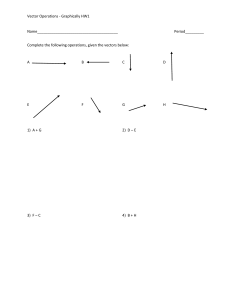
Name Unit 1: Correlates to text 3-1 & 3-2 Vector Operations and Trigonometry Your Notes go here: Quantities that are described with just a number, that is, quantities that have magnitude only are . That is, scalars have Examples: but no . - More descriptive quantities that have both magnitude and direction are Examples: . - Vectors are represented as .( ) of a vector is represented by its length. of a vector is represented by its direction Example: Using scale drawing In order to combine vectors, they must represent . When combining vectors, the order you combine them in is . That is, you can answer. and still get the same You can move them around, but you can’t change their . or The sum of any number of vectors is called the . Demo notes: To combine vectors, use the method. Draw the vectors lining them up so that the of the first vector touches the of the second vector. (Remember, order doesn’t matter!) Draw from the start of the vector to the end of the vector. This is called the resultant. Use a ruler to measure the of the resultant, and use your to determine the of your resultant. Use a to measure the direction of the resultant. Example: Adding vectors Example: Subtracting vectors To solve vector problems analytically, we use basic . Trig for Physics When defined on a right triangle such as the one shown here, sin, cos and tan are defined as the ratio of . The side opposite the right angle is called the ( The side directly opposite the angle is called the side because…well, it’s obvious . ). ( The side that, along with the hypotenuse, makes the angle is called the ( ) side. The sin, cos and tan are defined as follows: sin𝜃 = cos𝜃 = tan𝜃 = Exercises: Consider the triangle drawn and identify the value of each trig function indicated. B sin A= sin B= cos A= cos B= tan A= tan B= 5 4 A 3 When you are given two sides of a right triangle, use the to find the third side. ) When you are looking for the angle, use two sides of the right triangle and the . Example: A 65 meter rope is connected to the top of a building, and is attached to the ground 50 meters from the building. What angle does the rope make with the ground? And how tall is the building? Example: A projectile has an initial horizontal velocity of 5 m/s and an initial vertical velocity of 3 m/s upward. At what angle was the projectile fired? Breaking a vector into its vertical and horizontal parts is called and the pieces are called its . Question: The equilibrant of a resultant is exactly in direction. The equilibrant vectors. in magnitude and the effect of all the combined