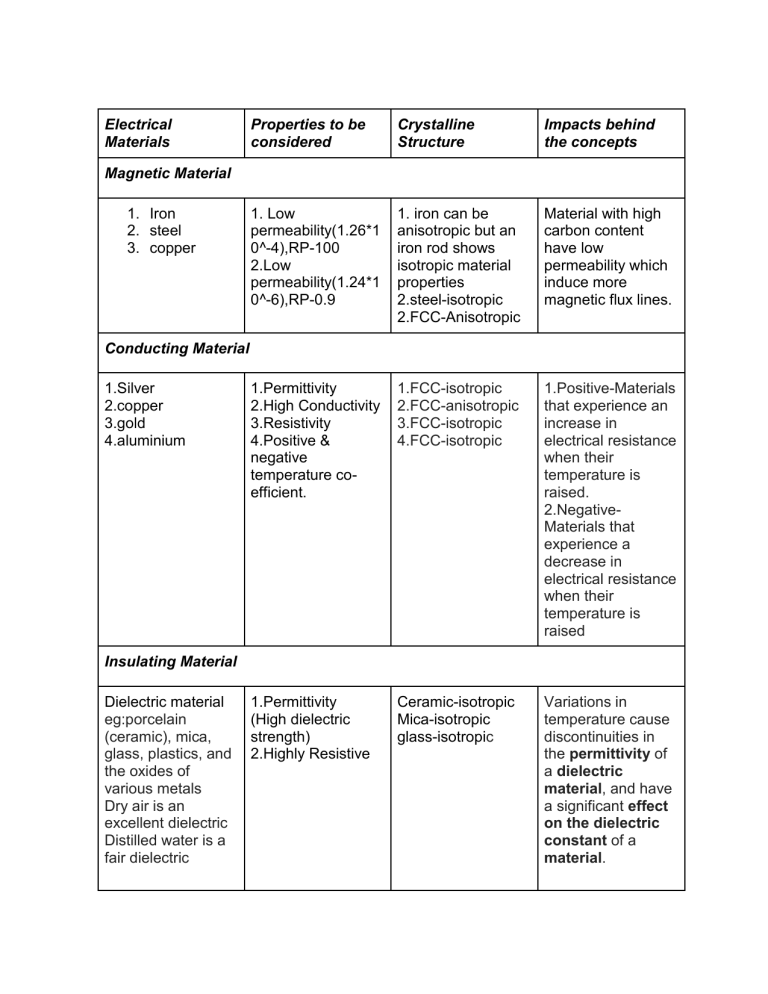
Electrical Materials Properties to be considered Crystalline Structure Impacts behind the concepts 1. Low permeability(1.26*1 0^-4),RP-100 2.Low permeability(1.24*1 0^-6),RP-0.9 1. iron can be anisotropic but an iron rod shows isotropic material properties 2.steel-isotropic 2.FCC-Anisotropic Material with high carbon content have low permeability which induce more magnetic flux lines. 1.Permittivity 2.High Conductivity 3.Resistivity 4.Positive & negative temperature coefficient. 1.FCC-isotropic 2.FCC-anisotropic 3.FCC-isotropic 4.FCC-isotropic 1.Positive-Materials that experience an increase in electrical resistance when their temperature is raised. 2.NegativeMaterials that experience a decrease in electrical resistance when their temperature is raised 1.Permittivity (High dielectric strength) 2.Highly Resistive Ceramic-isotropic Mica-isotropic glass-isotropic Variations in temperature cause discontinuities in the permittivity of a dielectric material, and have a significant effect on the dielectric constant of a material. Magnetic Material 1. Iron 2. steel 3. copper Conducting Material 1.Silver 2.copper 3.gold 4.aluminium Insulating Material Dielectric material eg:porcelain (ceramic), mica, glass, plastics, and the oxides of various metals Dry air is an excellent dielectric Distilled water is a fair dielectric The permittivity that a material exhibits when it is exposed to an electric field is dependent on the frequency of the voltage source. Semiconducting Material Intrinsic(Si,Ge) and 1.Dopping Extrinsic(GaP,Ga2.It behaves like an As) semiconductors insulator at 0 Kelvin and as temperature increases, it behaves like a conductor. Ge-highly anisotropic Si-fcc-anisotropic Semiconductor doping is the process that changes an intrinsic semiconductor to an extrinsic semiconductor. During doping, impurity atoms are introduced to an intrinsic semiconductor.