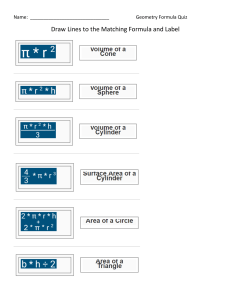
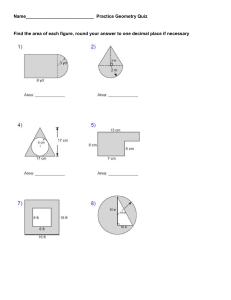
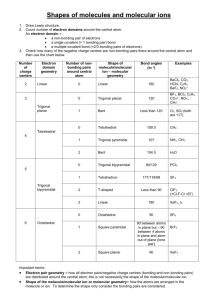
POLARITY RELATED TO PROPERTIES OF MOLECULES MOLECULAR POLARITY is one of the most important consequences of molecular geometry influences physical, chemical, and biological behavior of substances Molecular structure affects the properties of a substance and how it interacts with other chemicals substances .Chemistry design drugs that could inhibit the action of some pathogenic viruses and bacteria . An example of this is the antiviral drug Tamiflu. There are several geometrical shapes of molecules . For example,AB2 molecule can be linear or bent LINEAR BENT There are several shapes for AB3 molecules like the ones below. . pyramid Trigonal planar T-shaped Trigonal pyramaid 1.H2O is an AB2 molecule with a bent geometry .Water is polar BENT MOLECULAR GEOMETRY An of bent molecular geometry that results from tetrahedral electron pair geometry is H2O. The water molecule is bent molecular geometry example because the lone electron pairs, although still exerting influence on the shape, are invisible when looking at molecular geometry. The molecule is two dimensional and bent as opposed to the beryllium hydride case which was a linear or straight line molecular geometry because it did not have a lone electron pair. 2.CO2 is an AB2 molecule with a linear geometry. The bonds in CO2 are polar but the molecule is nonpolar. LINEAR MOLECULAR GEOMETRY In tis example, CO2, carbon at the center with no lone electron pairs. The carbon and both oxygen are bound through double bounds which counts as ‘‘two electron pairs’’. Hence the molecule has two electron pairs and is linear. Carbon dioxide is the major product of all combustion reactions involving carbon based materials such as natural gas, gasoline, and coal. Carbon dioxide is the end product of animal/human metabolism/respiration. It is also the gas that provides the carbonation in soda and beer. 3. NH3 is an AB3 molecule with a Trigonal pyramidal geometry TRIGONAL PYRAMID MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Ammonia an example of trigonal pyramid molecular geometry is NH3. The nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and thus needs 3 more electrons from 3 hydrogen atoms to complete the octet. The three hydrogen atoms and the lone electron pair as far as possible at nearly 109 degrees bond angle. This is tetrahedral electron pair geometry. The lone electron pairs exerts a little extra repulsion on the 3 bonding hydrogen atoms to create a slight compression to a 107 degree bond angle 4.BH3 is an AB3 molecule with Trigonal planar geometry. TRIGONAL PLANAR GEOMETRY Boron hydride an example of trigonal planar electron pair geometry is BH3.This molecule is electron and does not follow the octet rule it has only 6 valence electrons. The hydrogen atoms are as possible at 120 degree. This trigonal planar geometry. The molecule all in a plane and is two dimensional. This molecule exists in a gaseous state in only minute quantities under specialized condition as an intermediate in the making of other boron hydride type molecules. LESSON LEARNED Geometry of a molecule influences the physical, chemical, and biological properties of a substance. There are several geometrical shapes of molecules. Some them are following; AB2 molecules which are either linear or bent AB3 molecules which can be trigonal planar , Tshaped, or trigonal pyramid THE END….. Thank you PREPARED BY; Enrico C. Pescasio Jr. Cristy Rose Almodiel